Abstract
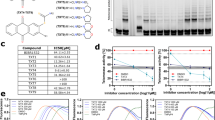
Human telomerase RNA (hTR), an important component of telomerase, is a possible target of telomerase-based cancer gene therapy. The present study was undertaken to assess the efficacy of antisense hTR therapy using newly developed 2-5A (5′-phosphorylated 2′-5′–linked oligoadenylate)–linked oligonucleotides against cervical cancer cells. ME180 and SiHa cells were treated with 2-5A–linked antisense hTR designed to complement the region of hTR between residues 76 and 94. The hTR expression, telomerase activity, cell viability, and apoptosis were then examined. The 2-5A anti-hTR effectively degraded hTR and inhibited telomerase activity. The 2-5A mutant anti-hTR and the anti-hTR without 2-5A were not capable of inhibiting telomerase activity. Inhibition of telomerase by 2-5A anti-hTR rapidly decreased cell viability only in telomerase-positive cells within 3–6 days after the treatment, when telomere length has not yet been shortened. This inhibition was associated with apoptosis, possibly through activation of caspase family members. These findings suggest that 2-5A–linked antisense-hTR therapy has a potent telomerase-inhibitory effect associated with a cytocidal effect from caspase-induced apoptosis, and may therefore be a potential tool in telomerase-based gene therapy against cervical cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackburn EH . Structure and function of telomeres Nature 1991 350: 569–573
Watson JD . Origin of concatemeric T7 DNA Nature (London) New Biol 1972 239: 197–201
Greider CW, Blackburn EH . A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis Nature 1989 337: 331–337
Harley CB, Futcher BA, Greider CW . Telomeres shorten during aging of human fibroblast Nature 1990 345: 458–460
Allsopp RC, Vaziri H, Patterson C . Telomere length predicts replicative capacity of human fibroblasts Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992 89: 10114–10118
Counter CM, Avilion AA, LeFeuvre CE et al. Telomere shortening associated with chromosome instability is arrested in immortal cells which express telomerase activity EMBO J 1992 11: 1921–1929
Kim NW, Piatyszek MA, Prowse KR et al. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer Science 1994 266: 2011–2015
Feng J, Funk WD, Wang SS et al. The RNA component of human telomerase Science 1995 269: 1236–1241
Harrington L, McPhail T, Mar V et al. A mammalian telomerase-associated protein Science 1997 275: 973–977
Nakayama J, Saito M, Nakamura H, Matsuura A, Ishikawa F . TLP1: a gene encoding a protein component of mammalian telomerase is a novel member of WD repeats family Cell 1997 88: 875–884
Meyerson M, Counter CM, Eaton EN et al. HEST2, the putative human telomerase catalytic subunit gene, is up-regulated in tumor cells and during immortalization Cell 1997 90: 785–795
Nakamura TM, Morin GB, Chapman KB et al. Telomerase catalytic subunit homologs from fission yeast and human Science 1997 277: 955–959
Liu Y, Snow BE, Hande MP et al. Telomerase-associated protein TEP1 is not essential for telomerase activity or telomere length maintenance in vivo Mol Cell Biol 2000 20: 8178–8184
Bisoffi M, Chakerian AE, Fore ML et al. Inhibition of human telomerase by a retrovirus expressing telomeric antisense RNA Eur J Cancer 1998 34: 1242–1249
Glukhov AI, Zimnik OV, Gordeev SA, Severin SE . Inhibition of telomerase activity of melanoma cells in vitro by antisense oligonucleotides Eur J Cancer 1998 34: 1242–1249
Naka K, Yokozaki H, Yasui W, Tahara H, Tahara E, Tahara E . Effect of antisense human telomerase RNA transfection on the growth of human gastric cancer cell lines Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999 255: 753–758
Norton JC, Piatyszek MA, Wright WE, Shay JW, Corey DR . Inhibition of human telomerase activity by peptide nucleic acids Nat Biotechnol 1996 14: 615–619
Pitts AE, Corey DR . Inhibition of human telomerase by 2′-O-methyl-RNA Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998 95: 11549–11554
Torrence PF, Maitra RK, Lesiak K, Khamnei S, Zhou A, Silverman RH . Targeting RNA for degradation with a (2′-5′)oligoadenylate-antisense chimera Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993 90: 1300–1304
Kyo S, Ueno H, Kanaya T, Inoue M . Telomerase activity in gynecological tumors Clin Cancer Res 1996 2: 2023–2028
Takakura M, Kyo S, Kanaya T, Tanaka M, Inoue M . Expression of human telomerase subunits and correlation with telomerase activity in cervical cancer Cancer Res 1998 58: 1558–1561
Kondo S, Kondo Y, Li G, Silverman RH, Cowell JK . Targeted therapy of human malignant glioma in a mouse model by 2-5A antisense directed against telomerase RNA Oncogene 1998 16: 3323–3330
Wen J, Cong YS, Bacchetti S . Reconstitution of wild-type or mutant telomerase activity in telomerase-negative immortal human cells Hum Mol Genet 1998 7: 1137–1141
Zhou A, Paranjape J, Brown TL et al. Interferon action and apoptosis are defective in mice devoid of 2′,5′-oligoadenylate–dependent RNase L EMBO J 1997 16: 6355–6363
Kondo Y, Koga S, Komata T, Kondo S . Treatment of prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo with 2-5A anti-telomerase RNA component Oncogene 2000 19: 2205–2211
Kushner DM, Paranjape JM, Bandyopadhyay B et al. 2-5A antisense directed against telomerase RNA produces apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells Gynecol Oncol 2000 76: 183–192
Saretzki G, Ludwig A, von Zglinicki T, Runnebaum IB . Ribozyme-mediated telomerase inhibition induces immediate cell loss but not telomere shortening in ovarian cancer Cancer Gene Ther 2001 8: 827–834
Ren JG, Xia HL, Tian YM, Just T, Cai GP, Dai YR . Expression of telomerase inhibits hydroxyl radical-induced apoptosis in normal telomerase negative human lung fibroblasts FEBS Lett 2001 Jan 19 488: 133–138
Zhu H, Fu W, Mattson MP . The catalytic subunit of telomerase protects neurons against amyloid beta-peptide–induced apoptosis J Neurochem 2000 75: 117–124
Fu W, Killen M, Culmsee C, Dhar S, Pandita TK, Mattson MP . The catalytic subunit of telomerase is expressed in developing brain neurons and serves a cell survival-promoting function J Mol Neurosci 2000 14: 3–15
Holt SE, Glinsky VV, Ivanova AB, Glinsky GV . Resistance to apoptosis in human cells conferred by telomerase function and telomere stability Mol Carcinog 1999 25: 241–248
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a grant-in-aid for the Second-Term Comprehensive 10-Year Strategy for Cancer Control from the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yatabe, N., Kyo, S., Kondo, S. et al. 2-5A antisense therapy directed against human telomerase RNA inhibits telomerase activity and induces apoptosis without telomere impairment in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther 9, 624–630 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700479
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700479
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Expression of targeted ribozyme against telomerase RNA causes altered expression of several other genes in tumor cells
Tumor Biology (2014)
-
Telomerase inhibitor GRN163L inhibits myeloma cell growth in vitro and in vivo
Leukemia (2008)
-
Telomerase and its potential for therapeutic intervention
British Journal of Pharmacology (2007)
-
The expression of hTR and hTERT in human breast cancer: correlation with clinico-pathological parameters
International Seminars in Surgical Oncology (2006)