Abstract
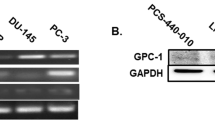
Studies on angiogenic cytokines usually are initially based upon their expression by available established cell lines. Our hypothesis is that established epithelial prostate cancer (CaP) cell lines do not accurately reflect angiogenic cytokine expression as compared to epithelial and stromal components of primary cultures generated from clinical CaP specimens. Serum free and growth factor free conditioned medium (CM) was collected from PC3, LNCaP, and their orthotopic selected prostate cancer sublines. Surgically acquired and pathologically confirmed neoplastic prostate tissue was selectively grown for selection of epithelial or stromal components, and CM was also collected. CM was assayed for urokinase (u-PA), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). u-PA was expressed only by androgen independent cell lines, but was detectable in the epithelial and stromal cultures of androgen sensitive primary cultures. bFGF was not secreted by cell lines nor epithelial primary cultures. VEGF was universally expressed, but TNF-α was not secreted by cells lines nor primary cultures. These data suggest that the expression of angiogenic cytokines by established epithelial CaP cell lines does not reflect epithelial and stromal primary cultures.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J, Shing J. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 1992 267 10931–10934.
Ausprunk DH, Folkman J. Migration and proliferation of endothelial cells in preformed and newly formed blood vessels during tumor angiogenesis. Microvascular Research 1977 14 53–65.
Folkman J, Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science 1987 235 442–447.
Goto F, Goto K, Weindel K, Folkman J. Synergistic effects of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor on the proliferation and cord formation of bovine capillary endothelial cells within collagen gels. Lab Invest 1993 69 509–517.
Mandriota SJ et al Vascular endothelial growth factor increases urokinase receptor expression in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 1995 270 9709–9716.
Pepper MS, Ferrara N, Orci L, Montesano R. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in microvascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1991 181 902–906.
Dvorak HG, Brown LF, Detmar M, Dvorak AM. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular hyperpermeability, and angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 1995 146 1029–1039.
Yoshida A, Anand-Apte B, Zetter BR. Differential endothelial migration and proliferation to basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor. Growth Factors 1996 13 57–64.
Kumar R, Yoneda J, Bucana CD, Fidler IJ. Regulation of distinct steps of angiogenesis by different angiogenic molecules. Int J Oncol 1998 12 749–757.
Melnyk O, Zimmerman M, Kim JK, Shuman M. Neutralizing anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody inhibits further growth of established prostate cancer and metastases in a pre-clinical model. J Urol 1999 161 960–963.
Ferrer FA et al Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in human prostate cancer: in situ and in vitro expression of VEGF by human prostate cancer cells. J Urol 1997 157 2329–2333.
Jackson MW, Bentel JM, Tilley WD. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 1997 157 2323–2328.
Pepper MS, Ferrara N, Orci L, Montesano R. Potent synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in the induction of angiogenesis in vitro Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992 189 824–831.
Sato Y, Rifkin DB. Autocrine activities of basic fibroblast growth factor: regulation of endothelial cell movement, plasminogen activator synthesis, and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol 1988 107 1199–1205.
Rifkin DB, Moscatelli D. Recent developments in the cell biology of basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol 1989 106 1–6.
Takahashi JA et al Inhibition of cell growth and tumorigenesis of human gliolastoma cells by a neutralizing antibody against human basic fibroblast growth factor. FEBS Lett 1991 288 65–71.
Giri D, Ropiquet F, Ittmann M. Alterations in expression of basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 2 and its receptor FGFR-1 in human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1999 5 1063–1071.
Presta M, Moscatelli D, Joseph-Silverstein J, Rifkin DB. Purification from a human hepatoma cell line of a basic fibroblast growth factor-like molcecule that stimulates capillary endothelial cell plasminogen activator production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Mol Cell Biol 1986 6 4060–4066.
Frater-Schroder M et al Tumor necrosis factor type-α, a potent inhibitor of endothelial cell growth in vitro, is angiogenic in vivo Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA 1987 84 5277–5281.
Niedbala MJ, Stein M. Tumor necrosis factor induction of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in human endothelial cells. Biomed Biochim Acta 1991 50 427–436.
Koolwijk P et al Cooperative effect of TNFα, bFGF, and VEGF on the formation of tubular structures of human microvascular endothelial cells in a fibrin matrix. Role of urokinase activity. J Cell Biol 1996 132 1177–1188.
Gaylis FD et al Plasminogen activators in human prostate cancer cell lines and tumors: correlation with the aggressive phenotype. J Urol 1989 142 193–198.
Hollas W et al Expression of urokinase and its receptor in invasive and non-invasive prostate cancer cell lines. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1992 68 662–666.
Van Veldhuizen PJ, Sadasivan R, Cherian R, Wyatt A. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression in human prostate carcinomas. Am J Med Sci 1996 312 8–11.
Pepper MS et al Angiogenesis: a paradigm for balanced extracellular proteolysis during cell migration and morphogenesis. Enzyme Protein 1996 49 138–162.
Evans CP et al Inhibition of prostate cancer neovascularization and growth by urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor blockade. Cancer Res. 1997 57 3594–3599.
Pettaway CA et al Selection of highly metastatic variants of different human prostatic carcinomas using orthotopic implantation in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res 1996 2 1627–1636.
Nakamoto T, Chang C, Li A, Chodak GW. Basic fibroblast growth factor in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 1992 52 571–577.
Folkman J et al Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia to neoplasia. Nature 1989 339 58–61.
Gimbrone MA Jr, Cotran RS, Leapman SB, Folkman J. Tumor growth and neovascularization: an experimental model using the rabbit cornea. J Natl Cancer Inst 1974 52 413–427.
Weidner N et al Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Path 1993 143 401–409.
Fregene T et al Tumor-associated angiogenesis in prostate cancer. Anticancer Res 1993 13 2377–2381.
Potgens AJG, Westphal HR, de Waal RMW, Ruiter DJ. The role of vascular permeability factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in tumor angiogenesis. Biol Chem 1995 376 57–70.
Joseph IBJK, Isaacs JT. Potentiation of the anti-angiogenic ability of linomide by androgen ablation involves down-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in human androgen responsive prostatic cancers. Cancer Res 1997 57 1054–1057.
Balbay MD et al Highly metastatic human prostate cancer growing within the prostate of athymic mice overexpresses vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 1999 5 783–789.
Dano K et al Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res 1985 44 139.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Donna Peehl (Stanford University) for her invaluable assistance with protocols for establishing primary prostate cultures. This research was supported by the University of California, Davis Health System Research Award, American Cancer Society Institutional Research Award no. 205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dall'Era, M., Shih, SJ., Yang, J. et al. Differential expression of angiogenic cytokines by cell lines and primary cultures of human prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 4, 106–111 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500515
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500515
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Elements regulating angiogenesis and correlative microvessel density in benign hyperplastic and malignant prostate tissue
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2003)