Abstract
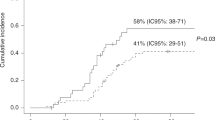
Disseminated adenoviral infection (AI) is associated with profound immunosuppression and poor outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT (allo-HSCT). A better understanding of AI in allo-HSCT recipients can serve as a basis to develop more effective management strategies. We evaluated all adult patients who received allo-HSCT at MD Anderson Cancer Center between 1999 and 2008. Among the 2879 allo-HSCT patients, 73 (2.5%) were diagnosed with AI. Enteritis (26%) and pneumonia (24%) were the most common clinical manifestations; pneumonia was the most common cause of adenovirus-associated death. A multivariable Bayesian logistic regression showed that when the joint effects of all covariates were accounted for, cord blood transplant, absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) ⩽200/mm3 and male gender were associated with a higher probability of disseminated AI. The OS was significantly worse for patients with AI that was disseminated rather than localized (median of 5 months vs median of 28 months, P<0.001) and for patients with ALC ⩽200/mm3 (P<0.001). Disseminated AI, in patients who received allo-HSCT, is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. Strategies for early diagnosis and intervention are essential, especially for high-risk patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chemaly RF, Hanmod SS, Rathod DB, Ghantoji SS, Jiang Y, Doshi A et al. The characteristics and outcomes of parainfluenza virus infections in 200 patients with leukemia or recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2012; 119: 2738–2745 (quiz 2969).
Flomenberg P, Babbitt J, Drobyski WR, Ash RC, Carrigan DR, Sedmak GV et al. Increasing incidence of adenovirus disease in bone marrow transplant recipients. J Infect Dis 1994; 169: 775–781.
Shah JN, Chemaly RF . Management of RSV infections in adult recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2011; 117: 2755–2763.
Baldwin A, Kingman H, Darville M, Foot AB, Grier D, Cornish JM et al. Outcome and clinical course of 100 patients with adenovirus infection following bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26: 1333–1338.
Blanke C, Clark C, Broun ER, Tricot G, Cunningham I, Cornetta K et al. Evolving pathogens in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: increased fatal adenoviral infections. AmJ Med 1995; 99: 326–328.
Chakrabarti S, Mautner V, Osman H, Collingham KE, Fegan CD, Klapper PE et al. Adenovirus infections following allogeneic stem cell transplantation: incidence and outcome in relation to graft manipulation, immunosuppression, and immune recovery. Blood 2002; 100: 1619–1627.
Hierholzer JC . Adenoviruses in the immunocompromised host. Clin Microbiol Rev 1992; 5: 262–274.
Howard DS, Phillips IG, Reece DE, Munn RK, Henslee-Downey J, Pittard M et al. Adenovirus infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 1999; 29: 1494–1501.
La Rosa AM, Champlin RE, Mirza N, Gajewski J, Giralt S, Rolston KV et al. Adenovirus infections in adult recipients of blood and marrow transplants. Clin Infect Dis 2001; 32: 871–876.
Leen AM, Bollard CM, Myers GD, Rooney CM . Adenoviral infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplanta 2006; 12: 243–251.
Munoz FM, Piedra PA, Demmler GJ . Disseminated adenovirus disease in immunocompromised and immunocompetent children. Clin Infect Dis 1998; 27: 1194–1200.
Robin M, Marque-Juillet S, Scieux C, Peffault de Latour R, Ferry C, Rocha V et al. Disseminated adenovirus infections after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: incidence, risk factors and outcome. Haematologica 2007; 92: 1254–1257.
Shields AF, Hackman RC, Fife KH, Corey L, Meyers JD . Adenovirus infections in patients undergoing bone-marrow transplantation. New Engl J Med 1985; 312: 529–533.
Suparno C, Milligan DW, Moss PA, Mautner V . Adenovirus infections in stem cell transplant recipients: recent developments in understanding of pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Leuk Lymphoma 2004; 45: 873–885.
Wasserman R, August CS, Plotkin SA . Viral infections in pediatric bone marrow transplant patients. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1988; 7: 109–115.
Kojaoghlanian THM . Infectious Diseases, In: Gorbach SLBJ, Blacklow NR, (eds). 3 Edn pp 1895–1902 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2004.
Bordigoni P, Carret A-S, Venard V, Witz F, Le Faou A . Treatment of adenovirus infections in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Infect Dis 2001; 32: 1290–1297.
Ljungman P, Ribaud P, Eyrich M, Matthes-Martin S, Einsele H, Bleakley M et al. Cidofovir for adenovirus infections after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a survey by the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 31: 481–486.
Lanier R, Trost L, Tippin T, Lampert B, Robertson A, Foster S et al. Development of CMX001 for the treatment of poxvirus infections. Viruses 2010; 2: 2740–2762.
Feuchtinger T, Lang P, Handgretinger R . Adenovirus infection after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Leuk Lymphoma 2007; 48: 244–255.
Leen AM, Myers GD, Bollard CM, Huls MH, Sili U, Gee AP et al. T-Cell Immunotherapy for Adenoviral Infections of Stem-Cell Transplant Recipients. AnnNY Acad Sci 2005; 1062: 104–115.
Tomblyn M, Chiller T, Einsele H, Gress R, Sepkowitz K, Storek J et al. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients: a global perspective. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 1143–1238.
R R . Introduction to the Theory of Nonparametric Statistics. John Wiley & Sons: New York, 1979.
Fisher RA . On the interpretation of χ2 from contingency tables, and the calculation of P. J Royal Stat Soc 1922; 85: 87–94.
Gelman ACJ, Stern HS, Rubin DB . Bayesian Data Analysis 2nd Edn Chapman & Hall/CRC: New York, 2004.
Spiegelhalter DJ, Best NG, Carlin BP, van der Linde A . Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit (with discussion). J Royal Stat Soc 2002; Series B 64: 583–639.
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Nonparametric estimator from incomplete observations. Jf Am Statl Assoc 1958, 457–481.
Mantel N . Evaluation of survival data and two new rank order statistics arising in its consideration. Cancer Chemother Rep 1966; 50: 163–170.
Asano Y, Kanda Y, Ogawa N, Sakata-Yanagimoto M, Nakagawa M, Kawazu M et al. Male predominance among Japanese adult patients with late-onset hemorrhagic cystitis after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 32: 1175–1179.
Childs R, Sanchez C, Engler H, Preuss J, Rosenfeld S, Dunbar C et al. High incidence of adeno- and polyomavirus-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in bone marrow allotransplantation for hematological malignancy following T cell depletion and cyclosporine. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 22: 889–893.
Gahrton G . Risk assessment in haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: impact of donor-recipient sex combination in allogeneic transplantation.. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2007; 20: 219–229.
Gallardo D, Perez-Garcia A, de la Camara R, Iriondo A, Jimenez-Velasco A, Torres A et al. Clinical outcome after sex-mismatched allogeneic stem cell transplantation from human lymphocyte antigen-identical sibling donors: influence of stem cell source. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1461–1464.
Leen AM, Rooney CM . Adenovirus as an emerging pathogen in immunocompromised patients. BrJ Haematol 2005; 128: 135–144.
Parody R, Martino R, Rovira M, Vazquez L, Vazquez MJ, de la Camara R et al. Severe infections after unrelated donor allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adults: comparison of cord blood transplantation with peripheral blood and bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 734–748.
Narimatsu H, Matsumura T, Kami M, Miyakoshi S, Kusumi E, Takagi S et al. Bloodstream infection after umbilical cord blood transplantation using reduced-intensity stem cell transplantation for adult patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 429–436.
Chemaly RF, Ghosh S, Bodey GP, Rohatgi N, Safdar A, Keating MJ et al. Respiratory viral infections in adults with hematologic malignancies and human stem cell transplantation recipients: a retrospective study at a major cancer center. Medicine 2006; 85: 278–287.
Nichols WG, Gooley T, Boeckh M . Community-acquired respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza virus infections after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center experience. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2001; 7 (Suppl): 11S–15S.
Nichols WG, Corey L, Gooley T, Davis C, Boeckh M . High risk of death due to bacterial and fungal infection among cytomegalovirus (CMV)-seronegative recipients of stem cell transplants from seropositive donors: evidence for indirect effects of primary CMV infection. J Infect Dis 2002; 185: 273–282.
Lindemans CA, Leen AM, Boelens JJ . How I treat adenovirus in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Blood 2010; 116: 5476–5485.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Cancer Center Support Grant (NCI Grant P30 CA016672).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yilmaz, M., Chemaly, R., Han, X. et al. Adenoviral infections in adult allogeneic hematopoietic SCT recipients: a single center experience. Bone Marrow Transplant 48, 1218–1223 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.33
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.33
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Novel Antiviral Agents for Respiratory Viral Infection in Immunocompromised Adults
Current Infectious Disease Reports (2013)