Abstract
Background:
Different antiangiogenics are currently indicated in the second-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC), following a first-line bevacizumab-containing treatment. The magnitude of benefit is limited, but no predictors of benefit have been identified.
Methods:
A total of 184 mCRC patients progressing to a first-line bevacizumab-containing treatment were randomised in the BEBYP study to continue or not the antiangiogenic in combination with a second-line chemotherapy. A subgroup analysis according to baseline serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels was carried out.
Results:
A significant interaction effect between LDH levels and treatment was found in terms of progression-free survival (PFS; P=0.002). Although patients with low LDH levels achieved significant PFS benefit from the continuation of bevacizumab (HR: 0.39 (95% CI: 0.23–0.65)), patients with high levels did not (HR: 1.10 (95% CI: 0.74–1.64)). Consistent results were reported in overall survival (OS; P=0.075).
Conclusions:
As preclinical evidence suggests that serum LDH may be a marker of tumour angiogenesis activation, low levels may indicate that bevacizumab is still efficacious in inhibiting angiogenesis. Validation of present results in subgroup analyses of other randomised trials of second-line angiogenesis inhibitors is warranted.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
In the last years, different antiangiogenic agents with peculiar mechanisms of action considerably contributed to the prolongation of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients’ survival through subsequent incremental advantages more than a single seismic effect (Sobrero and Bruzzi, 2009).
First, the combination of the anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) A bevacizumab (bev) with a fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy was demonstrated an efficacious option both in first and second line (Hurwitz et al, 2004; Giantonio et al, 2007; Saltz et al, 2008; Bennouna et al, 2013; Loupakis et al, 2014; Masi et al, 2015). Then, ML18147 and bevacizumab beyond progression (BEBYP) trials demonstrated that continuing bev after progression in combination with a switched fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy in patients already treated with first-line chemotherapy plus bev prolongs mCRC patients’ survival (Bennouna et al, 2013; Masi et al, 2015).
More recently, two new drugs enriched the armamentarium of angiogenesis inhibitors available for the treatment after progression: aflibercept, a recombinant fusion protein targeting VEGF-A, VEGF-B and Placental growth factor, and ramucirumab, a fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody targeting VEGF receptor (VEGFR) 2. The VELOUR trial demonstrated that the addition of aflibercept to second-line FOLFIRI significantly improves overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) in patients previously treated with an oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy, with no interaction between prior exposure to bev and treatment (Van Cutsem et al, 2012). The RAISE trial consistently demonstrated significant PFS and OS benefit for ramucirumab when added to second-line FOLFIRI in a homogeneous cohort of patients treated with first-line FOLFOX plus bev (Tabernero et al, 2015).
Overall, four randomised studies showed that a prolonged inhibition of angiogenesis beyond the clinical evidence of disease progression improves mCRC patients’ survival, with similar efficacy results across different studies and a limited although statistically significant magnitude of benefit (around 1.5 months benefit in median OS, HRs between 0.81 and 0.84). Therefore, the identification of predictors of benefit from available antiangiogenic drugs would be of paramount importance in order to optimise the cost/benefit ratio of these prolonged antiangiogenic strategies, and, hopefully, to orientate treatment choice towards the best antiangiogenic agent for each single patient.
Nevertheless, in spite of several attempts, up today no predictors of benefit from antiangiogenics have been identified, and the choice of the second-line treatment is mainly based on physicians’ preferences.
According to preclinical data, serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels are an indirect marker of tumour hypoxia and neoangiogenesis, and clinical experiences suggest their prognostic impact (Kemeny and Braun, 1983; Koukourakis et al, 2006; Azuma et al, 2007; Langhammer et al, 2011).
In a retrospective non-interventional study, high serum LDH levels were associated with poor prognosis in a cohort of patients treated with first-line chemotherapy, but not in a cohort of patients treated with first-line chemotherapy plus bev, thus suggesting a potential predictive value with regard to the antiangiogenic (Scartozzi et al, 2012). Similarly, a possible interaction between serum LDH levels and bev effect was assessed in the subgroup analysis of the randomised ITACA study (Passardi et al, 2015).
Nevertheless, the role of LDH levels as a dynamic marker of efficacy of angiogenesis inhibition and therefore a reliable predictor of benefit from continuing antiangiogenic strategies has never been evaluated. To this end, we investigated the prognostic and predictive impact of LDH levels in patients enrolled in BEBYP study, that randomised 184 mCRC patients treated with first-line chemotherapy plus bev to receive a second-line switched chemotherapy regimen alone or with bev. The relationship between LDH levels at baseline (i.e., at the time of disease progression to the first-line bev-containing treatment) and the efficacy of the continuation of bev beyond disease progression was investigated.
Patients and methods
Study population
The BEBYP trial was a prospective, open-label, multicentric, phase III randomised study, conducted in 19 Italian oncology units, in which initially unresectable patients treated with fluoropyrimidine-based first-line chemotherapy plus bev were randomised to receive a switched chemotherapy doublet alone (standard arm) or with bev (experimental arm) until disease progression (Masi et al, 2015).
Patients were eligible if they had experienced disease progression after or during first-line chemotherapy with fluoropyrimidine, FOLFIRI, FOLFOX plus bev or after at least 3 months from the last dose of first-line FOLFOXIRI plus bev. Other eligibility criteria included histological diagnosis of colorectal adenocarcinoma, age between 18 and 75 years, ECOG PS 0–2, unresectable and measurable metastatic disease according to RECIST v1.0, adequate haematological, hepatic and renal functions.
Exclusion criteria included peripheral neuropathy, evidence of bleeding diathesis or coagulopathy, clinically significant cardiovascular disease, uncontrolled hypertension, use of therapeutic anticoagulation, and history of thromboembolic or haemorrhagic events within 6 months before treatment.
The protocol was approved by the local Ethics Committees (NCT00720512), and patients provided their written informed consent to receive the treatment and to participate to translational analyses.
Tumour response was evaluated every 8 weeks by means of contrast enhanced CT scan according to RECIST v1.0.
Statistical analysis
Serum LDH values collected within 28 days before randomisation were taken into consideration. To avoid the exclusion of cases with missing data, the multiple imputation method was used (10 imputations). Regression method was used for imputation of LDH values. Missing-at-random assumption was made.
A cut-off value of 300 UI l−1, corresponding to 1.5 × ULN in most laboratories, was adopted to discriminate patients with low vs high levels, as primary analysis. This stratification criteria was also confirmed by the optimal cut point value determination performed according to Contal and O’Quigley (Contal and O’Quigley, 1999). As secondary analysis, LDH was also treated as an ordinal variable with five levels based on quintiles distribution. The association between LDH level and time to event variables was analysed in univariate and multivariate setting using the Cox proportional hazards model, combining the results of the analyses of imputations according to Rubin’s procedure (Rubin, 1987).
The predictive role of the LDH levels for the effect of bev was investigated by means of interaction test. PFS and OS curves were estimated with the Kaplan–Meier method, and results from multiple imputation analysis were summarised according to Rubin’s rules after complementary log transformation (Morisot et al, 2015). All statistical tests were two sided, and P-values of 0.05 or less were considered to be statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using SAS version 9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA).
Results
Out of 184 randomised patients, LDH levels before the beginning of the second-line treatment were available for 159. The median value was 333 UI l−1 (range: 106–3413). According to a cut-off value of 300 UI l−1, 66 (42%) and 93 (58%) patients had low and high-LDH levels, respectively. Main patients’ characteristics are summarised in Table 1.
Data about RAS and BRAF mutational status were available for 128 (70%) patients and missing for the remaining 56 (30%).
In terms of prognostic impact, in the overall population, no statistically significant correlation of LDH levels with clinical outcome was evident in PFS (high vs low HR: 1,22 (95% CI: 0.88–1.68), P: 0.232), and a trend towards significance was reported in OS (high vs low HR: 1.35 (95% CI: 0.96–1.88), P: 0.081). This result was not confirmed in the multivariate analysis, adjusting for other baseline characteristics (treatment arm, age, sex, ECOG performance status, liver-only disease).
At a median follow-up of 45.3 months, 182 (99%) patients progressed and 163 (89%) patients died.
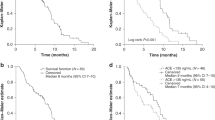
A significant interaction effect between LDH levels and treatment was detected. In particular, patients with low LDH levels achieved significant PFS benefit from the continuation of bev (median PFS: 9.0 vs 4.6 months; HR: 0.39 (95% CI: 0.23–0.65)), whereas patients with high-LDH levels did not (median PFS: 5.5 vs 5.0 months; HR: 1.10 (95% CI: 0.74–1.64); P for interaction: 0.002; Figure 1A and B).
Consistent results were reported for OS: patients with low LDH levels achieved higher benefit from bev in terms of OS (median OS: 23.0 vs 15.2 months; HR: 0.55 (95% CI: 0.33–0.92)) than did patients with high-LDH levels (median OS: 10.6 vs 15.4 months; HR: 1.01 (95% CI: 0.67–1.53); P for interaction: 0.075; Figure 1C and D). Consistent results (P for interaction: PFS, 0.007; OS, 0.106) were reported in the multivariable models including the following baseline characteristics: age, sex, ECOG performance status and number of metastatic sites).
Stratifying the study population on the quintiles of LDH levels, a significant P for interaction was reported in PFS (P=0.031) but not in OS (P=0.496). As shown in Figure 2, the estimates of HRs in the five strata seem to suggest that the benefit from the continuation of bev is clear among patients in the first and second lower quintiles, thus confirming the reliability of 300 UI l−1 as cut-off value.
Discussion
The search for biomarkers of benefit from antiangiogenic agents is a puzzling field of translational research. If a binary marker might hardly catch the complexity of multiple pathways and actors taking part to this biologic process, also more sophisticated approaches failed to identify promising strategies to recognise patients more likely to benefit from this class of drugs. At the same time, the opportunity to use antiangiogenics across different lines of treatment, the availability of targeted agents with different mechanisms of action and the relatively small magnitude of benefit observed in clinical trials make the identification of predictive markers an unmet need for medical oncologists. In fact, several clinical factors were explored as potential predictors of benefit from the continuation of the antiangiogenic strategy beyond disease progression, but no significant or plausible interactions were found (Bennouna et al, 2013; Kubicka et al, 2013; Tabernero et al, 2014; Masi et al, 2015; Obermannová et al, 2016).
Preclinical studies reported a relationship between LDH levels and angiogenesis and demonstrated that high-LDH levels were associated with overexpression of VEGF-A and VEGFR-1 (Harris, 2002; Azuma et al, 2007). A biological link between hypoxia, high-LDH levels and enhanced tumour-driven angiogenesis through the abnormal activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α was confirmed by in vivo studies (Granchi et al, 2010; Langhammer et al, 2011). As a clinical consequence, it has been speculated that LDH levels may represent an indirect indicator of activated tumour angiogenesis. Consistently with this hypothesis, higher LDH levels seem to be associated with benefit from VEGF-A inihibition by bev in first-line (Scartozzi et al, 2012; Passardi et al, 2015). In apparent contrast with these findings, here we report that the continuation of angiogenesis inhibition by bev beyond the evidence of disease progression seems more efficacious in patients with low LDH levels. According to the above reported hypothesis, this may indicate a low grade of tumour angiogenic activity, thus suggesting that in those cases angiogenesis is still efficaciously inhibited by bev. On the other hand, higher LDH levels would reveal active tumour angiogenesis though in the presence of VEGF-A blockade. Moreover, higher LDH levels may be associated with more aggressive disease progressions, where a change in treatment strategy is needed to achieve again disease control.
Differently from other recent experiences (Scartozzi et al, 2012; Passardi et al, 2015), we adopted a cut-off value of 300 UI l−1, to make these findings easily transferable to clinical practice, independently of ranges of normality adopted in every single laboratory.
A strong point of our observation is that it comes from a randomised study, that allows drawing suggestions about the predictive, rather than prognostic, role of this marker with respect to the efficacy of the continuation of bev. The significance of the interaction test in terms of PFS formally supports our findings, and the underlying biologic rationale provides a potential explanation. In fact, the lack of a significant interaction in terms of OS may be due to the low power of this analysis (the primary endpoint of BEBYP study was PFS and the accrual was prematurely interrupted as a consequence of results of the ML18147 study) and to the potential confounding effect of subsequent lines.
On the other hand, this was an unplanned subgroup analysis, thus able to provide only hypothesis-generating findings. A still open question is whether these results are reproducible with other antiangiogenic agents (i.e., aflibercept or ramucirumab) or apply only to the continuation of bev beyond disease progression.
To this end, considering that in the absence of a control arm the predictive role of a biomarker cannot be assessed, and this is especially true when biomarkers also have a prognostic impact, subgroup analyses of phase III randomised trials investigating the addition of an angiogenesis inhibitors to second-line chemotherapy following first-line bev-containing treatment (ML18147, VELOUR, RAISE) are urgently awaited.
Change history
31 January 2017
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Azuma M, Shi M, Danenberg KD, Gardner H, Barrett C, Jacques CJ, Sherod A, Iqbal S, El-Khoueiry A, Yang D, Zhang W, Danenberg PV, Lenz HJ (2007) Serum lactate dehydrogenase levels and glycolysis significantly correlate with tumor VEGFA and VEGFR expression in metastatic CRC patients. Pharmacogenomics 8 (12): 1705–1713.
Bennouna J, Sastre J, Arnold D, Osterlund P, Greil R, Van Cutsem E, von Moos R, Viéitez JM, Bouché O, Borg C, Steffens CC, Alonso-Orduña V, Schlichting C, Reyes-Rivera I, Bendahmane B, André T, Kubicka S ML18147 Study Investigators (2013) Continuation of bevacizumab after first progression in metastatic colorectal cancer (ML18147): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 14 (1): 29–37.
Contal C, O’Quigley J (1999) An application of changepoint methods in studying the effect of age on survival in breast cancer. Comput Stat Data Anal 30 (3): 253–270.
Giantonio BJ, Catalano PJ, Meropol NJ, O’Dwyer PJ, Mitchell EP, Alberts SR, Schwartz MA, Benson AB 3rd Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3200 (2007) Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin (FOLFOX4) for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer: results from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3200. J Clin Oncol 25 (12): 1539–1544.
Granchi C, Bertini S, Macchia M, Minutolo F (2010) Inhibitors of lactate dehydrogenase isoforms and their therapeutic potentials. Curr Med Chem 17 (7): 672–697.
Harris AL (2002) Hypoxia—a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2 (1): 38–47.
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S, Holmgren E, Ferrara N, Fyfe G, Rogers B, Ross R, Kabbinavar F (2004) Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 350 (23): 2335–2342.
Kemeny N, Braun DW Jr (1983) Prognostic factors in advanced colorectal carcinoma. Importance of lactic dehydrogenase level, performance status, and white blood cell count. Am J Med 74 (5): 786–789.
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Gatter KC, Harris AL Tumour Angiogenesis Research G (2006) Lactate dehydrogenase 5 expression in operable colorectal cancer: strong association with survival and activated vascular endothelial growth factor pathway—a report of the Tumour Angiogenesis Research Group. J Clin Oncol 24 (26): 4301–4308.
Kubicka S, Greil R, André T, Bennouna J, Sastre J, Van Cutsem E, von Moos R, Osterlund P, Reyes-Rivera I, Müller T, Makrutzki M, Arnold D ML18147 study investigators including AIO, GERCOR, FFCD, UNICANCER GI, TTD, BGDO, GEMCAD, and AGMT groups (2013) Bevacizumab plus chemotherapy continued beyond first progression in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer previously treated with bevacizumab plus chemotherapy: ML18147 study KRAS subgroup findings. Ann Oncol 24 (9): 2342–2349.
Langhammer S, Najjar M, Hess-Stumpp H, Thierauch KH (2011) LDH-A influences hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF1 alpha) and is critical for growth of HT29 colon carcinoma cells in vivo. Target Oncol 6 (3): 155–162.
Loupakis F, Cremolini C, Masi G, Lonardi S, Zagonel V, Salvatore L, Cortesi E, Tomasello G, Ronzoni M, Spadi R, Zaniboni A, Tonini G, Buonadonna A, Amoroso D, Chiara S, Carlomagno C, Boni C, Allegrini G, Boni L, Falcone A (2014) Initial therapy with FOLFOXIRI and bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 371 (17): 1609–1618.
Masi G, Salvatore L, Boni L, Loupakis F, Cremolini C, Fornaro L, Schirripa M, Cupini S, Barbara C, Safina V, Granetto C, Fea E, Antonuzzo L, Boni C, Allegrini G, Chiara S, Amoroso D, Bonetti A, Falcone A BEBYP Study Investigators (2015) Continuation or reintroduction of bevacizumab beyond progression to first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: final results of the randomized BEBYP trial. Ann Oncol 26 (4): 724–730.
Morisot A, Bessaoud F, Landais P, Rébillard X, Trétarre B, Daurès JP (2015) Prostate cancer: net survival and cause-specific survival rates after multiple imputation. BMC Med Res Methodol 15: 54.
Obermannová R, Van Cutsem E, Yoshino T, Bodoky G, Prausová J, Garcia-Carbonero R, Ciuleanu T, Garcia Alfonso P, Portnoy D, Cohn A, Yamazaki K, Clingan P, Lonardi S, Kim TW, Yang L, Nasroulah F, Tabernero J (2016) Subgroup analysis in RAISE: a randomized, double-blind phase III study of irinotecan, folinic acid, and 5-fluorouracil (FOLFIRI) plus ramucirumab or placebo in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma progression. Ann Oncol 27 (11): 2082–2090.
Passardi A, Scarpi E, Tamberi S, Cavanna L, Tassinari D, Fontana A, Pini S, Bernardini I, Accettura C, Ulivi P, Frassineti GL, Amadori D (2015) Impact of pre-treatment lactate dehydrogenase levels on prognosis and bevacizumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. PloS one 10 (8): e0134732.
Rubin DB (1987) Multiple Imputation for Nonresponse in Surveys. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York.
Saltz LB, Clarke S, Diaz-Rubio E, Scheithauer W, Figer A, Wong R, Koski S, Lichinitser M, Yang TS, Rivera F, Couture F, Sirzén F, Cassidy J (2008) Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol 26 (12): 2013–2019.
Scartozzi M, Giampieri R, Maccaroni E, Del Prete M, Faloppi L, Bianconi M, Galizia E, Loretelli C, Belvederesi L, Bittoni A, Cascinu S (2012) Pre-treatment lactate dehydrogenase levels as predictor of efficacy of first-line bevacizumab-based therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer 106 (5): 799–804.
Sobrero A, Bruzzi P (2009) Incremental advance or seismic shift? The need to raise the bar of efficacy for drug approval. J Clin Oncol 27 (35): 5868–5873.
Tabernero J, Van Cutsem E, Lakomý R, Prausová J, Ruff P, van Hazel GA, Moiseyenko VM, Ferry DR, McKendrick JJ, Soussan-Lazard K, Chevalier S, Allegra CJ (2014) Aflibercept versus placebo in combination with fluorouracil, leucovorin and irinotecan in the treatment of previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer: prespecified subgroup analyses from the VELOUR trial. Eur J Cancer 50 (2): 320–331.
Tabernero J, Yoshino T, Cohn AL, Obermannova R, Bodoky G, Garcia-Carbonero R, Ciuleanu TE, Portnoy DC, Van Cutsem E, Grothey A, Prausová J, Garcia-Alfonso P, Yamazaki K, Clingan PR, Lonardi S, Kim TW, Simms L, Chang SC, Nasroulah F RAISE Study Investigators (2015) Ramucirumab versus placebo in combination with second-line FOLFIRI in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma that progressed during or after first-line therapy with bevacizumab, oxaliplatin, and a fluoropyrimidine (RAISE): a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 16 (5): 499–508.
Van Cutsem E, Tabernero J, Lakomy R, Prenen H, Prausova J, Macarulla T, Ruff P, van Hazel GA, Moiseyenko V, Ferry D, McKendrick J, Polikoff J, Tellier A, Castan R, Allegra C (2012) Addition of aflibercept to fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan improves survival in a phase III randomized trial in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer previously treated with an oxaliplatin-based regimen. J Clin Oncol 30 (28): 3499–3506.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
LA reports serving on advisory board or having consultant role for Roche, Amgen, Eli-Lilly, Bayer, Novartis, Ipsen; FL reports serving on advisory board for Amgen and Sanofi-Aventis, receiving lecture fees from Sanofi-Aventis, Bayer, Roche and grant support from Roche and Merck Serono; AF reports serving on advisory board for Amgen, Bayer, Merck Serono, Roche and Sanofi-Aventis, receiving lecture fees from Merck Serono, Roche, Amgen, Bayer, Amgen, Bayer, Merck Serono, Roche and Sanofi-Aventis and grant support from Amgen, Merck Serono and Roche; CC reports serving on advisory board for Roche, Bayer, Amgen and Merck Serono and receiving lecture fees from Sanofi-Aventis and Bayer. All remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
This work is published under the standard license to publish agreement. After 12 months the work will become freely available and the license terms will switch to a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 4.0 Unported License.
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 4.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Marmorino, F., Salvatore, L., Barbara, C. et al. Serum LDH predicts benefit from bevacizumab beyond progression in metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 116, 318–323 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2016.413
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2016.413
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Advances in metabolic reprogramming of NK cells in the tumor microenvironment on the impact of NK therapy
Journal of Translational Medicine (2024)
-
The colon inflammatory index score can predict the survival outcome after resection of colorectal cancer: a retrospective multicentre study
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
The interplay of circulating tumor DNA and chromatin modification, therapeutic resistance, and metastasis
Molecular Cancer (2019)
-
Considering tumour volume for motion corrected DWI of colorectal liver metastases increases sensitivity of ADC to detect treatment-induced changes
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
A phase II trial to evaluate the efficacy of panitumumab combined with fluorouracil-based chemotherapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: the PF trial
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2018)