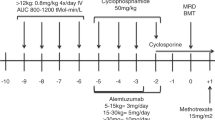
Abstract
The impact of ABO incompatibility on clinical outcomes following haematopoietic SCT (HSCT) remains controversial. This retrospective study assessed the effect of ABO mismatch on transplant outcomes and transfusion requirements in 594 patients undergoing reduced-intensity conditioned (RIC) HSCT with alemtuzumab in three UK transplant centres. We found no significant effects of minor, major or bidirectional ABO mismatch on overall survival, relapse-free survival, nonrelapse mortality or relapse incidence. Although the rate of acute GVHD was unaffected by ABO mismatch, the incidence of extensive chronic GVHD was higher in patients with minor and major mismatch compared with those who were ABO matched (hazard ratio (HR) 1.74, P=0.032 for minor, HR 1.69 P=0.0036 for major mismatch). Red cell and platelet transfusion requirements in the first 100 days post transplant did not differ by ABO mismatch. In this large UK series, ABO mismatch in RIC HSCT has no clinically significant effect on survival outcomes but appears to modify susceptibility to extensive chronic GVHD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rowley SD, Donato ML, Bhattacharyya P . Red blood cell-incompatible allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2011; 46: 1167–1185.
Kimura F, Sato K, Kobayashi S, Ikeda T, Sao H, Okamoto S et al. Impact of AB0-blood group incompatibility on the outcome of recipients of bone marrow transplants from unrelated donors in the Japan Marrow Donor Program. Haematologica 2008; 93: 1686–1693.
Wang Z, Sorror ML, Leisenring W, Schoch G, Maloney DG, Sandmaier BM et al. The impact of donor type and ABO incompatibility on transfusion requirements after nonmyeloablative haematopoietic cell transplantation. Br J Haematol 2010; 149: 101–110.
Resnick IB, Tsirigotis PD, Shapira MY, Aker M, Bitan M, Samuel S et al. ABO incompatibility is associated with increased non-relapse and GVHD related mortality in patients with malignancies treated with a reduced intensity regimen: a single center experience of 221 patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 409–417.
Gajewski JL, Petz LD, Calhoun L, O'Rourke S, Landaw EM, Lyddane NR et al. Hemolysis of transfused group O red blood cells in minor ABO-incompatible unrelated-donor bone marrow transplants in patients receiving cyclosporine without posttransplant methotrexate. Blood 1992; 79: 3076–3085.
Bolan CD, Childs RW, Procter JL, Barrett AJ, Leitman SF . Massive immune haemolysis after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation with minor ABO incompatibility. Br J Haematol 2001; 112: 787–795.
Worel N, Kalhs P, Keil F, Prinz E, Moser K, Schulenburg A et al. ABO mismatch increases transplant-related morbidity and mortality in patients given nonmyeloablative allogeneic HPC transplantation. Transfusion 2003; 43: 1153–1161.
Stussi G, Muntwyler J, Passweg JR, Seebach L, Schanz U, Gmur J et al. Consequences of ABO incompatibility in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 30: 87–93.
Benjamin RJ, Antin JH . ABO-incompatible bone marrow transplantation: the transfusion of incompatible plasma may exacerbate regimen-related toxicity. Transfusion 1999; 39: 1273–1274.
Sniecinski IJ, Oien L, Petz LD, Blume KG . Immunohematologic consequences of major ABO-mismatched bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 1988; 45: 530–534.
Klumpp TR . Immunohematologic complications of bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1991; 8: 159–170.
Seebach JD, Stussi G, Passweg JR, Loberiza FR Jr, Gajewski JL, Keating A et al. ABO blood group barrier in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation revisited. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 1006–1013.
Keever-Taylor CA, Bredeson C, Loberiza FR, Casper JT, Lawton C, Rizzo D et al. Analysis of risk factors for the development of GVHD after T cell-depleted allogeneic BMT: effect of HLA disparity, ABO incompatibility, and method of T-cell depletion. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2001; 7: 620–630.
Robin M, Guardiola P, Dombret H, Baruchel A, Esperou H, Ribaud P et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for acute myeloblastic leukaemia in remission: risk factors for long-term morbidity and mortality. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 31: 877–887.
Scholl S, Klink A, Mugge LO, Schilling K, Hoffken K, Sayer HG . Safety and impact of donor-type red blood cell transfusion before allogeneic peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation with major ABO mismatch. Transfusion 2005; 45: 1676–1683.
Worel N, Kalhs P . AB0-incompatible allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 2008; 93: 1605–1607.
Worel N, Greinix HT, Schneider B, Kurz M, Rabitsch W, Knobl P et al. Regeneration of erythropoiesis after related- and unrelated-donor BMT or peripheral blood HPC transplantation: a major ABO mismatch means problems. Transfusion 2000; 40: 543–550.
Worel N, Greinix HT, Keil F, Mitterbauer M, Lechner K, Fischer G et al. Severe immune hemolysis after minor ABO-mismatched allogeneic peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation occurs more frequently after nonmyeloablative than myeloablative conditioning. Transfusion 2002; 42: 1293–1301.
Curtin NJ, Schwarer AP . Nonmyeloablative peripheral blood stem cell transplant for T-cell prolymphocytic leukaemia complicated by fulminant haemolysis and acute renal failure at engraftment secondary to minor ABO incompatibility. Clin Lab Haematol 2005; 27: 206–208.
Noborio K, Muroi K, Izumi T, Toshima M, Kawano-Yamamoto C, Otsuki T et al. Massive immune hemolysis after non-myeloablative allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation with minor ABO-incompatibility. Leuk Lymphoma 2003; 44: 357–359.
Lapierre V, Oubouzar N, Auperin A, Tramalloni D, Tayebi H, Robinet E et al. Influence of the hematopoietic stem cell source on early immunohematologic reconstitution after allogeneic transplantation. Blood 2001; 97: 2580–2586.
Canals C, Muniz-Diaz E, Martinez C, Martino R, Moreno I, Ramos A et al. Impact of ABO incompatibility on allogeneic peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation after reduced intensity conditioning. Transfusion 2004; 44: 1603–1611.
Erker CG, Steins MB, Fischer RJ, Kienast J, Berdel WE, Sibrowski W et al. The influence of blood group differences in allogeneic hematopoietic peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation. Transfusion 2005; 45: 1382–1390.
Ozkurt ZN, Yegin ZA, Yenicesu I, Aki SZ, Yagci M, Sucak GT . Impact of ABO-incompatible donor on early and late outcome of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transplant Proc 2009; 41: 3851–3858.
Benjamin RJ, McGurk S, Ralston MS, Churchill WH, Antin JH . ABO incompatibility as an adverse risk factor for survival after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Transfusion 1999; 39: 179–187.
Mielcarek M, Leisenring W, Torok-Storb B, Storb R . Graft-versus-host disease and donor-directed hemagglutinin titers after ABO-mismatched related and unrelated marrow allografts: evidence for a graft-versus-plasma cell effect. Blood 2000; 96: 1150–1156.
Bacigalupo A, Van Lint MT, Occhini D, Margiocco M, Ferrari G, Pittaluga PA et al. ABO compatibility and acute graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 1988; 45: 1091–1094.
Blin N, Traineau R, Houssin S, Peffault de Latour R, Petropoulou A, Robin M et al. Impact of donor-recipient major ABO mismatch on allogeneic transplantation outcome according to stem cell source. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010; 16: 1315–1323.
Kim JG, Sohn SK, Kim DH, Baek JH, Lee KB, Min WS et al. Impact of ABO incompatibility on outcome after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 35: 489–495.
Michallet M, Le QH, Mohty M, Prebet T, Nicolini F, Boiron JM et al. Predictive factors for outcomes after reduced intensity conditioning hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hematological malignancies: a 10-year retrospective analysis from the Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle et de Therapie Cellulaire. Exp Hematol 2008; 36: 535–544.
Watz E, Remberger M, Ringden O, Lundahl J, Ljungman P, Mattsson J et al. Analysis of donor and recipient ABO incompatibility and antibody-associated complications after allogeneic stem cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 264–271.
Storb RF, Champlin R, Riddell SR, Murata M, Bryant S, Warren EH . Non-myeloablative transplants for malignant disease. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2001: 375–391.
Oran B, Giralt S, Saliba R, Hosing C, Popat U, Khouri I et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for the treatment of high-risk acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome using reduced-intensity conditioning with fludarabine and melphalan. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 454–462.
van Besien K, Kunavakkam R, Rondon G, De Lima M, Artz A, Oran B et al. Fludarabine-melphalan conditioning for AML and MDS: alemtuzumab reduces acute and chronic GVHD without affecting long-term outcomes. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 610–617.
Baron F, Labopin M, Blaise D, Lopez-Corral L, Vigouroux S, Craddock C et al. Impact of in vivo T-cell depletion on outcome of AML patients in first CR given peripheral blood stem cells and reduced-intensity conditioning allo-SCT from a HLA-identical sibling donor: a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2014; 49: 389–396.
Pawson R, Pamphilon D. Transfusion support in patients undergoing HSCT. In: The EBMT handbook on Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. 6th edn ed. http://ebmtonline.forumservice.net/2012.
Sullivan KM, Agura E, Anasetti C, Appelbaum F, Badger C, Bearman S et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease and other late complications of bone marrow transplantation. Semin Hematol 1991; 28: 250–259.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Sheppard D, Tay J, Bryant A, McDiarmid S, Huebsch L, Tokessy M et al. Major ABO-incompatible BMT: isohemagglutinin reduction with plasma exchange is safe and avoids graft manipulation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 953–957.
Raimondi R, Soli M, Lamparelli T, Bacigalupo A, Arcese W, Belloni M et al. ABO-incompatible bone marrow transplantation: a GITMO survey of current practice in Italy and comparison with the literature. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 34: 321–329.
Romee R, Weisdorf DJ, Brunstein C, Wagner JE, Cao Q, Blazar BR et al. Impact of ABO-mismatch on risk of GVHD after umbilical cord blood transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 1046–1049.
Liesveld J, Pawlowski J, Chen R, Hyrien O, Debolt J, Becker M et al. Clinical factors affecting engraftment and transfusion needs in SCT: a single-center retrospective analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 691–697.
Kanda J, Ichinohe T, Matsuo K, Benjamin RJ, Klumpp TR, Rozman P et al. Impact of ABO mismatching on the outcomes of allogeneic related and unrelated blood and marrow stem cell transplantations for hematologic malignancies: IPD-based meta-analysis of cohort studies. Transfusion 2009; 49: 624–635.
Kollman C, Howe CW, Anasetti C, Antin JH, Davies SM, Filipovich AH et al. Donor characteristics as risk factors in recipients after transplantation of bone marrow from unrelated donors: the effect of donor age. Blood 2001; 98: 2043–2051.
Booth GS, Gehrie EA, Bolan CD, Savani BN . Clinical guide to ABO-incompatible allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 1152–1158.
Matsui T, Shimoyama T, Matsumoto M, Fujimura Y, Takemoto Y, Sako M et al. ABO blood group antigens on human plasma von Willebrand factor after ABO-mismatched bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1999; 94: 2895–2900.
Eiz-Vesper B, Seltsam A, Blasczyk R . ABO glycosyltransferases as potential source of minor histocompatibility antigens in allogeneic peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation. Transfusion 2005; 45: 960–968.
Maciej Zaucha J, Mielcarek M, Takatu A, Little MT, Gooley T, Baker J et al. Engraftment of early erythroid progenitors is not delayed after non-myeloablative major ABO-incompatible haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol 2002; 119: 740–750.
Korbling M, Huh YO, Durett A, Mirza N, Miller P, Engel H et al. Allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation: peripheralization and yield of donor-derived primitive hematopoietic progenitor cells (CD34+ Thy-1dim) and lymphoid subsets, and possible predictors of engraftment and graft-versus-host disease. Blood 1995; 86: 2842–2848.
Salmon JP, Michaux S, Hermanne JP, Baudoux E, Gerard C, Sontag-Thull D et al. Delayed massive immune hemolysis mediated by minor ABO incompatibility after allogeneic peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation. Transfusion 1999; 39: 824–827.
Moog R, Melder C, Prumbaum M, Muller N, Schaefer UW . Rapid donor type isoagglutinin production after allogeneic peripheral progenitor cell transplantation. Beitr Infusionsther Transfusionsmed 1997; 34: 150–152.
Oziel-Taieb S, Faucher-Barbey C, Chabannon C, Ladaique P, Saux P, Gouin F et al. Early and fatal immune haemolysis after so-called 'minor' ABO-incompatible peripheral blood stem cell allotransplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 19: 1155–1156.
Kekre N, Christou G, Mallick R, Tokessy M, Tinmouth A, Tay J et al. Factors associated with the avoidance of red blood cell transfusion after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transfusion 2012; 52: 2049–2054.
Schmidt-Hieber M, Schwarck S, Stroux A, Ganepola S, Reinke P, Thiel E et al. Immune reconstitution and cytomegalovirus infection after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: the important impact of in vivo T cell depletion. Int J Hematol 2010; 91: 877–885.
The Trial to Reduce Alloimmunization to Platelets Study Group. Leukocyte reduction and ultraviolet B irradiation of platelets to prevent alloimmunization and refractoriness to platelet transfusions. N Engl J Med 1997; 337: 1861–1869.
Booth GS, Gehrie EA, Savani BN, Minor RBC . Ab and allo-SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2014; 49: 456–457.
Acknowledgements
CKB is grateful to the Department of Haematology, Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Bone Marrow Transplantation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brierley, C., Littlewood, T., Peniket, A. et al. Impact of ABO blood group mismatch in alemtuzumab-based reduced-intensity conditioned haematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 50, 931–938 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.51
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.51
This article is cited by
-
ABO, alemtuzumab and allogeneic transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2015)