Abstract
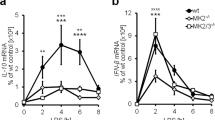
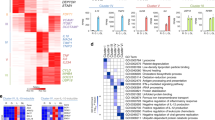
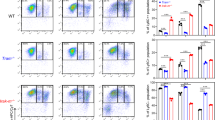
We examine the effects of IL18 on monocytes by performing microarray experiments using cell line KG1. Based on sensitivity to IL18, we identified three functionally distinct gene expression clusters (EC). We see little proinflammatory gene induction at low IL18 concentrations, but instead observe induction of diverse NFκB signaling inhibitors. Conversely, intermediate concentrations of IL18 induced proinflammatory genes including the activating subunits of NFκB. At the highest IL18 concentration, we observe a third gene cluster containing the proapoptotic Fas gene among others. Clustering of IL18-responsive genes based on cis-elements in their promoters agreed well with the ECs. We conclude that IL18 produces a dose-dependent transcriptional response that can in part be attributed to the composition of cis-elements in the promoters of IL18-responsive genes. These results also support a model for regulatory mechanisms that prevent spurious immune response due to weak cytokine fluctuations and a separate mechanism enabling induction of proinflammatory functions by higher levels of cytokine.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robinson D, Shibuya K, Mul A et al. IGIF does not drive Th1 development but synergizes with IL-12 for interferon-gamma production and activates IRAK and NFkappaB. Immunity 1997; 7: 571–581.
Kohno K, Kataoka J, Ohtsuki T et al. IFN-gamma-inducing factor (IGIF) is a costimulatory factor on the activation of Th1 but not Th2 cells and exerts its effect independently of IL-12. J Immunol 1997; 158: 1541–1550.
Micallef MJ, Tanimoto T, Kohno K et al. Interleukin 18 induces the sequential activation of natural killer cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes to protect syngeneic mice from transplantation with Meth A sarcoma. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 4557–4563.
Takeda K, Tsutsui H, Yoshimoto T et al. Defective NK cell activity and Th1 response in IL-18-deficient mice. Immunity 1998; 8: 383–390.
Kanakaraj P, Ngo K, Wu Y et al. Defective interleukin (IL)-18-mediated natural killer and T helper cell type 1 responses in IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK)-deficient mice. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 1129–1138.
Munder M, Mallo M, Eichmann K, Modolell M . Murine macrophages secrete interferon gamma upon combined stimulation with interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-18: a novel pathway of autocrine macrophage activation. J Exp Med 1998; 187: 2103–2108.
Kojima H, Aizawa Y, Yanaj Y et al. An essential role for NF-kappa B in IL-18-induced IFN-gamma expression in KG-1 cells. J Immunol 1999; 162: 5063–5069.
Puren AJ, Fantuzzi G, Gu Y et al. Interleukin-18 (IFNgamma-inducing factor) induces IL-8 and IL-1beta via TNFalpha production from non-CD14+ human blood mononuclear cells. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 711–721.
Yoshida A, Kohka Takahashi H, Iwagaki H et al. Essential role of ICAM-1/LFA-1 interaction in synergistic effect of IL- 18 and IL-12 on IFN-gamma production in human PBMC. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2002; 365: 181–186.
Schindler H, Lutz MB, Rollinghoff M, Bogdan C . The production of IFN-gamma by IL-12/IL-18-activated macrophages requires STAT4 signaling and is inhibited by IL-4. J Immunol 2001; 166: 3075–3082.
Parnet P, Garka KE, Bonnert TP et al. IL-1Rrp is a novel receptor-like molecule similar to the type I interleukin-1 receptor and its homologues T1/ST2 and IL-1R AcP. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 3967–3970.
Kojima H, Takeuchi M, Ohta T et al. Interleukin-18 activates the IRAK–TRAF6 pathway in mouse EL-4 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998; 244: 183–186.
Nakanishi K, Yoshimoto T, Tsutsui H, Okamura H . Interleukin-18 is a unique cytokine that stimulates both Th1 and Th2 responses depending on its cytokine milieu. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2001; 12: 53–72.
Adachi O, Kawai T, Takada K et al. Targeted disruption of the MyD88 gene results in loss of IL-1- and IL-18-mediated function. Immunity 1998; 9: 143–150.
Matsumoto S, Tsuji-Takayama K, Aizawa Y et al. Interleukin-18 activates NF-kappaB in murine T helper type 1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997; 234: 454–457.
Yoshimoto T, Takada K, Tanaka T et al. IL-12 up-regulates IL-18 receptor expression on T cells, Th1 cells, and B cells: synergism with IL-18 for IFN-gamma production. J Immunol 1998; 161: 3400–3407.
Ahn HJ, Maruo S, Tomura M et al. A mechanism underlying synergy between IL-12 and IFN-gamma-inducing factor in enhanced production of IFN-gamma. J Immunol 1997; 159: 2125–2131.
Micallef MJ, Ohtsuki T, Kohno K et al. Interferon-gamma-inducing factor enhances T helper 1 cytokine production by stimulated human T cells: synergism with interleukin-12 for interferon-gamma production. Eur J Immunol 1996; 26: 1647–1651.
Yoshimoto T, Okamura H, Tagawa YI et al. Interleukin 18 together with interleukin 12 inhibits IgE production by induction of interferon-gamma production from activated B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 3948–3953.
Nakahira M, Ahn HJ, Park WR et al. Synergy of IL-12 and IL-18 for IFN-gamma gene expression: IL-12-induced STAT4 contributes to IFN-gamma promoter activation by up-regulating the binding activity of IL-18-induced activator protein 1. J Immunol 2002; 168: 1146–1153.
Gracie JA, Forsey RJ, Chan WL et al. A proinflammatory role for IL-18 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest 1999; 104: 1393–1401.
Takaori-Kondo A, Hori T, Fukunaga K et al. Both amino- and carboxyl-terminal domains of TRAF3 negatively regulate NF-kappaB activation induced by OX40 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000; 272: 856–863.
Wu MX, Ao Z, Prasad KV, Wu R, Schlossman SF . IEX-1L, an apoptosis inhibitor involved in NF-kappaB-mediated cell survival. Science 1998; 281: 998–1001.
Xu LG, Shu HB . TNFR-associated factor-3 is associated with BAFF-R and negatively regulates BAFF-R-mediated NF-kappa B activation and IL-10 production. J Immunol 2002; 169: 6883–6889.
Uren AG, Pakusch M, Hawkins CJ et al. Cloning and expression of apoptosis inhibitory protein homologs that function to inhibit apoptosis and/or bind tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 4974–4978.
Mehta CR . The exact analysis of contingency tables in medical research. Stat Methods Med Res 1994; 3: 135–156.
Cotta CV, Zhang Z, Kim HG, Klug CA . Pax5 determines B versus T cell fate and does not block early myeloid-lineage development. Blood 2003; 30: 30.
Kuo CT, Leiden JM . Transcriptional regulation of T lymphocyte development and function. Annu Rev Immunol 1999; 17: 149–187.
Hoffmann A, Levchenko A, Scott ML, Baltimore D . The IkappaB-NF-kappaB signaling module: temporal control and selective gene activation. Science 2002; 298: 1241–1245.
Ohtsuki T, Michallef MJ, Kohno K et al. Interleukin 18 enhances Fas ligand expression and induces apoptosis in Fas-expressing human myelomonocytic KG-1 cells. Anticancer Res 1997; 17: 3253–3258.
Okano F, Yamada K . Canine interleukin-18 induces apoptosis and enhances Fas ligand mRNA expression in a canine carcinoma cell line. Anticancer Res 2000; 20: 3411–3415.
Hashimoto W, Osaki T, Okamura H et al. Differential antitumor effects of administration of recombinant IL-18 or recombinant IL-12 are mediated primarily by Fas–Fas ligand- and perforin-induced tumor apoptosis, respectively. J Immunol 1999; 163: 583–589.
Kent WJ, Sugnet CW, Furey TS et al The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res 2002; 12: 996–1006.
Acknowledgements
We thank Tom Briggs for performing quantitative PCR reactions and Hamish Allen and Tariq Ghayur for critical reading of the manuscript. DL and ZW were partially funded by NIH Grant 1R01HG03110-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity's website (http://www.nature.com/gene).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leyfer, D., Bond, A., Tworog, E. et al. cis-Element clustering correlates with dose-dependent pro- and antisignaling effects of IL18. Genes Immun 5, 354–362 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364099
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364099
This article is cited by
-
A comprehensive pathway map of IL-18-mediated signalling
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2020)