Abstract
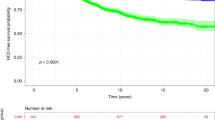
We used the National Institutes of Health (NIH) criteria for the diagnosis, classification and scoring of chronic GVHD (cGVHD) to reevaluate patients with cGVHD originally diagnosed using classic criteria. We retrieved data from 236 patients diagnosed with cGVHD on the basis of classic criteria. Excluding 20 ‘liver-alone’ patients, we re-categorized 216 patients in keeping with the NIH criteria. Twenty patients were reclassified as having acute GVHD and 196 patients as having cGVHD (170 ‘classic chronic’ (Cl-Ch) and 26 ‘overlap chronic’ (Ov-Ch)). The 5-year GVHD-specific survival (GSS) was significantly different between the two cGVHD subtypes, specifically 87.3% for Cl-Ch vs 70.2% for Ov-Ch (P=0.006). The NIH severity criteria were effective in expecting 5-year GSS rates at both the onset (93.5, 81.3 and 79.7% (P=0.047)) and peak intensity of the disease (100, 89.7 and 78.7% (P=0.004) for the mild, moderate and severe grade, respectively). Multivariate analysis showed that NIH severity criteria were independently significant prognostic factors for GSS (mild vs moderate, HR 4.35, P=0.036; mild vs severe, HR 5.25, P=0.020). Our results support the role of the NIH criteria in classifying cGVHD and in assessing the severity of the disease to predict patient prognosis of cGVHD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Socie G, Stone JV, Wingard JR, Weisdorf D, Henslee-Downey PJ, Bredeson C et al. Long-term survival and late deaths after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation Late Effects Working Committee of the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 14–21.
Sutherland HJ, Fyles GM, Adams G, Hao Y, Lipton JH, Minden MD et al. Quality of life following bone marrow transplantation: a comparison of patient reports with population norms. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 19: 1129–1136.
Duell T, van Lint MT, Ljungman P, Tichelli A, Socie G, Apperley JF et al. Health and functional status of long-term survivors of bone marrow transplantation EBMT Working Party on Late Effects and EULEP Study Group on Late Effects. European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Ann Intern Med 1997; 126: 184–192.
Syrjala KL, Chapko MK, Vitaliano PP, Cummings C, Sullivan KM . Recovery after allogeneic marrow transplantation: prospective study of predictors of long-term physical and psychosocial functioning. Bone Marrow Transplant 1993; 11: 319–327.
Wingard JR, Piantadosi S, Vogelsang GB, Farmer ER, Jabs DA, Levin LS et al. Predictors of death from chronic graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1989; 74: 1428–1435.
Karanes C, Nelson GO, Chitphakdithai P, Agura E, Ballen KK, Bolan CD et al. Twenty years of unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation for adult recipients facilitated by the National Marrow Donor Program. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14 (9 Suppl): 8–15.
Bensinger WI, Martin PJ, Storer B, Clift R, Forman SJ, Negrin R et al. Transplantation of bone marrow as compared with peripheral-blood cells from HLA-identical relatives in patients with hematologic cancers. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 175–181.
Symons HJ, Fuchs EJ . Hematopoietic SCT from partially HLA-mismatched (HLA-haploidentical) related donors. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 42: 365–377.
Chen YB, Spitzer TR . Current status of reduced-intensity allogeneic stem cell transplantation using alternative donors. Leukemia 2008; 22: 31–41.
Remberger M, Kumlien G, Aschan J, Barkholt L, Hentschke P, Ljungman P et al. Risk factors for moderate-to-severe chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2002; 8: 674–682.
Carlens S, Ringden O, Remberger M, Lonnqvist B, Hagglund H, Klaesson S et al. Risk factors for chronic graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation: a retrospective single centre analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 22: 755–761.
Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, McDonald GB, Striker GE, Sale GE et al. Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med 1980; 69: 204–217.
Sullivan KM, Shulman HM, Storb R, Weiden PL, Witherspoon RP, McDonald GB et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease in 52 patients: adverse natural course and successful treatment with combination immunosuppression. Blood 1981; 57: 267–276.
Hashino S, Imamura M, Kasai M, Higa T, Naohara T, Sakamaki S et al. Bone marrow transplantation for hematological diseases in Hokkaido—June 1985 to December 1991. Jpn J Clin Oncol 1993; 23: 166–172.
Grigg AP, Szer J, Beresford J, Dodds A, Bradstock K, Durrant S et al. Factors affecting the outcome of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for adult patients with refractory or relapsed acute leukaemia. Br J Haematol 1999; 107: 409–418.
Gratwohl A, Brand R, Apperley J, Biezen Av A, Bandini G, Devergie A et al. Graft-versus-host disease and outcome in HLA-identical sibling transplantations for chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 3877–3886.
Greinix HT, Nachbaur D, Krieger O, Eibl M, Knobl P, Kalhs P et al. Factors affecting long-term outcome after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for acute myelogenous leukaemia: a retrospective study of 172 adult patients reported to the Austrian Stem Cell Transplantation Registry. Br J Haematol 2002; 117: 914–923.
Akpek G . Clinical grading in chronic graft-versus-host disease: is it time for change? Leuk Lymphoma 2002; 43: 1211–1220.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 945–956.
Jagasia M, Giglia J, Chinratanalab W, Dixon S, Chen H, Frangoul H et al. Incidence and outcome of chronic graft-versus-host disease using National Institutes of Health consensus criteria. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 1207–1215.
Cho BS, Min CK, Eom KS, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Lee S et al. Feasibility of NIH consensus criteria for chronic graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia 2009; 23: 78–84.
Akpek G, Zahurak ML, Piantadosi S, Margolis J, Doherty J, Davidson R et al. Development of a prognostic model for grading chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2001; 97: 1219–1226.
Lee JH, Lee JH, Choi SJ, Kim S, Seol M, Lee YS et al. Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)-specific survival and duration of systemic immunosuppressive treatment in patients who developed chronic GVHD following allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation. Br J Haematol 2003; 122: 637–644.
Lee SJ, Klein JP, Barrett AJ, Ringden O, Antin JH, Cahn JY et al. Severity of chronic graft-versus-host disease: association with treatment-related mortality and relapse. Blood 2002; 100: 406–414.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DY., Lee, JH., Lee, JH. et al. Reevaluation of the National Institutes of Health criteria for classification and scoring of chronic GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant 45, 1174–1180 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2009.320
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2009.320
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Evolving concepts in prognostic scoring of chronic GvHD
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)
-
Chronic GVHD induced GVL effect after unmanipulated haploidentical hematopoietic SCT for AML and myelodysplastic syndrome
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2015)
-
Significantly worse survival of patients with NIH-defined chronic graft-versus-host disease and thrombocytopenia or progressive onset type: results of a prospective study
Leukemia (2012)
-
Clinical significance of subcategory and severity of chronic graft-versus-host disease evaluated by National Institutes of Health consensus criteria
International Journal of Hematology (2011)