Abstract
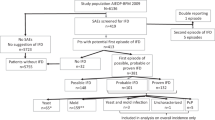
Caspofungin at standard dose was evaluated as first-line monotherapy of mycologically documented probable/proven invasive aspergillosis (IA) (unmodified European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Mycosis Study Group criteria) in allogeneic hematopoietic SCT patients. The primary efficacy end point was complete or partial response at end of caspofungin treatment. Response at week 12, survival and safety were additional end points. Enrollment was stopped prematurely because of low accrual, with 42 enrolled and 24 eligible, giving the study a power of 85%. Transplant was from unrelated donors in 16 patients; acute or chronic GVHD was present in 15. In all, 12 patients were neutropenic (<500/μl) at baseline, 10 received steroids and 16 calcineurin inhibitors or sirolimus. Median duration of caspofungin treatment was 24 days. At the end of caspofungin therapy, 10 (42%) patients had complete or partial response (95% confidence interval: 22–63%); 1 (4%) and 12 (50%) had stable and progressing disease, respectively; one was not evaluable. At week 12, eight patients (33%) had complete or partial response. Survival rates at week 6 and 12 were 79 and 50%, respectively. No patient had a drug-related serious adverse event or discontinued because of toxicity. Caspofungin first-line therapy was effective and well tolerated in allogeneic hematopoietic SCT patients with mycologically documented IA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marr K, Carter RA, Boeckh M, Martin P, Corey L . Invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: changes in epidemiology and risk factors. Blood 2002; 100: 4358–4366.
Martino R, Subira M . Invasive fungal infections in hematology: new trends. Ann Hematol 2002; 81: 233–243.
Ribaud P, Chastang C, Latgé JP, Baffroy-Lafitte L, Parquet N, Devergie A et al. Survival and prognostic factors of invasive aspergillosis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Clin Infect Dis 1999; 28: 322–330.
Nivoix Y, Velten M, Letscher-Bru V, Moghaddam A, Natarajan-Amé S, Fohrer C et al. Factors associated with overall and attributable mortality in invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47: 1176–1184.
Marr K, Carter RA, Crippa F, Wald A, Corey L . Epidemiology and outcome of mould infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34: 909–917.
Pagano L, Caira M, Nosari A, Van Lint MT, Candoni A, Offidani M . Fungal infections in recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplants: results of the SEIFEM B-2004 study—Sorveglianza Epidemiologica Infezioni Fungine Nelle Emopatie Maligne. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45: 1161–1170.
Cannon J, Garey KW, Danziper LH . A prospective and retrospective analysis of the nephtrotoxicity and efficacy of lipid-based amphotericin B formulations. Pharmacotherapy 2001; 21: 1107–1114.
Cornely O, Lasso M, Betts R, Klimko N, Vazquez J, Dobb G et al. Caspofungin for the treatment of less common forms of invasive candidiasis. J Antimicrobial Chemother 2007; 60: 363–369.
Ullmann A . Review of the safety, tolerability, and drug interactions of the new antifungal agents caspofungin and voriconazole. Curr Med Res Opin 2003; 19: 263–271.
Maertens J, Raad I, Petrikkos G, Boogaerts M, Selleslag D, Petersen FB et al. Efficacy and safety of caspofungin for treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients refractory to or intolerant of conventional antifungal therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 1563–1571.
Kartsonis N, Nielsen J, Douglas CM . Caspofungin: the first in a new class of antifungal agents. Drug Resist Update 2003; 6: 197–218.
Ascioglu S, Rex JH, de Pauw B, Bennett JE, Bille J, Crokaert F et al. Defining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplants: an international consensus. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34: 7–14.
Viscoli C, Herbrecht R, Akan H, Baila L, Sonet A, Gallamini A et al. Caspofungin as first-line therapy of invasive aspergillosis in haematological patients: a study of the EORTC Infectious Diseases Group. J Antimicrob 2009; 64: 1274–1281.
Viscoli C, Machetti M, Cappellano P, Bucci B, Bruzzi P, Van Lint MT et al. False-positive galactomannan platelia Apergillus test results for patients receiving piperacillin-tazobactam. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 38: 913–916.
Herbrecht R, Letscher-Bru V, Oprea C, Lioure B, Waller J, Campos F et al. Aspergillus galactomannan detection in the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 1898–1906.
Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF, Bennett JE, Greene RE, Oestmann JW et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 408–415.
Garcia-Vidal C, Upton A, Kirby KA, Marr KA . Epidemiology of invasive mold infections in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: biological risk factors for infection according to time after transplantation. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47: 1041–1050.
Cornely O, Maertens J, Bresnik M, Ebrahimi R, Ullmann AJ, Bouza E et al. Liposomal amphotericin B as initial therapy for invasive mold infection: a randomized trial comparing a high–loading dose regimen with standard dosing (AmBiLoad Trial). Clin Infect Dis 2007; 44: 1289–1297.
Cornely O, Maertens J, Ullmann AJ, Heussel CP, Herbrecht R . Reply to denning. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45: 1108–1109.
Segal B, Herbrecht R, Stevens DA, Ostrosky-Zeichner L, Sobel J, Viscoli C et al. Defining responses to therapy and study outcomes in clinical trials of invasive fungal diseases: Mycoses Study Group and European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Consensus Criteria. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47: 674–683.
Wingard J, Ribaud P, Schlamm HT, Herbrecht R . Changes in causes of death over time after treatment for invasive aspergillosis. Cancer 2008; 112: 2309–2312.
Walsh T, Teppler H, Donowitz GR, Maertens JA, Baden LR, Dmoszynska A et al. Caspofungin versus liposomal amphotericin B for empirical antifungal therapy in patients with persistent fever and neutropenia. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1391–1402.
Mora-Duarte J, Betts R, Rotstein C, Colombo AL, Thompson-Moya L, Smietana J et al. Comparison of caspofungin and amphotericin B for invasive candidiasis. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 2020–2029.
Wingard J, White MH, Anaissie E, Raffalli J, Goodman J, Arrieta A, L Amph/ABLC Collaborative Study Group. A randomized, double-blind comparative trial evaluating the safety of liposomal amphotericin B versus amphotericin B lipid complex in the empirical treatment of febrile neutropenia. Clin Infect Dis 2000; 31: 1155–1163.
Nivoix Y, Levêque D, Herbrecht R, Koffel JC, Beretz L, Ubeaud-Sequier G . The enzymatic basis of drug-drug interactions with systemic triazole antifungals. Clin Pharmacokinet 2008; 47: 77–792.
Morrissey C, Slavin MA, O’Reilly MA, Daffy JR, Seymour JF, Schwarer AP et al. Caspofungin as salvage monotherapy for invasive aspergillosis in patients with haematological malignancies or following allogeneic stem cell transplantation: efficacy and concomitant cyclosporin A. Mycoses 2007; 50 (Suppl 1): 24–37.
Acknowledgements
We thank Wendy Horn, PhD for writing and editorial assistance, which was funded by Merck & Co, Inc. Presented in part as a poster at the 48th Annual Meeting of the Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 25–28 October 2008, Washington, DC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
R Herbrecht has been a consultant or received honoraria or a grant from Astellas, Basilea, Gilead, Merck & Co, Novartis, Pfizer, Schering Plough, and Zeneus. J Maertens has been a consultant or received honoraria or a grant from Astellas, Gilead, Merck & Co, Pfizer, Schering Plough, Zeneus, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Myconostica and Basilea Pharmaceuticals. M Aoun has been a consultant or received honoraria or a grant from Pfizer, Schering-Plough and Merck & Co. W Heinz has been a consultant or received honoraria or a grant from Essex/Schering-Plough, Gilead, Merck & Co and Pfizer. S Schwartz has received travel grants and honoraria from Pfizer and Enzon. AJ Ullmann has received funds for speaking at symposia organized on behalf of Astellas, Gilead, Merck & Co, Pfizer, Schering Plough, and MSD, has also received funds for research from MSD, Schering-Plough, and Astellas and is a member of the MSD advisory board for caspofungin and further is a member of the advisory boards from Astellas, Basilea, Gilead, Aicuris, Pfizer, and Schering Plough. O Marchetti received research grants and honoraria as a consultant and/or speaker from Merck & Co, Novartis, Pfizer and Schering-Plough. H Akan has received travel grants and honoraria from MSD and Pfizer. M Shivaprakash is employed by Merck & Co, Inc. C Viscoli has been a consultant to Astellas, Gilead, Merck & Co, Pfizer, Schering-Plough, has been member of speaker’s bureaus for Gilead, Pfizer, Schering-Plough and has received research grant from Pfizer, Merck & Co, Gilead, BMS and Abbott. L Baila, L Ameye, L Meert, M Paesmans and R Martino declare no conflict of interest.
Data Review Committee: H Akan, L Baila, R Herbrecht (chairman), O Marchetti, R Martino, L Meert (data manager), M Paesmans (statistician) and AJ Ullmann.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herbrecht, R., Maertens, J., Baila, L. et al. Caspofungin first-line therapy for invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients: an European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer study. Bone Marrow Transplant 45, 1227–1233 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2009.334
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2009.334
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Safety and efficacy of non-reduced use of caspofungin in patients with Child–Pugh B or C cirrhosis: a real-world study
Infection (2024)
-
Antifungal Prophylaxis in the Era of Targeted Chemotherapy for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
Current Fungal Infection Reports (2023)
-
Azole-Resistant Aspergillus and Echinocandin-Resistant Candida: What Are the Treatment Options?
Current Fungal Infection Reports (2020)
-
Pharmacokinetics of antifungal drugs: practical implications for optimized treatment of patients
Infection (2017)
-
Prognostic value of galactomannan: current evidence for monitoring response to antifungal therapy in patients with invasive aspergillosis
Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics (2017)