Abstract
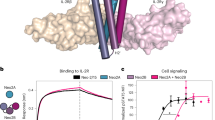
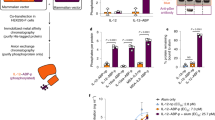
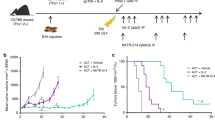
Modification of murine K1735 melanoma cells to express the immune costimulator B7-1 had no effect on tumor formation in syngeneic mice. In contrast, <40% of mice inoculated with K1735 cells modified to secrete murine interleukin-2 (IL-2) formed tumors, and no tumors formed when the K1735 cells coexpressed both murine IL-2 and B7-1. However, administration of systemic recombinant human IL-2 had no detectable effect on the formation of tumors by the B7-1-expressing K1735 cells. By contrast, admixtures of IL-2-secreting and B7-1-expressing K1735 cells formed fewer tumors than either cell type alone. Murine IL-2 was effective only when secreted locally, because the IL-2-secreting cells inoculated into the right flank did not affect the growth of the B7-1-expressing cells inoculated into the opposite flank.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barnard, A., Farzaneh, F., Gäken, J. et al. Local versus systemic interleukin-2: Tumor formation by wild-type and B7-1-positive murine melanoma cells. Cancer Gene Ther 7, 207–214 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700087
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700087
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
An immune edited tumour versus a tumour edited immune system: prospects for immune therapy of acute myeloid leukaemia
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2006)