Abstract
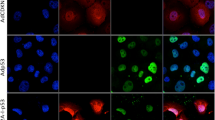
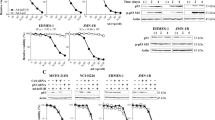
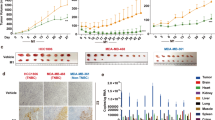
The tumor-suppressor gene p16INK4/CDKN2 (p16) is a cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk) inhibitor and important cell cycle regulator. Here, we show that adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of p16 (AdCMV.p16) into colon cancer cells induces uncoupling of S phase and mitosis and subsequently apoptosis. Flow cytometric analysis revealed that cells infected with AdCMV.p16 showed an initial G2-like arrest followed by S phase without intervening mitosis (DNA >4N). Using microscopic analysis, deformed polyploid cells were detectable only in cells infected with AdCMV.p16 but not in control-infected cells. Subsequently, AdCMV.p16-infected polyploid cells underwent apoptosis, as assessed by AnnexinV staining and DNA fragmentation, suggesting that cell cycle dysregulation is upstream of the onset of apoptosis. Treatment of mice with subcutaneously transplanted tumors of colorectal cancer cells with AdCMV.p16 but not AdCMV.p53 resulted in significantly reduced tumor volume and prolonged survival. Using an orthotopic model of liver metastasis, we observed both reduced local tumor growth and secondary intrahepatic metastasis after AdCMV.p16 treatment. Importantly, induction of apoptosis in vitro and reduction of tumor growth in vivo by p16 was p53- as well as bax-independent because identical results were obtained using cancer cells, either wild type or mutant for p53 or bax. The studies suggest that an AdCMV.p16-based treatment may be especially effective in patients with bax-negative colon cancer where overexpression of p53 appears not to be of therapeutic value.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen AM, Minsky BD, Schilsky RL . Cancer of the colon In: De Vita VT Jr, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, eds Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven 1997 1144–1196
Parker SL, Tong T, Bolden S, Wingo PA . Cancer statistics CA Cancer J Clin 1997 47: 5–27
Troisi RJ, Freedman AN, Devesa SS . Incidence of colorectal carcinoma in the U.S.: an update of trends by gender, race, age, subsite, and stage, 1975–1994 Cancer 1999 85: 1670–1676
Steinberg SM, Barkin JS, Kaplan RS, Stablein DM . Prognostic indicators of colon tumors. The gastrointestinal tumor study group experience Cancer 1986 57: 1866–1870
Leichman CG, Flemming T, Muggia FM et al. Phase II study of fluorouracil and its modulation in advanced colorectal cancer: a Southwest oncology group study J Clin Oncol 1995 13: 1303–1311
Marsh JC, Bertino JR, Katy KH et al. The influence of drug interval on the effect of methotrexate and fluorouracil in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer J Clin Oncol 1991 9: 371–380
Shibata D, Peinado MA, Ionov Y, Maklhosyan S, Perucho M . Genomic instability in repeated sequences is an early somatic event in colorectal tumorigenesis that persists after transformation Nat Genet 1994 6: 273–281
Lothe RA . Microsatellite instability in human solid tumors Mol Med Today 1997 2: 61–68
Rampino N, Yamamoto H, Ionov Y et al. Somatic frameshift mutations in the BAX gene in colon cancers of the microsatellite mutator phenotype Science 1997 275: 976–979
Gessner C, Liebers U, Kuhn H, Stiehl P, Schauer J, Wolff G . BAX and p16INK4A are independent positive prognostic markers for advanced tumor stage of non small cell lung cancer Eur Respir J 2002 19: 134–140
Sturm I, Kohne CH, Wolff G et al. Analysis of the p53/BAX pathway in colorectal cancer: low BAX is a negative prognostic factor in patients with resected liver metastases J Clin Oncol 1999 17: 1364–1374
Clayman GL, El-Naggar AK, Lippman SM et al. Adenovirus mediated p53 gene transfer in patients with advanced recurrent head and neck squamous cell carcinoma J Clin Oncol 1998 16: 2221–2232
Nemunaitis J, Swisher SG, Timmons T et al. Adenovirus-mediated p53 gene transfer in sequence with cisplatin to tumors of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer J Clin Oncol 2000 18: 609–614
Hayashi S, Emi N, Yokoyama I, Namii Y, Uchida K, Takagi H . Inhibition of establishment of hepatic metastasis in mice by combination gene therapy using both herpes simplex virus-thymidine kinase and granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor genes in murine colon cancer Cancer Gene Ther 1997 4: 339–344
Nielsen CS, Moorman DW, Levy JP, Link CJJ . Herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene transfer is required for complete regression of murine colon adenocarcinoma Am Surg 1997 63: 617–620
Wolff G, Korner IJ, Schumacher A, Arnold W, Dorken B, Mapara MY . Ex vivo breast cancer cell purging by adenovirus-mediated cytosine deaminase gene transfer and short-term incubation with 5-fluorocytosine completely prevents tumor growth after transplantation Hum Gene Ther 1998 10: 2277–2284
Wildner O, Blaese RM, Candotti F . Enzyme prodrug gene therapy: synergistic use of the herpes simplex virus-cellular thymidine kinase/ganciclovir system and thymidylate synthase inhibitors for the treatment of colon cancer Cancer Res 1999 59: 5233–5238
Bash JA . Recombinant vaccinia interleukin-2–infected tumor cell vaccines in immunotherapy of murine colon adenocarcinoma J Immunother 1993 14: 169–272
McLaughlin JP, Schlom J, Kantor JA, Greiner JW . Improved immunotherapy of a recombinant carcinoembryonic antigen vaccinia vaccine when given in combination with interleukin-2 Cancer Res 1996 56: 2361–2367
Mazzalini G, Qian C, Xie X et al. Regression of colon cancer and induction of antitumor immunity by intratumoral injection of adenovirus expressing interleukin-12 Cancer Gene Ther 1999 6: 514–522
Kaufman H, Schlom J, Kantor J . A recombinant vaccinia virus expressing human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) Int J Cancer 1991 48: 900
Hamilton JM, Chen AP, Nguyen B . Phase I study of recombinant vaccinia virus that expresses human carcinoembryonic antigen in adult patients with adenocarcinoma Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 1994 13: 295
Marshall JL, Hawkins MJ, Tsang KY et al. Phase I study in cancer patients of a replication-defective avipox recombinant vaccine that expresses human carcinoembryonic antigen J Clin Oncol 1999 17: 332–337
Kass E, Schlom J, Thompson J, Guadagni F, Graziano P, Greiner JW . Induction of protective host immunity to carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), a self-antigen in CEA transgenic mice, by immunizing with a recombinant vaccinia-CEA virus Cancer Res 1999 59: 676–683
Chen L, McGowan P, Ashe S et al. Tumor immunogenicity determines the effect of B7 costimulation on T cell-mediated tumor immunity J Exp Med 1994 179: 523–532
Carroll MW, Overwijk WW, Surman DR, Tsung K, Moss B, Restifo NP . Construction and characterization of a triple-recombinant vaccinia virus encoding B7-1, interleukin 12, anda model tumor antigen J Natl Cancer Inst 1998 90: 1881–1887
Fujiwara T, Grimm EA, Roth JA . Gene therapeutics and gene therapy Curr Opin Oncol 1994 6: 96–105
Sherr CJ . The Pezcoller lecture: cancer cell cycle revisited Cancer Res 2000 60: 3689–3695
Craig C, Kim M, Ohri E et al. Effects of adenovirus-mediated p16INK4A expression on cell cycle arrest are determined by endogenous p16 and Rb status in human cancer cells Oncogene 1998 16: 265–272
Lukas J, Sorensen CS, Lukas C, Santoni-Rugiu E, Bartek J . p16INK4A, but not constitutively active pRb, can impose a sustained G1 arrest: molecular mechanisms and implications for oncogenesis Oncogene 1999 18: 3930–3935
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM . CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression Genes Dev 1999 1: 1501–1512
Sandig V, Brand K, Herwig S, Lukas J, Bartek J, Strauss M . Adenovirally transferred p16INK4A/CDKN2 and p53 genes cooperate to induce apoptotic tumor cell death Nat Med 1997 3: 313–319
Kim M, Katayose Y, Rojanala L et al. Induction of apoptosis in p16INK4A mutant cell lines by adenovirus-mediated overexpression of p16INK4A protein Cell Death Differ 2000 7: 706–711
Jin X, Nguyen D, Zhang WW, Kyritsis A, Roth JA . Cell cycle arrest and inhibition of tumor cell proliferation by the p16INK4 gene mediated by an adenovirus vector Cancer Res 1995 55: 3250–3253
Sharpless NE, Bardeesy N, Lee KH et al. Loss of p16Ink4a with retention of p19Arf predisposes mice to tumorigenesis Nature 2001 413: 86–91
Fu XY, Zhang SW, Ran RQ, Shen ZH, Gu JX, Cao SL . Restoration of the p16 gene is related to increased radiosensitivity of p16-deficient lung adenocarcinoma cell lines J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 1998 124: 621–626
Schreiber M, Muller WJ, Singh G, Graham FL . Comparison of the effectiveness of adenovirus vectors expressing cyclin kinase inhibitors p16INK4A, p18INK4C, p19INK4D, p21 (WAF/CIP1) and p27KIP1 in inducing cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and inhibition of tumorigenicity Oncogene 1999 18: 1663–1676
Chintala SK, Fuezo J, Gomey-Manyano C et al. Adenovirus-mediated p16/CDKN2 gene transfer suppresses glioma invasion in vitro Oncogene 1997 15: 2049–2057
Jen J, Harper J, Bigner S et al. Deletion of p16 and p15 genes in brain tumors Cancer Res 1994 54: 6353–6358
Spruck CI, Gonzalez-Zulueta M, Shibata A et al. p16 gene in uncultured tumours Nature 1994 370: 183–184
Sherr C, Roberts JM . Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases Genes Dev 1995 9: 1149–1163
Reed AL, Califano J, Cairns P et al. High frequency of (CDKN2/MTS-1/INK4A) inactivation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma Cancer Res 1996 56: 3630–3633
Sellers WR, Kaelin WG . Role of the retinoblastoma protein in the pathogenesis of human cancer J Clin Oncol 1997 15: 3301–3312
Merlo A, Herman J, Mao L et al. 5′ CpG island methylation is associated with transcriptional silencing of the tumor suppressor p16/CDKN2/Mts1 in human cancers Nat Med 1995 1: 686–692
Gonzalez-Zulueta M, Bender CM, Yang AS et al. Methylation of the 5′ CpG island of the p16/CDKN2 tumor suppressor gene in normal and transformed human tissues correlates with gene silencing Cancer Res 1995 55: 4531–5435
Geradts J, Wilson PA . High frequency of aberrant p16(INK4A) expression in human breast cancer Am J Pathol 1996 149: 15–20
Pocard M, Chevillard S, Villaudy J, Poupon MF, Dutrillaux B, Remvikos Y . Different p53 mutations produce distinct effects on the ability of colon carcinoma cells to become blocked atthe G1/S boundary after irradiation Oncogene 1996 12: 875–882
Te Poele RH, Joel SP . Schedule-dependent cytotoxicity of SN-38 in p53 wild-type and mutant colon adenocarcinoma cell lines Br J Cancer 1999 81: 1285–1293
Tominaga O, Nita ME, Nagawa H, Fujii S, Tsuruo T, Muto T . Expressions of cell cycle regulators in human colorectal cancer cell lines Jpn J Cancer Res 1997 88: 855–860
Nüssler AK, Di SM, Billiar TR et al. Stimulation of the nitric oxide synthase pathway in human hepatocytes by cytokines and endotoxin J Exp Med 1992 176: 261–264
Dorko K, Freeswick PD, Bartoli F et al. A new technique for isolating and culturing human hepatocytes from whole or split livers not used for transplantation Cell Transplant 1994 3: 387–395
Zhang WW, Fang X, Mazur W, French BA, Georges RN, Roth JA . High-efficiency gene transfer and high-level expression of wild-type p53 in human lung cancer cells mediated by recombinant adenovirus Cancer Gene Ther 1994 1: 5–13
Wolff G, Mastrangeli A, Heinflink M, Falck-Pedersen E, Gershengorn MC, Crystal RG . Ectopic expression of thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) receptors in liver modulates organ function to regulate blood glucose by TRH Nat Genet 1996 12: 274–279
Kay MA, Holterman AX, Meuse L et al. Long-term hepatic adenovirus-mediated gene expression in mice following CTLA4Ig admission Nat Genet 1995 11: 191–197
Rosenfeld MA, Siegfried W, Yoshimura K et al. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of a recombinant alpha 1-antitrypsin gene to the lung epithelium in vivo Science 1991 252: 431–434
Rosenfeld MA, Yoshimura K, Trapnell BC et al. In vivo transfer of the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene to the airway epithelium Cell 1992 68: 431–434
Karawajew L, Ruppert V, Wuchter C et al. Inhibition of in vitro spontaneous apoptosis by IL-7 correlates with upregulation of Bcl-2, cortical/mature immunophenotype, and better cytoreduction in childhood T-ALL Blood 2000 96: 297–306
Karawajew L, Glibin E, Maleev V et al. Role of crown-likeside chains in the biological activity of substituted-phenoxazone drugs Anticancer Drug Des 2000 15: 331–338
Wersto RP, Rosenthal ER, Seth PK, Eissa NT, Donahue RE . Recombinant replication-defective adenovirus gene transfer vectors induce cell cycle dysregulation and inappropriate expression of cyclin proteins J Virol 1998 72: 9491–9502
Brand K, Wolff G, Strauss M . Gene therapy for cancer Gene Therapy: Therapeutic Mechanisms and Strategies New York: Marcel Dekker 2000 439–472
Miyashita T, Reed JC . Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene Cell 1995 80: 293–299
Arafat WO, Gomez-Navarro J, Xiang J et al. An adenovirus encoding proapoptotic bax induces apoptosis and enhances the radiation effect in human ovarian cancer Mol Ther 2000 6: 545–554
Pietersen AM, v.d. Eb MM, Rademaker HJ et al. Specific tumor-cell killing with adenovirus vectors containing the apoptin gene Gene Ther 1999 6: 882–892
Shinoura N, Yamamoto N, Yoshida Y, Asai A, Kirino T, Hamada H . Adenovirus-mediated transfer of caspase-8 in combination with superrepressor of NF-kappaB drastically induced apoptosis in gliomas Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000 271: 544–552
Shinoura N, Muramatsu Y, Yoshida Y, Asai A, Kirino T, Hamada H . Adenovirus-mediated transfer of caspase-3 with Fas ligand induces drastic apoptosis in U-373MG glioma cells Exp Cell Res 2000 256: 423–433
Schwartz SJ, Yamamoto H, Navarro M, Maestro M, Reventos J, Perucho M . Frameshift mutations at mononucleotide repeats in caspase-5 and other target genes in endometrial and gastrointestinal cancer of the microsatellite mutator phenotype Cancer Res 1999 59: 2995–3002
Craig C, Wersto R, Kim M et al. A recombinant adenovirus expressing p27Kip1 induces cell cycle arrest and loss of cyclin-Cdk activity in human breast cancer cells Oncogene 1997 14: 2283–2289
Rocco JW, Li D, Liggett WH et al. p16INK4A adenovirus-mediated gene therapy for human head and neck squamous cell cancer Clin Cancer Res 1998 4: 1697–1704
Fueyo J, Gomez-Manzano C, Yung WK et al. Overexpression of E2F-1 in glioma triggers apoptosis and suppresses tumor growth in vitro and in vivo Nat Med 1998 4: 685–690
Hirai H, Roussel MF, Kato JY, Ashmun RA, Sherr CJ . Novel INK4 proteins, p19 and p18, are specific inhibitors of the cyclin D-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6 Mol Cell Biol 1995 15: 2672–2681
Wang XQ, Gabrielli BG, Milligan A, Dickinson JL, Antalis TM, Ellem KAO . Accumulation of p16CDKN2A in response to ultraviolet irradiation correlates with a late SG2 phase cell cycle delay Cancer Res 1996 56: 2510–2514
Brand K, Loser P, Arnold W, Bartels T, Strauss M . Tumor cell–specific transgene expression prevents liver toxicity of the adeno-HSVtk/GCV approach Gene Ther 1998 5: 1363–1371
Gorospe M, Cirielli C, Wang X, Seth P, Capogrossi MC, Holbrook NJ . p21(Waf1/Cip1) protects against p53-mediated apoptosis of human melanoma cells Oncogene 1997 14: 929–935
Lu Y, Yamagishi N, Yagi I, Takebe H . Mutated p21(WAF1/CIP1/SDI1) lacking CDK-inhibitory activity fails to prevent apoptosis in human colorectal carcinoma cells Oncogene 1998 16: 705–712
Harper JW, Elledge SJ . Cdk inhibitors in development and cancer Curr Opin Genet Dev 1996 6: 56–64
Deng C, Zhang P, Harper W, Elledge SJ, Leder P . Mice lackingp21CIP1/WAF1 undergo normal development, but are defective in G1 checkpoint control Cell 1995 82: 675–684
Sherr CJ . Cancer cell cycles Science 1996 47: 1672–1677
Saltz LB, Kelsen DP . Adjuvant treatment of colorectal cancer Annu Rev Med 1997 48: 191–202
Reed JC . Survivin' cell-separation anxiety Nat Cell Biol 1999 1: 199–200
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC . A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma Nat Med 1997 3: 917–921
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E et al. IAP-family protein survivin inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD95), Bax, caspases, and anticancer drugs Cancer Res 1998 58: 5315–5320
Suzuki A, Hayashida M, Ito T et al. Survivin initiates cell cycle entry by the competitive interaction with Cdk-4/p16INK4a and Cdk2/Cyclin E complex activation Oncogene 2000 19: 3225–3234
Patel SD, Tran AC, Ge Y et al. The p53-independent tumoricidal activity of an adenoviral vector encoding a p27–p16 fusion tumor suppressor gene Mol Ther 2000 2: 161–169
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr Mark Kay (Stanford University, Stanford, CA) Dr Ronald Crystal (Cornell University, New York, NY), and Dr Michael Strauss (Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine, Berlin, Germany, deceased) for generously providing the adenoviral vectors. Furthermore, we thank B Durieux, M Gries, K Jäger, and P Pierschalek for expert technical assistance and M Dittmar for help in preparing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamm, I., Schumacher, A., Karawajew, L. et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of P16INK4/CDKN2 into bax-negative colon cancer cells induces apoptosis and tumor regression in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther 9, 641–650 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700480
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700480
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
In vivo comparison of transduction efficiency with recombinant adenovirus-mediated p53 in a human colon cancer mouse model by different delivery routes
The Chinese-German Journal of Clinical Oncology (2008)
-
Paclitaxel induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells requires cell cycle transit but not Cdc2 activity
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2006)
-
The tumor suppressor p16INK4a gene is a regulator of apoptosis induced by ultraviolet light and cisplatin
Oncogene (2004)
-
The fate of pancreatic tumor cell lines following p16 overexpression depends on the modulation of CDK2 activity
Cell Death & Differentiation (2004)