Abstract
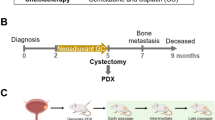
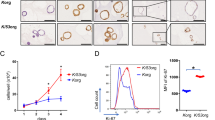
Orthotopic implantation of human bladder cancer cells into immunodeficient mice is an important tool for studying the biology and effects of therapy. Nevertheless, the incidence of tumor implantation and growth by transurethral instillation of the human bladder cancer cells into murine bladders has been low or not reproducible. However, using a modified intravesical technique and the human bladder cancer cell lines, KU-7 and UM-UC-2, we have been able to obtain a high and reproducible incidence of superficial bladder tumors. Furthermore, intravesical administration of the LacZ adenovirus vector resulted in significant β-galactosidase expression in these bladder tumors as well as the normal urothelium, which was associated with the removal of the glycosoaminoglycan layer. Because this modified technique produces a high incidence of superficial human tumor growth and allows the efficacy of gene transfer to be evaluated, it should be a useful model for the study of intravesical gene therapy for human bladder cancer. Cancer Gene Therapy (2000) 7, 1575–1580.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, T., Shinohara, N., Sazawa, A. et al. An improved intravesical model using human bladder cancer cell lines to optimize gene and other therapies. Cancer Gene Ther 7, 1575–1580 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700261
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700261
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A surgical orthotopic approach for studying the invasive progression of human bladder cancer
Nature Protocols (2019)
-
How cancer cells attach to urinary bladder epithelium in vivo: study of the early stages of tumorigenesis in an orthotopic mouse bladder tumor model
Histochemistry and Cell Biology (2019)
-
An orthotopic xenograft model for high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer in mice: influence of mouse strain, tumor cell count, dwell time and bladder pretreatment
BMC Cancer (2017)
-
Aldo-keto reductase 1C1 induced by interleukin-1β mediates the invasive potential and drug resistance of metastatic bladder cancer cells
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Investigation of CCL18 and A1AT as potential urinary biomarkers for bladder cancer detection
BMC Urology (2013)