Abstract
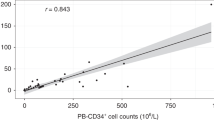
PBSCs are usually mobilized using G-CSF with or without chemotherapy. With the emergence of newer mobilizing agents, predicting poor mobilization may allow early intervention and prevent the costs and complications associated with remobilization. We retrospectively evaluated a cohort of 1556 patients seen between January 2000 and September 2008 with multiple myeloma (565; 36%), non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) (562; 36%), amyloidosis (345; 22%) or Hodgkin's disease (94; 6%), who were initially mobilized with single agent G-CSF. Sensitivity and specificity analysis was used to identify ideal peripheral blood CD34 count (PB-CD34) cutoff points that predicted successful collection. In patients with plasma cell disorders, a PB-CD34 count of 11, 17, 21 and 28/μL by day 4 or 5 was required to collect a target of 2, 4, 8 or 12 million cells/kg, respectively. A CD34 yield of <0.8 million cells/kg on first apheresis also predicted for <2 million CD34 cells/kg. For patients with NHL or Hodgkin's disease, a PB-CD34 count of <6 and <15/μL on day 4 or 5 predicted failure to achieve a target collection of 2 and 4 million cells/kg, respectively. This study suggests that PB-CD34 thresholds should be based on collection target to allow for early intervention and to prevent collection failures.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attal M, Harousseau JL, Stoppa AM, Sotto JJ, Fuzibet JG, Rossi JF et al. A prospective, randomized trial of autologous bone marrow transplantation and chemotherapy in multiple myeloma. Intergroupe Francais du Myelome. N Engl J Med 1996; 335: 91–97.
Barlogie B, Kyle RA, Anderson KC, Greipp PR, Lazarus HM, Hurd DD et al. Standard chemotherapy compared with high-dose chemoradiotherapy for multiple myeloma: final results of phase III US Intergroup Trial S9321. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 929–936.
Blade J, Rosinol L, Sureda A, Ribera JM, Diaz-Mediavilla J, Garcia-Larana J et al. High-dose therapy intensification compared with continued standard chemotherapy in multiple myeloma patients responding to the initial chemotherapy: long-term results from a prospective randomized trial from the Spanish cooperative group PETHEMA. Blood 2005; 106: 3755–3759.
Child JA, Morgan GJ, Davies FE, Owen RG, Bell SE, Hawkins K et al. High-dose chemotherapy with hematopoietic stem-cell rescue for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1875–1883.
Fermand JP, Katsahian S, Divine M, Leblond V, Dreyfus F, Macro M et al. High-dose therapy and autologous blood stem-cell transplantation compared with conventional treatment in myeloma patients aged 55 to 65 years: long-term results of a randomized control trial from the Group Myelome-Autogreffe. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 9227–9233.
Philip T, Guglielmi C, Hagenbeek A, Somers R, Van der Lelie H, Bron D et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation as compared with salvage chemotherapy in relapses of chemotherapy-sensitive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 1540–1545.
Shipp MA, Abeloff MD, Antman KH, Carroll G, Hagenbeek A, Loeffler M et al. International Consensus Conference on High-Dose Therapy with Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Aggressive Non-Hodgkin's Lymphomas: report of the jury. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 423–429.
Schmitz N, Pfistner B, Sextro M, Sieber M, Carella AM, Haenel M et al. Aggressive conventional chemotherapy compared with high-dose chemotherapy with autologous haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation for relapsed chemosensitive Hodgkin's disease: a randomised trial. Lancet 2002; 359: 2065–2071.
Gratwohl A, Baldomero H, Frauendorfer K, Urbano-Ispizua A . EBMT activity survey 2004 and changes in disease indication over the past 15 years. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 37: 1069–1085.
de la Rubia J, Blade J, Lahuerta JJ, Ribera JM, Martinez R, Alegre A et al. Effect of chemotherapy with alkylating agents on the yield of CD34+ cells in patients with multiple myeloma. Results of the Spanish Myeloma Group (GEM) Study. Haematologica 2006; 91: 621–627.
Kumar S, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Hayman SR, Buadi FK, Gastineau DA et al. Impact of lenalidomide therapy on stem cell mobilization and engraftment post-peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma. Leukemia 2007; 21: 2035–2042.
Mark T, Stern J, Furst JR, Jayabalan D, Zafar F, LaRow A et al. Stem cell mobilization with cyclophosphamide overcomes the suppressive effect of lenalidomide therapy on stem cell collection in multiple myeloma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 795–798.
Mazumder A, Kaufman J, Niesvizky R, Lonial S, Vesole D, Jagannath S . Effect of lenalidomide therapy on mobilization of peripheral blood stem cells in previously untreated multiple myeloma patients. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1280–1281 (author reply 1281–1282).
Paripati H, Stewart AK, Cabou S, Dueck A, Zepeda VJ, Pirooz N et al. Compromised stem cell mobilization following induction therapy with lenalidomide in myeloma. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1282–1284.
Perea G, Sureda A, Martino R, Altes A, Martinez C, Cabezudo E et al. Predictive factors for a successful mobilization of peripheral blood CD34+ cells in multiple myeloma. Ann Hematol 2001; 80: 592–597.
Tricot G, Jagannath S, Vesole D, Nelson J, Tindle S, Miller L et al. Peripheral blood stem cell transplants for multiple myeloma: identification of favorable variables for rapid engraftment in 225 patients. Blood 1995; 85: 588–596.
DiPersio JF, Stadtmauer EA, Nademanee A, Micallef IN, Stiff PJ, Kaufman JL et al. Plerixafor and G-CSF versus placebo and G-CSF to mobilize hematopoietic stem cells for autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood 2009; 113: 5720–5726.
DiPersio JF, Micallef IN, Stiff PJ, Bolwell BJ, Maziarz RT, Jacobsen E et al. Phase III prospective randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of plerixafor plus granulocyte colony-stimulating factor compared with placebo plus granulocyte colony-stimulating factor for autologous stem-cell mobilization and transplantation for patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 4767–4773.
Burgstaler E, Pineda A, Winters JL . Effects of high whole blood flow rates and high peripheral white blood cell counts on CD34+ yield and cross-cellular contamination. Cytotherapy 2003; 5: 446.
Burgstaler E, Pineda A . The negative effect of high peripheral white blood cell count on CD34+ cell recovery. J Clin Apher 2002; 17: 148.
Cooling L, Hoffmann S, Herrst M, Muck C, Armelagos H, Davenport R . A prospective randomized trial of two popular mononuclear cell collection sets for autologous peripheral blood stem cell collection in multiple myeloma. Transfusion 2010; 50: 100–119.
Burgstaler E, Porrata LF, Markovic SN, Winters JL . Use of various offset settings in the Fenwal Amicus during hematopoietic progenitor cell collection to increase lymphocyte yield and reduce cross-cellular contamination. J Clin Apher 2010; 25 (Epub ahead of print).
Pusic I, Jiang SY, Landua S, Uy GL, Rettig MP, Cashen AF et al. Impact of mobilization and remobilization strategies on achieving sufficient stem cell yields for autologous transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 1045–1056.
Gordan LN, Sugrue MW, Lynch JW, Williams KD, Khan SA, Wingard JR et al. Poor mobilization of peripheral blood stem cells is a risk factor for worse outcome in lymphoma patients undergoing autologous stem cell transplantation. Leuk Lymphoma 2003; 44: 815–820.
Kuittinen T, Nousiainen T, Halonen P, Mahlamaki E, Jantunen E . Prediction of mobilisation failure in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 907–912.
Gertz MA, Kumar SK, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, Hayman SR, Buadi FK et al. Comparison of high-dose CY and growth factor with growth factor alone for mobilization of stem cells for transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 43: 619–625.
Aiuti A, Webb IJ, Bleul C, Springer T, Gutierrez-Ramos JC . The chemokine SDF-1 is a chemoattractant for human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells and provides a new mechanism to explain the mobilization of CD34+ progenitors to peripheral blood. J Exp Med 1997; 185: 111–120.
Lapidot T . Mechanism of human stem cell migration and repopulation of NOD/SCID and B2mnull NOD/SCID mice. The role of SDF-1/CXCR4 interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2001; 938: 83–95.
Liles WC, Broxmeyer HE, Rodger E, Wood B, Hubel K, Cooper S et al. Mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells in healthy volunteers by AMD3100, a CXCR4 antagonist. Blood 2003; 102: 2728–2730.
Liles WC, Rodger E, Broxmeyer HE, Dehner C, Badel K, Calandra G et al. Augmented mobilization and collection of CD34+ hematopoietic cells from normal human volunteers stimulated with granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor by single-dose administration of AMD3100, a CXCR4 antagonist. Transfusion 2005; 45: 295–300.
Flomenberg N, Devine SM, Dipersio JF, Liesveld JL, McCarty JM, Rowley SD et al. The use of AMD3100 plus G-CSF for autologous hematopoietic progenitor cell mobilization is superior to G-CSF alone. Blood 2005; 106: 1867–1874.
Cottler-Fox MH, Lapidot T, Petit I, Kollet O, DiPersio JF, Link D et al. Stem cell mobilization. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2003, 419–437.
Micallef I, Ansell SM, Buadi F, Dingli D, Dispenzieri A, Gastineau D et al. A risk adapted approach utilizing plerixafor in autologous peripheral blood stem cell mobilization. ASH Annu Meet Abstr 2009; 114: 3211.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Hematological Malignancies Program (Mayo Clinic Cancer Center) and CA90628 (SK) from National Cancer Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Dr Shaji Kumar: research funding from Celegene, Genzyme, Millenium, Novartis, Bayer, Advisory board, Genzyme. Dr Ivana Micallef: research funding from Genzyme, Advisory board, Genzyme. Dr Morie Gertz: research funding from Genzyme.
Additional information
Presented in part at American Society of Hematology Annual meeting, December 2009, New Orleans, LA, USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, S., Gastineau, D., Micallef, I. et al. Predicting PBSC harvest failure using circulating CD34 levels: developing target-based cutoff points for early intervention. Bone Marrow Transplant 46, 943–949 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2010.236
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2010.236
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Plerixafor in patients with lymphoma and multiple myeloma: effectiveness in cases with very low circulating CD34+ cell levels and preemptive intervention vs remobilization
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2015)
-
Phase 2 trial of intravenously administered plerixafor for stem cell mobilization in patients with multiple myeloma following lenalidomide-based initial therapy
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
Autologous haematopoietic stem cell mobilisation in multiple myeloma and lymphoma patients: a position statement from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
Effectiveness of etoposide chemomobilization in lymphoma patients undergoing auto-SCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2013)
-
Plerixafor and G-CSF for autologous stem cell mobilization in patients with NHL, Hodgkin’s lymphoma and multiple myeloma: results from the expanded access program
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2013)