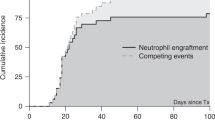
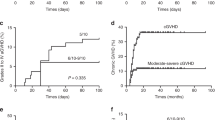
Abstract
The diagnosis of aplastic anemia in children requires exclusion of a variety of inherited or acquired BM failure syndromes with similar phenotypes. An efficient diagnostic plan is important because time from diagnosis to ‘final’ treatment is directly related to outcome regardless of the therapeutic option chosen. The gold standard of therapy remains hematopoietic SCT with a graft of BM cells for those children with matched sibling donors. Conversely for children without a sibling donor the high response and markedly improved overall survival rates of combined immunosuppressive therapy have proven robust, especially when horse derived anti-thymocyte globuline plus ciclosporine A are used. Incomplete response, relapse and progression to myelodysplasia/leukemia however have emerged as significant long-term issues. Improvements in outcome of alternative donor transplantation and the use of established and novel immunosuppressive agents provide multiple alternatives for treating refractory or relapsed patients. Regardless of the type of therapeutic approach, patients require centralized treatment in a center of excellence, ongoing monitoring for recurrence of disease and/or therapy-related immediate side effects and long-term effects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guinan EC . Diagnosis and management of aplastic anemia. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2011; 2011: 76–81.
Chessells JM . Pitfalls in the diagnosis of childhood leukemia. Br J Haematol 2001; 114: 506–511.
Afable MG, Tiu RV, Maciejewski J . Clonal evolution in aplastic anemia. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2011; 2011: 90–95.
Niemeyer C, Baumann I . Classification of childhood aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2011; 2011: 84–89.
Marsh JC, Ball SE, Cavenagh J, Darbyshire P, Dokal I, Gordon-Smith EC et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aplastic anemia. Br J Haematol 2009; 147: 43–70.
Alter BP . Current diagnosis of inherited bone marrow failure syndromes. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2007; 24: 87–99.
Dokal I, Vulliamy T . Inherited bone marrow failure syndromes. Haematologica 2010; 95: 1236–1240.
Afable MG, Wlodarski M, Makishima H, Shaik M, Sekeres MA, Tiu RV et al. SNP array-based karyo-typing: differences and similarities between aplastic anemia and hypocellular myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2011; 117: 6876–6884.
Kojima S, Ohara A, Tsuchida M, Kudoh T, Hanada R, Okimoto Y et al. Risk factors for evolution of acquired aplastic anemia into myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia after immunosuppressive therapy in children. Blood 2002; 100: 786–790.
Pu JJ, Mukhina G, Wang H, Savage WJ, Brodsky RA . Natural history of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clones in patients presenting as aplastic anemia. Eur J Haematol 2011; 87: 37–45.
Iwasaki T, Murakami M, Sugisaki C, Sobue S, Ohashi H, Asano H et al. Characterization of myelodysplastic syndrome and aplastic anemia by immunostaining of p53 and hemoglobin F and karyotype analysis: differential diagnosis between refractory anemia and aplastic anemia. Pathol Int 2008; 58: 353–360.
Maciejewski JP, Risitano A, Sloand EM, Nunez O, Young NS . Distinct clinical outcomes for cytogenetic abnormalities evolving from aplastic anemia. Blood 2002; 99: 3129–3135.
Maciejewski JP, Risitano A . Hematopoietic stem cells in aplastic anemia. Arch Med Res 2003; 34: 520–527.
Young NS, Scheinberg P, Calado RT . Aplastic anemia. Curr Opin Hematol 2008; 15: 162–168.
DeZern AE, Guinan EC . Therapy for aplastic anemia. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2011; 2011: 82–83.
Bacigalupo A, Passweg J . Diagnosis and treatment of acquired aplastic anemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2009; 23: 159–170.
Valdez JM, Scheinberg P, Young NS, Walsh T . Infections in patients with aplastic anemia. Semin Hematol 2009; 46: 269–276.
Davies JK, Guinan EC . An update on the management of severe idiopathic aplastic anemia in children. Br J Haematol 2007; 136: 549–564.
Marsh J, Socie G, Tichelli A, Schrezenmeier H, Hochsmann B, Risitano AM et al. Should irradiated blood products be given routinely to all patients with aplastic anaemia undergoing immunosuppressive therapy with antithymocyte globulin (ATG)? A survey from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Severe Aplastic Anaemia Working Party. Br J Haematol 2010; 150: 377–379.
Quillen K, Wong E, Scheinberg P, Young NS, Walsh TJ, Wu CO et al. Granulocyte transfusions in severe aplastic anemia: an eleven-year experience. Haematologica 2009; 94: 1661–1668.
Lee JW, Yoon SS, Shen ZX, Ganser A, Hsu HC, Habr D et al. Iron chelation therapy with deferasirox in patients with aplastic anemia: a subgroup analysis of 116 patients from the EPIC trial. Blood 2010; 116: 2448–2454.
Takatoku M, Uchiyama T, Okamoto S, Kanakura Y, Sawada K, Tomonaga M et al. Retrospective nationwide survey of Japanese patients with transfusion-dependent MDS and aplastic anemia highlights the negative impact of iron overload on morbidity/mortality. Eur J Haematol 2007; 78: 487–494.
Pullarkat V, Blanchard S, Tegtmeier B, Dagis A, Patane K, Ito J et al. Iron overload adversely affects outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 42: 799–805.
Storey JA, Connor RF, Lewis ZT, Hurd D, Pomper G, Keung YK et al. The transplant iron score as a predictor of stem cell transplant survival. J Hematol Oncol 2009; 2: 44.
Koh KN, Park M, Kim BE, Im HJ, Seo JJ . Restoration of hematopoiesis after iron chelation therapy with deferasirox in 2 children with severe aplastic anemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2010; 32: 611–614.
Park SJ, Han CW . Complete hematopoietic recovery after continuous iron chelation therapy in a patient with severe aplastic anemia with secondary hemochromatosis. J Korean Med Sci 2008; 23: 320–323.
Locasciulli A, Oneto R, Bacigalupo A, Socié G, Korthof E, Bekassy A et al. Outcome of patients with acquired aplastic anemia given first line bone marrow transplantation or immunosuppressive treatment in the last decade: a report from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica 2007; 92: 11–18.
Scheinberg P, Wu CO, Nunez O, Young NS . Long-term outcome of pediatric patients with severe aplastic anemia treated with antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine. J Pediatr 2008; 153: 814–819.
Passweg JR, Marsh JCW . Aplastic Anemia: First line Treatment by Immunosuppression and Sibling Marrow Transplantation. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program Hematol 2010; 153: 36–42.
Kojima S, Horibe K, Inaba J, Yoshimi A, Takahashi Y, Kudo K et al. Long-term outcome of acquired aplastic anemia in children: comparison between immunosuppressive therapy and bone marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol 2000; 111: 321–328.
Unal S, Cetin M, Tavil B, Calıskan N, Calişkan N, Yetgin S et al. Favorable outcome with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric acquired aplastic anemia patients. Pediatr Transpl 2007; 11: 788–791.
Myers KC, Davies SM . Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for bone marrow failure syndromes in children. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 279–292.
Schrezenmeier H, Passweg JR, Marsh JC, Bacigalupo A, Bredeson CN, Bullorsky E et al. Worse outcome and more chronic GVHD with peripheral blood progenitor cells than bone marrow in HLA-matched sibling donor transplants for young patients with severe acquired aplastic anemia. Blood 2007; 110: 1397–1400.
Tichelli A, Schrezenmeier H, Socie G, Marsh J, Bacigalupo A, Dührsen U et al. A randomized controlled study in patients with newly diagnosed severe aplastic anemia receiving antithymocyte globulin (ATG), cyclosporine, with or without G-CSF: a study of the SAA Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood 2011; 117: 4434–4441.
Békássy NA, Locasciulli A, Marsh JCV, Socié G, Fuehrer M, Passweg J . Immunosuppression with ALG and CsA is first line treatment in children with SAA lacking an HLA identical sibling. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2006; 45: 359–360.
Scheinberg P, Nunez O, Weinstein B, Scheinberg P, Biancotto A, Wu CO et al. Horse versus rabbit antithymocyte globulin in acquired aplastic anemia. N Engl J Med 2011; 365: 430–438.
Atta EH, Dias DS, Marra VL, de Azevedo AM . Comparison between horse and rabbit antithymocyte globulin as first-line treatment for patients with severe aplastic anemia: a single-center retrospective study. Ann Hematol 2010; 89: 851–859.
Saracco P, Quarello P, Iori AP, Zecca M, Longoni D, Svahn J et al. Cyclosporin A response and dependence in children with acquired aplastic anemia: a multicentre retrospective study with long-term observation follow-up. Br J Haematol 2008; 140: 197–205.
Gurion R, Gafter-Gvili A, Paul M, Vidal L, Ben-Bassat I, Yeshurun M et al. Hematopoietic growth factors in aplastic anemia patients treated with immunosuppressive therapy - systematic review and meta-analysis. Haematologica 2009; 94: 712–719.
Führer M, Rampf U, Baumann I, Faldum A, Niemeyer C, Janka-Schaub G et al. Immunosuppressive therapy for aplastic anemia in children: a more severe disease predicts better survival. Blood 2005; 106: 2102–2104.
Yoshida N, Yagasaki H, Hama A, Takahashi Y, Kosaka Y, Kobayashi R et al. Predicting response to immunosuppressive therapy in childhood aplastic anemia. Haematologica 2011; 96: 771–774.
Pongtanakul B, Das PK, Charpentier K, Dror Y . Outcome of children with aplastic anemia treated with immunosuppressive therapy. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2008; 50: 52–57.
Locasciulli A, Arcese W, Locatelli F, Di Bona E, Bacigalupo A . Treatment of aplastic anemia with granulocyte-colony stimulating factor and risk of malignancy. Italian Aplastic Anemia Study Group. Lancet 2001; 357: 43–44.
Scheinberg P, Nunez O, Wu C, Young NS . Treatment of severe aplastic anemia with combined immunosuppression: anti-thymocyte globulin, ciclosporin and mycophenolate mofetil. Br J Haematol 2006; 133: 606–611.
Scheinberg P, Wu CO, Nunez O, Boss C, Sloand EM, Young NS . Treatment of severe aplastic anemia with a combination of horse antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine, with or without sirolimus: a prospective randomized study. Haematologica 2009; 94: 348–354.
Selleri C, Serio B, Risitano AM . Novel immunosuppressive strategies for bone marrow failure syndromes: a focus on alemtuzumab. Mini Rev Med Chem 2011; 11: 536–543.
Scheinberg P, Nunez O, Young NS . Retreatment with rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin and ciclosporin for patients with relapsed or refractory severe aplastic anemia. Br J Haematol 2006; 133: 622–627.
Kamio T, Ito E, Ohara A, Kosaka Y, Tsuchida M, Yagasaki H et al. Relapse of aplastic anemia in children after immunosuppressive therapy: a report from the Japan Childhood Aplastic Anemia Study Group. Haematologica 2011; 96: 814–819.
Kosaka Y, Yagasaki H, Sano K, Kobayashi R, Ayukawa H, Kaneko T et al. Prospective multicenter trial comparing repeated immunosuppressive therapy with stem-cell transplantation from an alternative donor as second-line treatment for children with severe and very severe aplastic anemia. Blood 2008; 111: 1054–1059.
Eapen M, Horowitz M . Alternative donor transplantation for aplastic anemia. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2010; 2010: 43–46.
Bacigalupo A, Socie G, Lanino E, Prete A, Locatelli F, Locasciulli A et al. Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, antithymocyte globulin, with or without low dose total body irradiation, for alternative donor transplants, in acquired severe aplastic anemia: a retrospective study from the EBMT-SAA working party. Haematologica 2010; 95: 976–982.
Viollier R, Socie G, Tichelli A, Bacigalupo A, Korthof ET, Marsh J et al. Recent improvement in outcome of unrelated donor transplantation for aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 41: 45–50.
Kennedy-Nasser AA, Leung KS, Mahajan A, Weiss HL, Arce JA . Comparable outcomes of matched-related and alternative donor stem cell transplantation for pediatric severe aplastic anemia. BBMT 2011; 12: 1277–1284.
Perez-Albuerne ED, Eapen M, Klein J, Gross TJ, Lipton JM, Baker KS et al. Outcome of unrelated donor stem cell transplantation for children with severe aplastic anemia. Br J Haematol 2008; 141: 216–223.
Jaing TH, Huang IA, Chen SH, Yang CP, Liang DC, Hung IJ . Cord blood transplantation in children with relapsed or refractory severe aplastic anemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2011; 33: 18–21.
Yoshimi A, Kojima S, Taniguchi S, Hara J, Matsui T, Takahashi Y et al. Unrelated cord blood transplantation for severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 1057–1063.
Li Y, Li X, Ge M, Shi J, Qian L, Zheng Y et al. Long-term follow-up of clonal evolutions in 802 aplastic anemia patients: a single-center experience. Ann Hematol 2011; 90: 529–537.
Ades L, Mary J-Y, Robin M, Ferry C, Porcher R, Esperou H et al. Long-term outcome after bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia. Blood 2004; 103: 2490–249.
Eapen M, Ramsay NKC, Mertens AC, Robison LL, DeFor T, Davies SM . Late outcomes after bone marrow transplant for aplastic anemia. Br J Haematol 2000; 111: 754–760.
Mohty B, Mohty M . Long-term complications and side effects after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: an update. Blood Cancer J 2011; 1: e16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korthof, E., Békássy, A., Hussein, A. et al. Management of acquired aplastic anemia in children. Bone Marrow Transplant 48, 191–195 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.235
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.235