Abstract
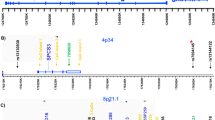
Parent-of-origin effects have been implicated as mediators of genetic susceptibility for a number of complex disease phenotypes, including bipolar disorder. Specifically, evidence for linkage on chromosome 18 is modified when allelic parent-of-origin is accommodated in the analysis. Our goal was to characterize the susceptibility locus for bipolar I disorder on chromosome 18p11 and investigate this parent-of-origin hypothesis in an association context. This was achieved by genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) at a high density (1 SNP/5 kb) along 13.6 megabases of the linkage region. To increase our ability to detect a susceptibility locus, we restricted the phenotype definition to include only bipolar I probands. We also restricted our study population to Ashkenazi Jewish individuals; this population has characteristics of a genetic isolate and may therefore facilitate detection of variants for complex disease. Three hundred and forty-four pedigrees (363 parent/child trios) where probands were affected with bipolar 1 disorder were genotyped. Transmission disequilibrium test analysis revealed no statistically significant association to SNPs or haplotypes within this region in this sample. However, when parent-of-origin of transmitted SNPs was taken into account, suggestive association was revealed for two separate loci.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kleinman L, Lowin A, Flood E, Gandhi G, Edgell E, Revicki D . Costs of bipolar disorder. Pharmacoeconomics 2003; 21: 601–622.
McGuffin P, Rijsdijk F, Andrew M, Sham P, Katz R, Cardno A . The heritability of bipolar affective disorder and the genetic relationship to unipolar depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003; 60: 497–502.
Kieseppa T, Partonen T, Haukka J, Kaprio J, Lonnqvist J . High concordance of bipolar I disorder in a nationwide sample of twins. Am J Psychiatry 2004; 161: 1814–1821.
Berrettini WH, Ferraro TN, Goldin LR, Weeks DE, Detera-Wadleigh S, Nurnberger Jr JI et al. Chromosome 18 DNA markers and manic-depressive illness: evidence for a susceptibility gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 5918–5921.
Stine OC, Xu J, Koskela R, McMahon FJ, Gschwend M, Friddle C et al. Evidence for linkage of bipolar disorder to chromosome 18 with a parent-of-origin effect. Am J Hum Genet 1995; 57: 1384–1394.
Lin JP, Bale SJ . Parental transmission and D18S37 allele sharing in bipolar affective disorder. Genet Epidemiol 1997; 14: 665–668.
Detera-Wadleigh SD, Badner JA, Berrettini WH, Yoshikawa T, Goldin LR, Turner G et al. A high-density genome scan detects evidence for a bipolar-disorder susceptibility locus on 13q32 and other potential loci on 1q32 and 18p11.2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 5604–5609.
Bennett P, Segurado R, Jones I, Bort S, McCandless F, Lambert D et al. The Wellcome trust UK–Irish bipolar affective disorder sibling-pair genome screen: first stage report. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 189–200.
Fallin MD, Lasseter VK, Wolyniec PS, McGrath JA, Nestadt G, Valle D et al. Genomewide linkage scan for bipolar-disorder susceptibility loci among Ashkenazi Jewish families. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 204–219.
Segurado R, Detera-Wadleigh SD, Levinson DF, Lewis CM, Gill M, Nurnberger Jr JI et al. Genome scan meta-analysis of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, part III: bipolar disorder. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 49–62.
Badner JA, Gershon ES . Meta-analysis of whole-genome linkage scans of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 405–411.
Nothen MM, Cichon S, Rohleder H, Hemmer S, Franzek E, Fritze J et al. Evaluation of linkage of bipolar affective disorder to chromosome 18 in a sample of 57 German families. Mol Psychiatry 1999; 4: 76–84.
Tsiouris SJ, Breschel TS, Xu J, McInnis MG, McMahon FJ . Linkage disequilibrium analysis of G-olf alpha (GNAL) in bipolar affective disorder. Am J Med Genet 1996; 67: 491–494.
Yoshikawa T, Padigaru M, Karkera JD, Sharma M, Berrettini WH, Esterling LE et al. Genomic structure and novel variants of myo-inositol monophosphatase 2 (IMPA2). Mol Psychiatry 2000; 5: 165–171.
Ishiguro H, Ohtsuki T, Okubo Y, Kurumaji A, Arinami T . Association analysis of the pituitary adenyl cyclase activating peptide gene (PACAP) on chromosome 18p11 with schizophrenia and bipolar disorders. J Neural Transm 2001; 108: 849–854.
McInnes LA, Service SK, Reus VI, Barnes G, Charlat O, Jawahar S et al. Fine-scale mapping of a locus for severe bipolar mood disorder on chromosome 18p11.3 in the Costa Rican population. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 11485–11490.
Washizuka S, Kakiuchi C, Mori K, Kunugi H, Tajima O, Akiyama T et al. Association of mitochondrial complex I subunit gene NDUFV2 at 18p11 with bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2003; 120: 72–78.
Sjoholt G, Ebstein RP, Lie RT, Berle JO, Mallet J, Deleuze JF et al. Examination of IMPA1 and IMPA2 genes in manic-depressive patients: association between IMPA2 promoter polymorphisms and bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2004; 9: 621–629.
Washizuka S, Iwamoto K, Kazuno AA, Kakiuchi C, Mori K, Kametani M et al. Association of mitochondrial complex I subunit gene NDUFV2 at 18p11 with bipolar disorder in Japanese and the National Institute of Mental Health pedigrees. Biol Psychiatry 2004; 56: 483–489.
Lohoff FW, Berrettini WH . Lack of association between variations in the melanocortin 5 receptor gene and bipolar disorder. Psychiatr Genet 2005; 15: 255–258.
Weller AE, Dahl JP, Lohoff FW, Ferraro TN, Berrettini WH . Analysis of variations in the NAPG gene on chromosome 18p11 in bipolar disorder. Psychiatr Genet 2006; 16: 3–8.
Puffenberger EG, Hosoda K, Washington SS, Nakao K, deWit D, Yanagisawa M et al. A missense mutation of the endothelin-B receptor gene in multigenic Hirschsprung's disease. Cell 1994; 79: 1257–1266.
Puffenberger EG, Kauffman ER, Bolk S, Matise TC, Washington SS, Angrist M et al. Identity-by-descent and association mapping of a recessive gene for Hirschsprung disease on human chromosome 13q22. Hum Mol Genet 1994; 3: 1217–1225.
Chakravarti A . Endothelin receptor-mediated signaling in hirschsprung disease. Hum Mol Genet 1996; 5: 303–307.
Amundadottir LT, Sulem P, Gudmundsson J, Helgason A, Baker A, Agnarsson BA et al. A common variant associated with prostate cancer in European and African populations. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 652–658.
Grant SF, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, Benediktsson R, Manolescu A, Sainz J et al. Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 320–323.
Struewing JP, Hartge P, Wacholder S, Baker SM, Berlin M, McAdams M et al. The risk of cancer associated with specific mutations of BRCA1 and BRCA2 among Ashkenazi Jews. N Engl J Med 1997; 336: 1401–1408.
Neuhausen SL, Godwin AK, Gershoni-Baruch R, Schubert E, Garber J, Stoppa-Lyonnet D et al. Haplotype and phenotype analysis of nine recurrent BRCA2 mutations in 111 families: results of an international study. Am J Hum Genet 1998; 62: 1381–1388.
Foulkes WD, Thiffault I, Gruber SB, Horwitz M, Hamel N, Lee C et al. The founder mutation MSH2*1906G–>C is an important cause of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 1395–1412.
Lynch HT, Coronel SM, Okimoto R, Hampel H, Sweet K, Lynch JF et al. A founder mutation of the MSH2 gene and hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer in the United States. JAMA 2004; 291: 718–724.
Gauderman WJ, Morrison JM . QUANTO 1.1: a computer program for power and sample size calculations for genetic-epidemiology studies, http://hydra.usc.edu/gxe, 2006.
Gauderman WJ . Sample size calculations for matched case–control studies of gene-environment interaction. Statistics in Medicine 2002; 21: 35–50.
Oliphant A, Barker DL, Stuelpnagel JR, Chee MS . BeadArray technology: enabling an accurate, cost-effective approach to high-throughput genotyping. Biotechniques Suppl 2002; 32: S56–S61.
Altshuler D, Brooks LD, Chakravarti A, Collins FS, Daly MJ, Donnelly P . A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature 2005; 437: 1299–1320.
Pruitt KD, Tatusova T, Maglott DR . NCBI Reference Sequence (RefSeq): a curated non-redundant sequence database of genomes, transcripts and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33 (Database issue): D501–D504.
Douglas JA, Skol AD, Boehnke M . Probability of detection of genotyping errors and mutations as inheritance inconsistencies in nuclear-family data. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 70: 487–495.
Spielman RS, McGinnis RE, Ewens WJ . Transmission test for linkage disequilibrium: the insulin gene region and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Am J Hum Genet 1993; 52: 506–516.
Lin S, Chakravarti A, Cutler DJ . Exhaustive allelic transmission disequilibrium tests as a new approach to genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 1181–1188.
Lin S, Chakravarti A, Cutler DJ . Haplotype and missing data inference in nuclear families. Genome Res 2004; 14: 1624–1632.
Lin S, Cutler DJ, Zwick ME, Chakravarti A . Haplotype inference in random population samples. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 1129–1137.
Lin PI, McInnis MG, Potash JB, Willour VL, Mackinnon DF, Miao K et al. Assessment of the effect of age at onset on linkage to bipolar disorder: evidence on chromosomes 18p and 21q. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 77: 545–555.
Weinberg CR . Methods for detection of parent-of-origin effects in genetic studies of case–parents triads. Am J Hum Genet 1999; 65: 229–235.
Le Stunff C, Fallin D, Bougneres P . Paternal transmission of the very common class I INS VNTR alleles predisposes to childhood obesity. Nat Genet 2001; 29: 96–99.
Petronis A . Epigenetics and bipolar disorder: new opportunities and challenges. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2003; 123: 65–75.
Bjornsson HT, Fallin MD, Feinberg AP . An integrated epigenetic and genetic approach to common human disease. Trends Genet 2004; 20: 350–358.
Jiang YH, Bressler J, Beaudet AL . Epigenetics and human disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2004; 5: 479–510.
Marchini J, Cardon LR, Phillips MS, Donnelly P . The effects of human population structure on large genetic association studies. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 512–517.
Campbell CD, Ogburn EL, Lunetta KL, Lyon HN, Freedman ML, Groop LC et al. Demonstrating stratification in a European American population. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 868–872.
Morison IM, Ramsay JP, Spencer HG . A census of mammalian imprinting. Trends Genet 2005; 21: 457–465.
OMIM Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM (TM) McKusick–Nathans Institute for Genetic Medicine, Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, MD) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (Bethesda, MD), world wide web URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim.
Corradi JP, Ravyn V, Robbins AK, Hagan KW, Peters MF, Bostwick R et al. Alternative transcripts and evidence of imprinting of GNAL on 18p11.2. Mol Psychiatry 2005; 10: 1017–1025.
Lettice LA, Horikoshi T, Heaney SJ, van Baren MJ, van der Linde HC, Breedveld GJ et al. Disruption of a long-range cis-acting regulator for Shh causes preaxial polydactyly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 7548–7553.
Washizuka S, Kametani M, Sasaki T, Tochigi M, Umekage T, Kohda K et al. Association of mitochondrial complex I subunit gene NDUFV2 at 18p11 with schizophrenia in the Japanese population. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2006; 141: 301–304.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mulle, J., Fallin, M., Lasseter, V. et al. Dense SNP association study for bipolar I disorder on chromosome 18p11 suggests two loci with excess paternal transmission. Mol Psychiatry 12, 367–375 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001916
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001916
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genome-Wide Searches for Bipolar Disorder Genes
Current Psychiatry Reports (2011)
-
Maternal transmission effects of the PAX genes among cleft case–parent trios from four populations
European Journal of Human Genetics (2009)
-
The genetics of bipolar disorder: genome ‘hot regions,’ genes, new potential candidates and future directions
Molecular Psychiatry (2008)