Abstract
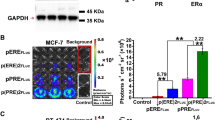
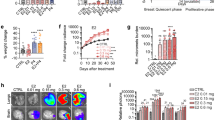
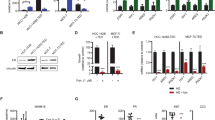
Expression of the sodium iodide symporter (hNIS) has been detected in breast cancer tissue, but frequently, not at the levels necessary to mediate 131I accumulation. Transducing the hNIS gene into breast cancer cells with adenovirus could be a tractable strategy to render breast cancer susceptible to radioiodide therapy. We constructed the replication-incompetent virus, AdSERE, in which an estrogen-responsive promoter directs the expression of hNIS. In vitro, we demonstrate that AdSERE mediates hNIS expression and iodide uptake in ER+ breast cancer cells. In vivo, we show that AdSERE-infected ER+ tumors can be imaged due to tracer accumulation; in addition, AdSERE in combination with therapeutic doses of 131I suppresses tumor growth.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bundred NJ . Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 2001; 27: 137–142.
Clarke R, Leonessa F, Welch JN, Skaar TC . Cellular and molecular pharmacology of antiestrogen action and resistance. Pharmacol Rev 2001; 53: 25–71.
Key TJ, Verkasalo PK, Banks E . Epidemiology of breast cancer. Lancet Oncol 2001; 2: 133–140.
Cho JY, Shen DH, Yang W, Williams B, Buckwalter TL, La Perle KM . In vivo imaging and radioiodine therapy following sodium iodide symporter gene transfer in animal model of intracerebral gliomas. Gene Ther 2002; 9: 1139–1145.
Groot-Wassink T, Aboagye EO, Glaser M, Lemoine NR, Vassaux G . Adenovirus biodistribution and noninvasive imaging of gene expression in vivo by positron emission tomography using human sodium/iodide symporter as reporter gene. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 1723–1735.
Groot-Wassink T, Aboagye EO, Wang Y, Lemoine NR, Keith WN, Vassaux G . Noninvasive imaging of the transcriptional activities of human telomerase promoter fragments in mice. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 4906–4911.
Dwyer RM, Bergert ER, O'connor MK, Gendler SJ, Morris JC . In vivo radioiodide imaging and treatment of breast cancer xenografts after MUC1-driven expression of the sodium iodide symporter. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 1483–1489.
Dadachova E, Nguyen A, Lin EY, Gnatovskiy L, Lu P, Pollard JW . Treatment with rhenium-188-perrhenate and iodine-131 of NIS-expressing mammary cancer in a mouse model remarkably inhibited tumor growth. Nucl Med Biol 2005; 32: 695–700.
Tazebay UH, Wapnir IL, Levy O, Dohan O, Zuckier LS, Zhao QH et al. The mammary gland iodide transporter is expressed during lactation and in breast cancer. Nat Med 2000; 6: 871–878.
Wapnir IL, van de Rijn M, Nowels K, Amenta PS, Walton K, Montgomery K et al. Immunohistochemical profile of the sodium/iodide symporter in thyroid, breast, and other carcinomas using high density tissue microarrays and conventional sections. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 1880–1888.
Wapnir IL, Goris M, Yudd A, Dohan O, Adelman D, Nowels K et al. The Na+/I− symporter mediates iodide uptake in breast cancer metastases and can be selectively down-regulated in the thyroid. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 4294–4302.
Kogai T, Kanamoto Y, Che LH, Taki K, Moatamed F, Schultz JJ . Systemic retinoic acid treatment induces sodium/iodide symporter expression and radioiodide uptake in mouse breast cancer models. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 415–422.
Spitzweg C, Joba W, Eisenmenger W, Heufelder AE . Analysis of human sodium iodide symporter gene expression in extrathyroidal tissues and cloning of its complementary deoxyribonucleic acids from salivary gland, mammary gland, and gastric mucosa. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998; 83: 1746–1751.
Ali S, Coombes C . Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 101–112.
Bachleitner-Hofmann T, Pichler-Gebhard B, Rudas M, Gnant M, Taucher S, Kandioler D et al. Pattern of hormone receptor status of secondary contralateral breast cancers in patients receiving adjuvant tamoxifen. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 3427–3432.
Gutierrez MC, Detre S, Johnston S, Mohsin SK, Shou J, Allred DC et al. Molecular changes in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: relationship between estrogen receptor, HER-2, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 2469–2476.
Unterholzner S, Willhauck MJ, Cengic N, Schütz M, Göke B, Morris JC et al. Dexamethasone stimulation of retinoic acid-induced sodium iodide symporter expression and cytotoxicity of 131-I in breast cancer cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91: 69–78.
Martin-Duque P, Jezzard S, Kaftansis L, Vassaux G . Direct comparison of the insulating properties of two genetic elements in an adenoviral vector containing two different expression cassettes. Hum Gene Ther 2004; 15: 995–1002.
Boland A, Magnon C, Filetti S, Bidart JM, Schlumberger M, Yeh P et al. Transposition of the thyroid iodide uptake and organification system in nonthyroid tumor cells by adenoviral vector-mediated gene transfers. Thyroid 2002; 12: 19–26.
Dadachova E, Bouzahzah B, Zuckier LS, Pestell RG . Rhenium-188 as an alternative to Iodine-131 for treatment of breast tumors expressing the sodium/iodide symporter (NIS). Nucl Med Biol 2002; 29: 13–18.
Petrich T, Helmeke HJ, Meyer GJ, Knapp WH, Pötter E . Establishment of radioactive astatine and iodine uptake in cancer cell lines expressing the human sodium/iodide symporter. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002; 29: 842–854.
Sathya G, Li W, Klinge CM, Anolik JH, Hilf R, Bambara RA . Effects of multiple estrogen responsive elements, their spacing, and location on estrogen response of reporter genes. Mol Endocrinol 1997; 11: 1994–2003.
He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, Yu J, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 2509–2514.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Cancer Research UK program Grant C355/A6253. Claudia Montiel-Equihua was supported by a Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia (CONACyT) scholarship. Pilar Martin-Duque is supported by grants from the program of Ramon y Cajal and FISS from the Spanish Ministery of Science and Health and FIDES fund. Special acknowledgments to Ma. Teresa Macias, Fernando Nuñez, Yaohe Wang, Jennelle Francis and Krishna Caulee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montiel-Equihua, C., Martín-Duque, P., de la Vieja, A. et al. Targeting sodium/iodide symporter gene expression for estrogen-regulated imaging and therapy in breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 15, 465–473 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2008.6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2008.6
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Virotheranostics, a double-barreled viral gun pointed toward cancer; ready to shoot?
Cancer Cell International (2020)
-
Sodium iodide symporter (NIS) in extrathyroidal malignancies: focus on breast and urological cancer
BMC Cancer (2014)
-
Assessment of the Na/I symporter as a reporter gene to visualize oncolytic adenovirus propagation in peritoneal tumours
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2010)