Abstract
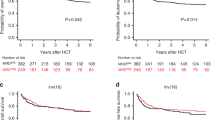
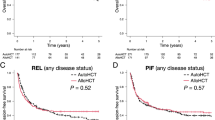
High-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL) is a reasonable option for a subset of patients. The impact of response status, according to positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) results and/or presence of circulating EBV DNA prior to ASCT, has not yet been established. We analyzed 27 ENKTL patients with pre-ASCT circulating EBV DNA who had undergone pre-ASCT PET/CT between 2009 and 2014. We classified patients into two groups based on the result of pretransplantation assessment: a favorable risk group (pretransplant five-point Deauville score (DS) of 1–2 based on PET/CT and no detectable EBV DNA) and an unfavorable risk group (DS 1–2 with detectable EBV DNA, DS 3–5 with or without detectable EBV DNA). After a median follow-up of 37 months, overall survival and PFS were significantly different between the two groups (median OS: not reached for favorable risk group vs 7.0 months for unfavorable risk group, P=0.017; median PFS: 16.0 vs 5.0 months, P=0.019). Multivariate analysis revealed that pre-ASCT DS and EBV DNA was the only independent prognostic factor considering stage, IPI and NKPI. Precise assessment of the status of disease before transplantation may provide more benefit from ASCT to ENKTL patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vose J, Armitage J, Weisenburger D . International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 4124–4130.
Kim SJ, Kim K, Kim BS, Kim CY, Suh C, Huh J et al. Phase II trial of concurrent radiation and weekly cisplatin followed by VIPD chemotherapy in newly diagnosed, stage IE to IIE, nasal, extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma: Consortium for Improving Survival of Lymphoma study. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 6027–6032.
Yamaguchi M, Tobinai K, Oguchi M, Ishizuka N, Kobayashi Y, Isobe Y et al. Phase I/II study of concurrent chemoradiotherapy for localized nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG0211. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 5594–5600.
Yong W, Zheng W, Zhu J, Zhang Y, Wang X, Xie Y et al. L-asparaginase in the treatment of refractory and relapsed extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Hematol 2009; 88: 647–652.
Yamaguchi M, Kwong YL, Kim WS, Maeda Y, Hashimoto C, Suh C et al. Phase II study of SMILE chemotherapy for newly diagnosed stage IV, relapsed, or refractory extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: the NK-Cell Tumor Study Group study. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 4410–4416.
Kwong YL, Kim WS, Lim ST, Kim SJ, Tang T, Tse E et al. SMILE for natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: analysis of safety and efficacy from the Asia Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 2012; 120: 2973–2980.
Lee J, Au WY, Park MJ, Suzumiya J, Nakamura S, Kameoka J et al. Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma: a multinational, multicenter, matched controlled study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 1356–1364.
Suzuki R, Suzumiya J, Nakamura S, Kagami Y, Kameoka JI, Sakai C et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for natural killer-cell lineage neoplasms. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 37: 425–431.
Kim HJ, Bang SM, Lee J, Kwon HC, Suh C, Kim HJ et al. High-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplantation in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: a retrospective comparison with non-transplantation cases. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 37: 819–824.
Bang SM, Kim YK, Park YH, Sohn SK, Lee JJ, Cho EK et al. High-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplantation in Korean patients with aggressive T/NK-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 2005; 46: 1599–1604.
Au WY, Lie AK, Liang R, Kwong YL, Yau CC, Cheung MM et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation for nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma: a progress report on its value. Ann Oncol 2003; 14: 1673–1676.
Kim SJ, Choi JY, Hyun SH, Ki CS, Oh D, Ahn YC et al. Risk stratification on the basis of Deauville score on PET-CT and the presence of Epstein-Barr virus DNA after completion of primary treatment for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: a multicentre, retrospective analysis. Lancet Haematol 2015; 2: e66–e74.
Meignan M, Gallamini A, Itti E, Barrington S, Haioun C, Polliack A . Report on the Third International Workshop on Interim Positron Emission Tomography in Lymphoma held in Menton, France, 26-27 September 2011 and Menton 2011 consensus. Leuk Lymphoma 2012; 53: 1876–1881.
Barrington SF, Mikhaeel NG, Kostakoglu L, Meignan M, Hutchings M, Mueller SP et al. Role of imaging in the staging and response assessment of lymphoma: consensus of the International Conference on Malignant Lymphomas Imaging Working Group. J Clin Oncol 2014; 32: 3048–3058.
Kim HS, Kim KH, Kim KH, Chang MH, Ji SH, Lim do H et al. Whole blood Epstein-Barr virus DNA load as a diagnostic and prognostic surrogate: extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 2009; 50: 757–763.
Germi R, Lupo J, Semenova T, Larrat S, Magnat N, Grossi L et al. Comparison of commercial extraction systems and PCR assays for quantification of Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in whole blood. J Clin Microbiol 2012; 50: 1384–1389.
Lee J, Suh C, Park YH, Ko YH, Bang SM, Lee JH et al. Extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a prognostic model from a retrospective multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 612–618.
Liang R, Chen F, Lee CK, Kwong YL, Chim CS, Yau CC et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation for primary nasal T/NK cell lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 19: 91–93.
Fox CP, Boumendil A, Schmitz N, Finel H, Luan JJ, Sucak G et al. High-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplantation for extra-nodal NK/T lymphoma in patients from the Western hemisphere: a study from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Leuk Lymphoma 2015; 56: 3295–3300.
Yhim HY, Kim JS, Mun YC, Moon JH, Chae YS, Park Y et al. Clinical Outcomes and Prognostic Factors of Up-Front Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Extranodal Natural Killer/T Cell Lymphoma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2015; 21: 1597–1604.
Kim CY, Hong CM, Kim DH, Son SH, Jeong SY, Lee SW et al. Prognostic value of whole-body metabolic tumour volume and total lesion glycolysis measured on (1)(8)F-FDG PET/CT in patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2013; 40: 1321–1329.
Biggi A, Gallamini A, Chauvie S, Hutchings M, Kostakoglu L, Gregianin M et al. International validation study for interim PET in ABVD-treated, advanced-stage hodgkin lymphoma: interpretation criteria and concordance rate among reviewers. J Nucl Med 2013; 54: 683–690.
Sauter CS, Matasar MJ, Meikle J, Schoder H, Ulaner GA, Migliacci JC et al. Prognostic value of FDG-PET prior to autologous stem cell transplantation for relapsed and refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2015; 125: 2579–2581.
Alcantara M, Dupuis J, Mareschal S, Julian A, Cottereau AS, Becker S et al. PET/CT before autologous stem cell transplantation predicts outcome in refractory/relapsed follicular lymphoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2015; 42: 215–221.
Khong PL, Huang B, Phin Lee EY, Sum Chan WK, Kwong YL . Midtreatment 18 F-FDG PET/CT Scan for Early Response Assessment of SMILE Therapy in Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: A Prospective Study from a Single Center. J Nucl Med 2014; 55: 911–916.
Ito Y, Kimura H, Maeda Y, Hashimoto C, Ishida F, Izutsu K et al. Pretreatment EBV-DNA copy number is predictive of response and toxicities to SMILE chemotherapy for extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 4183–4190.
Suzuki R, Yamaguchi M, Izutsu K, Yamamoto G, Takada K, Harabuchi Y et al. Prospective measurement of Epstein-Barr virus-DNA in plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood 2011; 118: 6018–6022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, S., Hyun, S., Kim, H. et al. Prognostic relevance of pretransplant Deauville score on PET-CT and presence of EBV DNA in patients who underwent autologous stem cell transplantation for ENKTL. Bone Marrow Transplant 51, 807–812 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.6
This article is cited by
-
Evaluating the Predictive Ability of Initial Staging F-18 FDG PET/CT for the Prognosis of Non-Hodgkin Malignant Lymphoma Patients Who Underwent Stem Cell Transplantation
Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2018)
-
PD-L1 is upregulated by EBV-driven LMP1 through NF-κB pathway and correlates with poor prognosis in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016)