Abstract
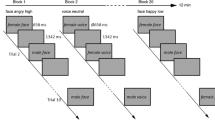
Previous studies have suggested that men and women process emotional stimuli differently. In this study, we examined if there would be any consistency in regions of activation in men and women when processing stimuli portraying happy or sad emotions presented in the form of facial expressions, scenes, and words. A blocked design BOLD functional magnetic resonance imaging paradigm was employed to monitor the neural activities of male and female healthy volunteers while they were presented with the experimental stimuli. The imaging data revealed that the right insula and left thalamus were consistently activated for men, but not women, during emotion recognition of all forms of stimuli studied. To further understand the imaging data acquired, we conducted the protocol analysis method to identify the cognitive processes engaged while the men and women were viewing the emotional stimuli and deciding whether they were happy or sad. The findings suggest that men rely on the recall of past emotional experiences to evaluate current emotional experiences. This may explain why the insula, a structure important for self-induced or internally generated recalled emotions, was consistently activated in men while processing emotional stimuli. Our findings suggest possible gender-related neural responses to emotional stimuli.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gur RC, Turetsky BI, Matsui M, Yan M, Bilker W, Hughett P et al. Sex differences in brain gray and white matter in healthy young adults: correlations with cognitive performance. J Neurosci 1999; 19: 4065–4072.
De Bellis MD, Keshavan MS, Beers SR, Hall J, Frustaci K, Masalehdan A et al. Sex differences in brain maturation during childhood and adolescence. Cereb Cortex 2001; 11: 552–557.
Seidlitz I, Diener E . Sex differences in the recall of affective experiences. J Pers Soc Psychol 1998; 74: 262–271.
Caplan PF, Crawford M, Hyde JS, Richardson JTE . Gender Differences in Human Cognition. Oxford University Press: New York, 1997.
Gur RC, Gunning-Dixon F, Bilker WB, Gur RE . Sex differences in temporo-limbic and frontal brain volumes of healthy adults. Cereb Cortex 2002; 12: 998–1003.
Kesler/West ML, Andersen AH, Smith CD, Avison MJ, Davis CE, Kryscio RJ et al. Neural substrates of facial emotion processing using fMRI. Cogn Brain Res 2001; 11: 213–226.
Lane RD, Reiman EM, Bradley MM, Lang PJ, Ahern GL, Davidson RJ et al. Neuroanatomical correlates of pleasant and unpleasant emotion. Neuropsychologia 1997; 35: 1437–1444.
Canli T, Desmond JE, Zhao Z, Gabrieli JDE . Sex differences in the neural basis of emotional memories. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 10789–10794.
Lang PJ, Greenward MK . International Affective Picture System Standardization Procedure and Results for Affective Judgment: Technical Reports 1A–1C. University of Florida Center for Research in Psychophysiology: Gainesville, FC, 1993.
Lee TMC, Liu HL, Hoosain R, Liao WT, Wu CT, Yuen KSL et al. Gender differences in neural correlates of recognition of happy and sad faces in humans assessed by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosci Lett 2002; 333: 13–16.
Matsumoto D, Ekman P . Japanese and Caucasian Facial Expressions of Emotion (JACFEE) and Neutral Faces (JACNeuF). University of California: San Francisco, 1988.
Risch SC, Kalin NH, Murphy DL . Neurochemical mechanisms in the affective disorders and neuroendocrine correlates. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1981; 1: 180–185.
Phan KL, Wager T, Taylor SF, Liberzon I . Functional neuroanatomy of emotion: a meta-analysis of emotion activation studies in PET and fMRI. Neuroimage 2002; 16: 331–348.
Snyder PJ, Harris LJ . Handedness, sex and familiar sinistrality effects on spatial tasks. Cortex 1993; 29: 115–134.
Center for the Study of Emotion and Attention [CSEA-NIMH]. The International Affective Picture System: Digitized Photographs. The Center for Research in Psychophysiology, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, 1999.
Lang PJ, Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN . International Affective Picture System (IAPS): Instruction Manual and Affective Ratings. Technical Report A-4. The Center for Research in Psychophysiology, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, 1999.
Beijing Institute of Language Teaching and Research. A Frequency Dictionary of Modern Chinese. Beijing Language Institute Press: Beijing, 1986.
Fox PT, Perlmutter JS, Raichle ME . A stereostatic method of anatomical localization for positron emission tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1985; 9: 141–153.
Xiong J, Gao JH, Lancaster JL, Fox PT . Cluster pixels analysis for functional MRI activation studies in the human brain. Hum Brain Mapp 1995; 3: 209–223.
Lancaster JL, Fox PT, Downs H, Nickerson DS, Hander TA, Mallah ME et al. Global spatial normalization of human brain using convex hulls. J Nucl Med 1999; 40: 942–955.
Lerner Y, Pianka P, Azmon B, Leiba H, Stolovitch C, Loewenstein A et al. Area-specific amblyopic effects in human occipitotemporal object representations. Neuron 2003; 40: 1023–1029.
Sala JB, Rämä P, Courtney SM . Functional topography of a distributed neural system for spatial and nonspatial information maintenance in working memory. Neuropsychologia 2003; 41: 341–356.
Lancaster JL, Rainey LH, Summerlin JL, Freitas CS, Fox PT, Toga AW et al. Automated labeling of the human brain: a preliminary report on the development and evaluation of a forward-transformation method. Hum Brain Mapp 1997; 5: 238–242.
Friston KJ, Holmes AP, Price CJ, Büchel C, Worsley KJ . Multi-subject fMRI studies and conjunction analyses. NeuroImage 1999; 10: 385–396.
Blair RJR, Morris JS, Frith CD, Perrett DI, Dolan RJ . Dissociable neural responses to facial expressions of sadness and anger. Brain 1999; 122: 883–893.
Phillips ML, Bullmore ET, Howard R, Woodruff PWR, Wright IC, Williams SCR et al. Investigation of facial recognition memory and happy and sad facial expression perception: an fMRI study. Psychiatry Res 1998; 83: 127–138.
Lane RD, Fink GR, Chau PM, Dolan RJ . Neural activation during selective attention to subjective emotional responses. Neuroreport 1997; 8: 3969–3972.
Reiman EM, Lane RD, Ahern GL, Schwartz GE, Davidson RJ, Friston KJ et al. Neuroanatomical correlates of externally and internally generated human emotion. Am J Psychiatry 1997; 154: 918–925.
Damasio AR, Grabowski TJ, Bechara A, Damasio H, Ponto LLB, Parvizi J et al. Subcortical and cortical brain activity during the feeling of self-generated emotions. Nat Neurosci 2000; 3: 1049–1056.
Schneider RJ, Friedman DP, Mishkin M . A modality-specific somatosensory area within the insula of the rhesus monkey. Brain Res 1993; 621: 116–120.
Critchley HD, Mathias CJ, Dolan RJ . Fear conditioning in humans: the influence of awareness and autonomic arousal on functional neuroanatomy. Neuron 2002; 33: 653–663.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, T., Liu, HL., Chan, C. et al. Neural activities associated with emotion recognition observed in men and women. Mol Psychiatry 10, 450–455 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001595
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001595
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A review of Deep Learning based methods for Affect Analysis using Physiological Signals
Multimedia Tools and Applications (2023)
-
Gender-related differences in moral judgments
Cognitive Processing (2010)
-
Healing Men and Community: Predictors of Outcome in a Men's Initiatory and Support Organization
American Journal of Community Psychology (2010)