Abstract
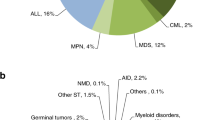
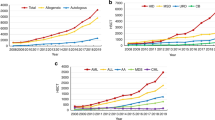
The adult transplant programme at Singapore General Hospital (SGH) was established in 1985 and more than 820 transplants have been performed to date. An average of about 60 adult transplants (autologous and allogeneic) are performed each year. Transplants offered at SGH run the range from autologous to mismatched cord and unrelated transplants. Special interests of the transplant programme include non-myeloablative transplants in aplastic anaemia, cell therapy protocols including cytokine-induced killer cells, patterns of GVHD, cord blood transplantation for autoimmune diseases and graft engineering. A cGMP (good manufacturing practice) cell therapy laboratory was recently established to facilitate bench-to-bedside translational cell therapy trials. A BMT consortium has been formed among the various paediatric and adult transplant centres for harmonization of protocols and research activities.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan DCL, Hsu LY, Koh LP, Goh YT, Koh M . Severe conidiobolomycosis complicating induction chemotherapy in a patient with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2005; 129: 447.
Cornely OA, Maertens J, Winston DJ, Perfect J, Ullmann AJ, Walsh TJ et al. Posaconazole vs fluconazole or itraconazole prophylaxis in patients with neutropenia. N Eng J Med 2007; 356: 348–359.
Koh LP, Koh MBC, Goh YT, Tan P . Allogeneic HSCT for patients with severe aplastic anaemia following non myeloablative conditioning with 200 cGy TBI and fludarabine. Biol Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 887–890.
Koh LP, Chen CS, Tai BC, Hwang WY, Tan LK, Koh MBC et al. The impact of post grafting immunosuppression on non relapse mortality and survival after non myeloablative transplantation using fludarabine and 200 cGy total body irradiation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 790–805.
Koh MBC, Prentice HG, Corbo M, Cotter FE, Morgan M, Lowdell MW . Alloantigen-specific T-cell depletion in a major histocompatibility complex fully mismatched murine model provides effective graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in the presence of lymphoid engraftment. Br J Haematol 2002; 118: 108–116.
Koh MBC, Lim TJ, Niam M, Suck G, Chan M, Goh YT et al. A Translational Clinical Trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of graded infusions of ex-vivo expanded cytokine induced killer (CIK) cells for haematologic malignancies. Cytotherapy 2007, abstract.
Linn YC, Wang SM, Hui KM . Comparative gene expression profiling of cytokine-induced killer cells in response to acute myloid leukemic and acute lymphoblastic leukemic stimulators using oligonucleotide arrays. Exp Haem 2005; 33: 671–681.
Suck G . Novel approaches using natural killer cells in cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol 2006; 16: 412–418.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koh, M., Goh, Y., Tan, P. et al. Stem cell transplantation programme at Singapore General Hospital. Bone Marrow Transplant 42 (Suppl 1), S121–S124 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.139
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.139
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hematopoietic SCT activity in Asia: a report from the Asia-Pacific Blood and Marrow Transplantation Group
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2010)