Abstract
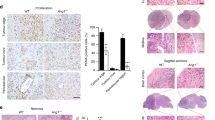
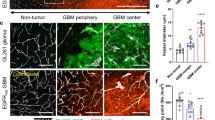
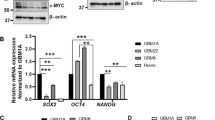
Glioblastomas are the most common primary brain tumors in adults. These tumors exhibit a high degree of vascularization, and malignant progression from astrocytoma to glioblastoma is often accompanied by increased angiogenesis and the upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors. In this study, we investigated the in vivo antiangiogenic and antitumor effects of brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1) using human glioblastoma cell lines. Glioblastoma cells were transduced with an adenoviral vector encoding BAI1 (AdBAI1), and Northern and Western blot analyses, respectively, demonstrated BAI1 mRNA and protein expression in the transduced tumor cells. Using an in vivo neovascularization assay, we found that angiogenesis surrounding AdBAI1-transduced glioblastoma cells transplanted into transparent skinfold chambers of SCID mice was significantly impaired compared to control treated cells. Additionally, in vivo inoculation with AdBAI1 of established subcutaneous or intracerebral transplanted tumors significantly impaired tumor growth and promoted increased mouse survival. Morphologically, the tumors exhibited signs of impaired angiogenesis, such as extensive necrosis and reduced intratumoral vascular density. Taken together, these data strongly indicate that BAI1 may be an excellent gene therapy candidate for the treatment of brain tumors, especially human glioblastomas.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ram Z, Culver KW, Oshiro EM, Viola JJ, DeVroom HL, Otto E et al. Therapy of malignant brain tumors by intratumoral implantation of retroviral vector-producing cells. Nat Med 1997; 12: 1354–1361.
Marcia R, Machein WR, Karl HP . Antiangiogenitic gene therapy in a dominant-negative vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2. Hum Gene Ther 1999; 10: 1117–1128.
Folkman J . What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent. J NatCancer Inst 1989; 82: 4–6.
Folkman J . Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med 1995; 1: 27–31.
Nein L, Lemoineishimori H, Ichise H, Nakamura Y, Tokino T . Cloning and characterization of BAP3, a C2 domain-containing protein that interacts with BAI1. Biochem Biophys Res commun 1998; 251: 158–165.
Nishizaki M, Fujiwara T, Tanida T, Hizuta A, Nishimori H, Tokino T et al. Recombinant adenovirus expressing wild-type p53 is antiangiogenic: a proposed mechanism for bystander effect. Clin Cancer Res 1999; 5: 1015–1023.
Kaur B, Brat DJ, Calkin CC, Van Meir EG . Brain angiogenesis inhibitor 1 is differentially expressed in normal brain and glioblastoma independently of p53 expression. Am J Pathol 2003; 162: 19–27.
Nishimori H, Shiratsuchi T, Urano T, Kimura Y, Kiyono K, Tatsumi K et al. A novel brain-specific p53-target gene, BAI1, containing thrombospondin type 1 repeats inhibits experimental angiogenesis. Oncogene 1997; 15: 2145–2150.
Kanegae Y, Fukushima Y, Oshika Y, Tsuchita T, Tokunaga T, Hatanaka H et al. Brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 expression is inversely correlated with vascularity and distand metastasis of colorectal cancer. Intern J Oncol 1998; 13: 967–970.
Hatanaka H, Oshika Y, Abe Y, Yoshida Y, Hashimoto T, Handa A et al. Vascularization is decreased in pulmonary adenocarcinoma expressing brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1). Int J Mol Med 2000; 5: 181–183.
Lee JH, Koh JT, Shin BA, Ahn KY, Roh JH, Kim YJ et al. Comparative study of angiostatic and anti-invasive gene expressions as prognostic factors in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol 2001; 18: 355–361.
Ghaneh P, Greenhalf W, Humphreys M, Wilson D, Zumshiratsuchi T, Neoptolemos JP . Adenovirys-mediated adenovirus transfer of p53 and p16INK4a results in pancreatic cancer regression in vitro and in vivo. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 199–208.
Li H, Alonso-Vanegas M, Colicos MA, Jung SS, Lochmuller H, Sadikot AF et al. Intracerebral adenovirus-mediated p53 tumor suppressor gene therapy for experimental human glioma. Clin Cancer Res 1999; 5: 637–642.
Hsin-I M, Guo P, Li J, Lin SZ, Chiang YH, Xiao X et al. Suppression of intracranial human glioma growth after intramuscular administration of an adeno-associated viral vector expressing angiostatin1. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 756–763.
Xu M, Kumar D, Srinivas S, Detolla LJ, Yu SF, Stass SA et al. Parenteral gene therapy with p53 inhibits human breast tumors in vivo through a bystander mechanism without evidence of toxicity. Hum Gene Ther 1997; 8: 177–185.
Kaur B, Brat DJ, Devi NS, Van Meir EG . Vasculostatin, a proteolytic fragment of brain angiogenesis inhibitor 1, is an antiangiogenic and antitumorigenic factor. Oncogene 2005; 24: 3632–3642.
Sherif ZA, Nakai S, Pirollo KF, Rait A, Chang EH . Downmodulation of bFGF-binding protein expression following restoration of p53 function. Cancer Gene Ther 2001; 8: 771–782.
Voravud N, Charuruk N . Tumor angiogenesis. J Med Assoc Thai 1999; 82: 394–404.
Rugo HS . Bevacizumab in the treatment of breast cancer: rationale and current data. The Oncologist 2004; 9 (Suppl 1): 43–49.
Miyake S, Makimura M, Kanekana Y, Harada S, Sato Y, Takamori K et al. Efficient generation of recombinant adenoviruses using adenovirus DNA-terminal protein complex and a cosmid bearing the full-length virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 1320–1324.
Hibino H, Tani K, Sugiyama H, Suzuki S, Wu M-S, Izawa K et al. Haemopoietic progenitor cells from the common marmoset as targets of gene transduction by retroviral and adenoviral vectors. Eur J Haematol 2001; 66: 272–280.
Knut HF, Einar K, Rofstad BT, Marton P . A transparent chamber for the dorsal skin fold of athymic mice. Expl Cell Biol 1984; 52: 260–268.
Martuza RL, Malick A, Markert JM, Ruffner KL, Coen DM . Experimental therapy of human glioma by means of a genetically engineered virus mutant. Science 1991; 252: 854–856.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare and the Ministry of education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, X., Xiao, X., Harata, M. et al. Antiangiogenic activity of BAI1 in vivo: implications for gene therapy of human glioblastomas. Cancer Gene Ther 13, 385–392 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700898
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700898
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Adhesion GPCRs are widely expressed throughout the subsections of the gastrointestinal tract
BMC Gastroenterology (2012)
-
Enhanced Antitumor Efficacy of Vasculostatin (Vstat120) Expressing Oncolytic HSV-1
Molecular Therapy (2010)
-
BAI1 is an engulfment receptor for apoptotic cells upstream of the ELMO/Dock180/Rac module
Nature (2007)