Abstract
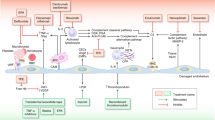
Diagnosis and management of hematopoietic cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (TA-TMA) are very complex and controversial, given multiple ongoing issues and comorbidities in sick transplant recipients. Complement activation via classic and alternative pathways is emerging as a potential pathogenetic mechanism in the development of TA-TMA. Complement-centric diagnostic strategy using functional and genetic tests may possibly support diagnosis, enhance molecular understanding and direct drug development. Complement blockade using eculizumab has shown some promising rates of hematologic responses, however, survival may still be poor. Early discontinuation of calcineurin inhibitor where feasible, use of eculizumab, aggressive infection prophylaxis, close monitoring and early treatment of potential complications including GvHD and organ failure may improve outcomes. A number of complement inhibitors are in the development and may change treatment paradigm. Future studies are important to better understand TA-TMA as a disease process and may aim to confirm the role of complement activation in TA-TMA, enhance diagnostic strategy, determine therapeutic approaches and strategies to reduce the risk of other complications particularly infection and GvHD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elsallabi O, Bhatt VR, Dhakal P, Foster KW, Tendulkar KK . Hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2016; 22: 12–20.
Batts ED, Lazarus HM . Diagnosis and treatment of transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: real progress or are we still waiting? Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 40: 709–719.
Hingorani S . Chronic kidney disease in long-term survivors of hematopoietic cell transplantation: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: 1995–2005.
Laskin BL, Goebel J, Davies SM, Jodele S . Small vessels, big trouble in the kidneys and beyond: hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood 2011; 118: 1452–1462.
Cho BS, Yahng SA, Lee SE, Eom KS, Kim YJ, Kim HJ et al. Validation of recently proposed consensus criteria for thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Transplantation 2010; 90: 918–926.
Daly AS, Xenocostas A, Lipton JH . Transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: twenty-two years later. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 30: 709–715.
Martinez MT, Bucher C, Stussi G, Heim D, Buser A, Tsakiris DA et al. Transplant-associated microangiopathy (TAM) in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 36: 993–1000.
Ye Y, Zheng W, Wang J, Hu Y, Luo Y, Tan Y et al. Risk and prognostic factors of transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a nested case control study. Hematol Oncol 2016 (e-pub ahead of print 1 June 2016; doi:10.1002/hon.2310).
Jodele S, Hirsch R, Laskin B, Davies S, Witte D, Chima R . Pulmonary arterial hypertension in pediatric patients with hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 202–207.
George JN . How I treat patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: 2010. Blood 2010; 116: 4060–4069.
George JN, Li X, McMinn JR, Terrell DR, Vesely SK, Selby GB . Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura‐hemolytic uremic syndrome following allogeneic HPC transplantation: a diagnostic dilemma. Transfusion 2004; 44: 294–304.
Choi C, Schmaier A, Snell M, Lazarus H . Thrombotic microangiopathy in haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Drugs 2009; 69: 183–198.
Hingorani S . Renal complications of hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med 2016; 374: 2256–2267.
Verbiest A, Pirenne J, Dierickx D . De novo thrombotic microangiopathy after non-renal solid organ transplantation. Blood Rev 2014; 28: 269–279.
Chapin J, Shore T, Forsberg P, Desman G, Van Besien K, Laurence J . Hematopoietic transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: case report and review of diagnosis and treatments. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2014; 12: 565–573.
Worel N, Greinix HT, Leitner G, Mitterbauer M, Rabitsch W, Rosenmayr A et al. ABO-incompatible allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation following reduced-intensity conditioning: close association with transplant-associated microangiopathy. Transfus Apher Sci 2007; 36: 297–304.
Ferrara JL, Levine JE, Reddy P, Holler E . Graft-versus-host disease. Lancet 2009; 373: 1550–1561.
Furlong T, Storb R, Anasetti C, Appelbaum F, Deeg H, Doney K et al. Clinical outcome after conversion to FK 506(tacrolimus) therapy for acute graft-versus-host disease resistant to cyclosporine or for cyclosporine-associated toxicities. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26: 985–991.
Boyer NL, Niven A, Edelman J . Tacrolimus-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in a lung transplant recipient. BMJ Case Rep 2013; bcr2012007351.
Chhajed PN, Tamm M, Glanville AR . Role of flexible bronchoscopy in lung transplantation. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2004; 25: 413–423.
Fishman JA . Infection in solid-organ transplant recipients. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 2601–2614.
Legro IR, Shah S, Kaza V . Tacrolimus induced hemolytic uremic syndrome in a lung transplant patient. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010; 181: A5834.
Humar A, Jessurun J, Sharp HL, Gruessner RW . Hemolytic uremic syndrome in small-bowel transplant recipients: the first two case reports. Transpl Int 1999; 12: 387–390.
Paramesh AS, Grosskreutz C, Florman SS, Gondolesi GE, Sharma S, Kaufman SS et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy associated with combined sirolimus and tacrolimus immunosuppression after intestinal transplantation. Transplantation 2004; 77: 129–131.
Cutler C, Henry NL, Magee C, Li S, Kim HT, Alyea E et al. Sirolimus and thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 551–557.
Ho VT, Cutler C, Carter S, Martin P, Adams R, Horowitz M et al. Blood and marrow transplant clinical trials network toxicity committee consensus summary: thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 571–575.
Wolff D, Wilhelm S, Hahn J, Gentilini C, Hilgendorf I, Steiner B et al. Replacement of calcineurin inhibitors with daclizumab in patients with transplantation-associated microangiopathy or renal insufficiency associated with graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 38: 445–451.
George JN, Terrell DR, Vesely SK, Kremer Hovinga JA, Lammle B . Thrombotic microangiopathic syndromes associated with drugs, HIV infection, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and cancer. Presse Med 2012; 41: e177–e188.
Iacopino P, Pucci G, Arcese W, Bosi A, Falda M, Locatelli F et al. Severe thrombotic microangiopathy: an infrequent complication of bone marrow transplantation. Gruppo Italiano Trapianto Midollo Osseo (GITMO). Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 24: 47–51.
Jodele S, Laskin BL, Goebel J, Khoury JC, Pinkard SL, Carey PM et al. Does early initiation of therapeutic plasma exchange improve outcome in pediatric stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy? Transfusion 2013; 53: 661–667.
Riedl M, Fakhouri F, Le Quintrec M, Noone DG, Jungraithmayr TC, Fremeaux-Bacchi V et al. Spectrum of complement-mediated thrombotic microangiopathies: pathogenetic insights identifying novel treatment approaches. Semin Thromb Hemost 2014; 40: 444–464.
Sarode R, McFarland JG, Flomenberg N, Casper JT, Cohen EP, Drobyski WR et al. Therapeutic plasma exchange does not appear to be effective in the management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome following bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 16: 271–275.
Au WY, Ma ES, Lee TL, Ha SY, Fung AT, Lie AK et al. Successful treatment of thrombotic microangiopathy after haematopoietic stem cell transplantation with rituximab. Br J Haematol 2007; 137: 475–478.
Carella AM, D'Arena G, Greco MM, Nobile M, Cascavilla N . Rituximab for allo-SCT-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 41: 1063–1065.
Marr H, McDonald EJ, Merriman E, Smith M, Mangos H, Stoddart C et al. Successful treatment of transplant-associated microangiopathy with rituximab. N Z Med J 2009; 122: 72–74.
Ostronoff M, Ostronoff F, Calixto R, Florencio R, Florencio M, Domingues MC et al. Life-threatening hemolytic-uremic syndrome treated with rituximab in an allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipient. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 39: 649–651.
Jodele S, Fukuda T, Vinks A, Mizuno K, Laskin BL, Goebel J et al. Eculizumab therapy in children with severe hematopoietic stem cell transplantation–associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 518–525.
Mengel M, Sis B, Haas M, Colvin RB, Halloran PF, Racusen LC et al. Banff 2011 meeting report: new concepts in antibody-mediated rejection. Am J Transplant 2012; 12: 563–570.
Solez K, Colvin RB, Racusen LC, Haas M, Sis B, Mengel M et al. Banff 07 classification of renal allograft pathology: updates and future directions. Am J Transplant 2008; 8: 753–760.
Laskin BL, Maisel J, Goebel J, Yin HJ, Luo G, Khoury JC et al. Renal arteriolar C4d deposition: a novel characteristic of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Transplantation 2013; 96: 217–223.
Jodele S, Licht C, Goebel J, Dixon BP, Zhang K, Sivakumaran TA et al. Abnormalities in the alternative pathway of complement in children with hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood 2013; 122: 2003–2007.
Jodele S, Laskin BL, Dandoy CE, Myers KC, El-Bietar J, Davies SM et al. A new paradigm: diagnosis and management of HSCT-associated thrombotic microangiopathy as multi-system endothelial injury. Blood Rev 2015; 29: 191–204.
Jodele S, Davies SM, Lane A, Khoury J, Dandoy C, Goebel J et al. Diagnostic and risk criteria for HSCT-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a study in children and young adults. Blood 2014; 124: 645–653.
Noris M, Galbusera M, Gastoldi S, Macor P, Banterla F, Bresin E et al. Dynamics of complement activation in aHUS and how to monitor eculizumab therapy. Blood 2014; 124: 1715–1726.
Afshar-Kharghan V . COMPLEMENTing the diagnosis of aHUS. Blood 2014; 124: 1699–1700.
Cohen D, Colvin RB, Daha MR, Drachenberg CB, Haas M, Nickeleit V et al. Pros and cons for C4d as a biomarker. Kidney Int 2012; 81: 628–639.
Jodele S, Zhang K, Zou F, Laskin B, Dandoy CE, Myers KC et al. The genetic fingerprint of susceptibility for transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood 2016; 127: 989–996.
Kim SS, Patel M, Yum K, Keyzner A . Hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: review of pharmacologic treatment options. Transfusion 2014; 55: 452–458.
Jodele S, Dandoy CE, Myers KC, El-Bietar J, Nelson A, Wallace G et al. New approaches in the diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment of pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Transfus Apher Sci 2016; 54: 181–190.
Dhakal P, Giri S, Pathak R, Bhatt VR . Eculizumab in transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2015 (e-pub ahead of print 9 August 2016; doi:10.1177/1076029615599439).
de Fontbrune FS, Galambrun C, Sirvent A, Huynh A, Faguer S, Nguyen S et al. Use of eculizumab in patients with allogeneic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a study from the SFGM-TC. Transplantation 2015; 99: 1953–1959.
Vasu S, Wu H, Satoskar A, Puto M, Roddy J, Blum W et al. Eculizumab therapy in adults with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Bone Marrow Transplant 2016; 51: 1241–1244.
Fernández C, Lario A, Forés R, Cabrera R . Eculizumab treatment in a patient with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy and steroid-refractory acute graft versus host disease. Hematol Rep 2015; 7: 6107.
Morales E, Rabasco C, Gutierrez E, Praga M . A case of thrombotic micro‐angiopathy after heart transplantation successfully treated with eculizumab. Transpl Int 2015; 28: 878–880.
Sevindik ÖG, Alacacıoğlu İ, Katgı A, Solmaz ŞM, Acar C, Pişkin Ö et al. Renal and neurological response with eculizumab in a patient with transplant associated thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation. Case Rep Hematol 2015; 2015: 425410.
Hillmen P, Young NS, Schubert J, Brodsky RA, Socie G, Muus P et al. The complement inhibitor eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 1233–1243.
Jodele S, Dandoy CE, Danziger-Isakov L, Myers KC, El-Bietar J, Nelson A et al. Terminal complement blockade after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is safe without meningococcal vaccination. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2016; 22: 1337–1340.
Struijk GH, Bouts AHM, Rijkers GT, Kuin EAC, ten Berge IJM, Bemelman FJ . Meningococcal sepsis complicating eculizumab treatment despite prior vaccination. Am J Transplant 2013; 13: 819–820.
Legendre CM, Licht C, Muus P, Greenbaum LA, Babu S, Bedrosian C et al. Terminal complement inhibitor eculizumab in atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med 2013; 368: 2169–2181.
Gavriilaki E, Thanassi JA, Yang G, Yuan X, Huang M, Brodsky RA . Small molecule factor D inhibitors block complement activation in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 2015; 126: 275.
Keizer MP, Pouw RB, Kamp AM, Patiwael S, Marsman G, Hart MH et al. TFPI inhibits lectin pathway of complement activation by direct interaction with MASP-2. Eur J Immunol 2015; 45: 544–550.
Risitano AM, Ricklin D, Huang Y, Reis ES, Chen H, Ricci P et al. Peptide inhibitors of C3 activation as a novel strategy of complement inhibition for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2014; 123: 2094–2101.
Shi J, Rose EL, Singh A, Hussain S, Stagliano NE, Parry GC et al. TNT003, an inhibitor of the serine protease C1s, prevents complement activation induced by cold agglutinins. Blood 2014; 123: 4015–4022.
Acknowledgements
VR Bhatt is supported by the 2016–2017 Physician-Scientist Training Program Grant from the College of Medicine, University of Nebraska Medical Center. We extend our gratitude to Dr James N George, MD, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, for kindly reviewing this article and providing useful insight.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhakal, P., Bhatt, V. Is complement blockade an acceptable therapeutic strategy for hematopoietic cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy?. Bone Marrow Transplant 52, 352–356 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.253
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.253
This article is cited by
-
Acute graft-versus-host disease increase risk and accuracy in prediction model of transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome
Annals of Hematology (2022)
-
Pre-transplant use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and transplant associated thrombotic microangiopathy - a single centre analysis of incidence, risk factors and outcomes
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: current paradigm and novel therapies
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2018)