Abstract
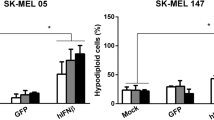
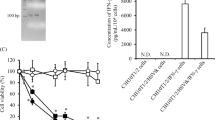
We have previously shown that intravesical administration of adenovirus encoding human interferon α-2b (Ad-IFN) induced a marked regression of superficial human bladder tumors derived from cells that are resistant to over 1 million units/ml of IFNα protein in vitro. In addition, Ad-IFN appeared to produce strong bystander effects. In this study, we show that Ad-IFN causes marked inhibition of cell growth and apoptosis in cells of various tumor types, all of which are resistant to IFNα protein. In addition, strong perinuclear IFN staining was seen in all cell lines following Ad-IFN transfection and was never observed after exposure to the IFN protein. Ad-IFN induced proteolytic processing of caspases 3, 8 and 9, indicative of enzymatic activation. However, the caspase-8-selective inhibitor, IETDfmk, blocked apoptosis only in the cell lines that were sensitive to the IFNα protein and had minimal effect on Ad-IFN-induced caspase-3 or -9 processing and cell death, indicating that death receptor-independent mechanism(s) were involved in the cytotoxic effects observed for cancer cell lines resistant to the IFNα protein. Moreover, we document that a yet to be identified soluble factor(s) is responsible for causing the bystander effect observed following Ad-IFN treatment in IFN protein-resistant cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papageorgiou A, Lashinger L, Millikan R, Benedict WF, Dinney CP, McConkey DJ . Autocrine TRAIL production mediates interferon-induced apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 8973–8979.
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S, Lawrence DA, Marsters SA et al. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest 1999; 104: 155–162.
Benedict WF, Tao Z, Kim CS, Zhang X, Zhou JH, Adam L et al. Intravesical Ad-IFNα causes marked regression of human bladder cancer growing orthotopically in nude mice and overcomes resistance to IFNα protein. Mol Ther 2004; 10: 525–532.
Tao Z, Connor RJ, Ashoori F, Dinney CP, Munsell M, Philopena JA et al. Intravesical adenoviral-mediated α-interferon in the presence of Syn3 causes marked regression of human bladder cancer growing orthotopically in nude mice: correlations with dose and urine α-interferon concentrations. Cancer Gene Ther 2006; 13: 125–130.
Puthenveettil JA, Frederickson SM, Reznikoff CA . Apoptosis in human pillomavirus16 E7-, but not E6-immortalized human uroepithelial cells. Oncogene 1996; 13: 1123–1131.
Sabichi A, Keyhani A, Tanaka N, Delacerda J, Lee IL, Zou C et al. Characterization of a panel of cell lines derived from urothelial neoplasms: genetic alterations, growth in vivo, and the relationship of adenoviral-mediated gene transfer to Coxsackie adenovirus receptor expression. J Urology 2006; 175: 1133–1137.
Connor RJ, Engler H, Machemer T, Philopena JM, Horn MT, Sutjipto S et al. Identification of polyamides that enhance adenovirus-mediated gene expression in the urothelium. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 41–48.
Yamashita M, Rosser CJ, Zhou JH, Zhang XQ, Connor RJ, Engler H et al. Syn3 provides high levels of intravesical adenoviral-mediated gene transfer for gene therapy of genetically altered urothelium and superficial bladder cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 2002; 9: 687–691.
Acknowledgements
Supported by a GU SPORE in Bladder Cancer (P50 CA91846) to WFB and DJM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Yang, Z., Dong, L. et al. Adenoviral-mediated interferon α overcomes resistance to the interferon protein in various cancer types and has marked bystander effects. Cancer Gene Ther 14, 241–250 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7701011
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7701011
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The development of interferon-based gene therapy for BCG unresponsive bladder cancer: from bench to bedside
World Journal of Urology (2019)
-
Oncolytic viruses: adenoviruses
Virus Genes (2017)
-
Use of monitoring levels of soluble forms of cytokeratin 18 in the urine of patients with superficial bladder cancer following intravesical Ad-IFNα/Syn3 treatment in a phase l study
Cancer Gene Therapy (2014)
-
Aspirin enhances IFN-α-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via JAK1/STAT1 pathway
Cancer Gene Therapy (2013)
-
Direct gene transfer of adenoviral-mediated interferon α into human bladder cancer cells but not the bystander factors produced induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-related cytotoxicity
Cancer Gene Therapy (2011)