Abstract
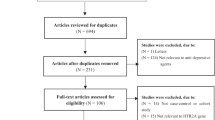
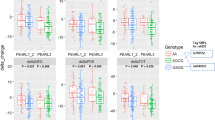
The aim of the present study was to test a possible effect of the A218C tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) gene variant on the antidepressant activity of fluvoxamine in a sample of major and bipolar depressives, with or without psychotic features. Two hundred and seventeen inpatients were treated with fluvoxamine 300?mg and either placebo or pindolol in a double blind design for 6 weeks. The severity of depressive symptoms was weekly assessed with the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression. TPH allelic variants were determined in each subject by using a PCR-based technique. No significant finding was observed in the overall sample as well as in the pindolol group, while TPH*A/A was associated with a slower response to fluvoxamine treatment in subjects not taking pindolol (P = 0.001). This effect was independent from the previously reported influence of 5-HTTLPR polymorphism. If confirmed, these results may shed further light on the genetically determined component of the response to pharmacological treatments, thus helping the clinician to individualize each patient's therapy according to their genetic pattern.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
O'Reilly RL, Bouge L, Singh FM . Pharmacogenetic response to antidepressants in a multicase family with affective disorder Biol Psychiatry 1994 36: 467–471
Pare CMB, Rees L, Sainsbury MJ . Differentiation of two genetically specific types of depression by the response to antidepressant Lancet 1962 1340–1343
Sederer LI . Depression. In: Sederer LI (ed) Inpatients Psychiatry Diagnosis and Treatment William & Wilkins: Baltimore 1986 p 20
Orsini A . Antidepressant responses and segregation analyses in affective families. In: Racagni G, Smeraldi E (eds) Anxious Depression: Assessment and Treatment Raven Press: New York 1987
Serretti A, Franchini L, Gasperini M, Rampoldi R, Smeraldi E . Mode of inheritance in mood disorders families according to fluvoxamine response Acta Psychiatr Scand 1998 98: 443–450
Franchini L, Serretti A, Gasperini M, Smeraldi E . Familial concordance of fluvoxamine response as a tool for differentiating mood disorder pedigrees J Psychiatr Res 1998 32: 255–259
Berrettini W . Progress and pitfalls: bipolar molecular linkage studies J Affect Disord 1998 50: 287–297
Lesch K, Bengel D, Heils A, Sabol S, Greenberg B, Petri S et al. Association of anxiety-related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region Science, 1996 274: 1527–1530
Heils A, Teufel A, Petri S, Stöber G, Riederer P, Bengel D et al. Allelic variation of human serotonin trasporter gene expression J Neurochem 1996 66: 2621–2624
Smeraldi E, Zanardi R, Benedetti F, Dibella D, Perez J, Catalano M . Polymorphism within the promoter of the serotonin transporter gene and antidepressant efficacy of fluvoxamine Mol Psychiatry 1998 3: 508–511
Zanardi R, Serretti A, Rossini D, Franchini L, Cusin C. Lattuada E et al. Factors affecting fluvoxamine antidepressant activity: influence of pindolol and 5-HTTLPR in delusional and nondelusional depression Biol Psychiatry (submitted)
Zanardi R, Benedetti F, DiBella D, Catalano M, Smeraldi E . Efficacy of paroxetine in depression is influenced by a functional polymorphism within the promoter of serotonin transporter gene J Clin Psychopharmacol 2000 20: 105–107
Pollock BG, Ferrell RE, Mulsant BH, Mazumdar S, Miller M, Sweet RA et al. Allelic variation in the serotonin transporter promoter affects onset of paroxetine treatment response in late-life depression Neuropsychopharmacology 2000 23: 587–590
Comings D . Polygenic inheritance in psychiatric disorders. In: Blum K, Noble EP (eds) Handbook of Psychiatric Genetics CRC Press: Boca Raton 1997 pp?235–260
Risch N . Linkage strategies for genetically complex traits: I. Multilocus models Am J Med Gen 1990 46: 222–228
Frankel W, Schork N . Who's afraid of epistasis? Nat Genet 1996 14: 371–373
Sandyk R . L-tryptophan in neuropsychiatric disorders: a review Int J Neurosci 1992 67: 127–144
Walinder J, Skott A, Carlsson A, Nagy A, Bjorn-Erik R . Potentiation of the antidepressant action of clomipramine by tryptophan Arch Gen Psychiatry 1976 33: 1384–1389
Young SN . Use of tryptophan in combination with other antidepressant treatments: a review J Psychiatry Neurosci 1991 16: 241–246
Smith KA, Fairburn CG, Cowen PJ . Relapse of depression after rapid depletion of tryptophan Lancet 1997 349: 915–919
Boularand S, Darmon MC, Ganem Y, Launay JM, Mallet J . Complete coding sequence of human tryptophan hydroxylase Nucleic Acid Res 1990 18: 4257
Craig SP, Boularand S, Darmon MC, Mallet J, Craig IW . Localization of human tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) to chromosome 11p15.3—p14 by in situ hybridization Cytogenet Cell Genet 1991 56: 157–159
Nielsen DA, Jenkins GL, Stefanisko KM, Jefferson KK, Goldman D . Sequence, splice site and population frequency distribution analyses of the polymorphic human tryptophan hydroxylase intron 7 Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1997 45: 145–148
Jonsson EG, Goldman D, Spurlock G, Gustavsson JP, Nielsen DA, Linnoila M et al. Tryptophan hydroxylase and catechol-O-methyltransferase gene polymorphisms: relationships to monoamine metabolite concentrations in CSF of healthy volunteers Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 1997 247: 297–302
Benedetti F, Serretti A, Colombo C, Campori E, Barbini B, Di Bella D et al. Influence of a functional polymorphism within the promoter of the serotonin transporter gene on the effects of total sleep deprivation in bipolar depression Am J Psychiatry 1999 156: 1450–1452
McGuffin P, Katz R . Nature, nurture and affective disorder. In: Royal College of Psychiatrists (ed). The Biology of Affective Disorders Gaskell Press: London 1986
Winokur G, Coryell W, Keller M, Endicott J, Leon A . A family study of manic-depressive (bipolar I) disease Is it a distinct illness separable from primary unipolar depression? Arch Gen Psychiatry 1995 52: 367–373
Kim DK, Lim SW, Lee S, Sohn SE, Kim S, Hahn CG et al. Serotonin transporter gene polymorphism and antidepressant response Neuroreport 2000 11: 215–219
Kunugi H, Hattori M, Kato T, Tatsumi M, Sakai T, Sasaki T et al. Serotonin transporter gene polymorphisms: ethnic difference and possible association with bipolar affective disorder Mol Psychiatry 1997 2: 457–462
Nielsen DA, Dean M, Goldman D . Genetic mapping of the human tryptophan hydroxylase gene on chromosome 11, using an intronic conformational polymorphism Am J Hum Genet 1992 51: 1366–1371
Gelernter J, Kranzler H, Lacobelle J . Population studies of polymorphisms at loci of neuropsychiatric interest (tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH), dopamine transporter protein (SLC6A3), D3 dopamine receptor (DRD3), apolipoprotein E (APOE), mu opioid receptor (OPRM1), and ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF)) Genomics 1998 52: 289–297
Gasparini P, Estivill X, Volpini V, Totaro A, Castellvi-Bel S, Govea N et al. Linkage of DFNB1 to non-syndromic neurosensory autosomal-recessive deafness in Mediterranean families Eur J Hum Genet 1997 5: 83–88
Bellivier F, Leboyer M, Courtet P, Buresi C, Beaufils B, Samolyk D et al. Association between the tryptophan hydroxylase gene and manic-depressive illness Arch Gen Psychiatry 1998 55: 33–37
Frisch A, Postilnick D, Rockah R, Michaelovsky E, Postilnick S, Birman E et al. Association of unipolar major depressive disorder with genes of the serotonergic and dopaminergic pathways Mol Psychiatry 1999 4: 389–392
Furlong RA, Ho L, Rubinsztein JS, Walsh C, Paykel ES, Rubinsztein DC . No association of the tryptophan hydroxylase gene with bipolar affective disorder, unipolar affective disorder, or suicidal behaviour in major affective disorder Am J Med Gen 1998 81: 245–247
Kunugi H, Ishida S, Kato T, Sakai T, Tatsumi M, Hirose T et al. No evidence for an association of polymorphisms of the tryptophan hydroxylase gene with affective disorders or attempted suicide among Japanese patients Am J Psychiatry 1999 156: 774–776
McQuillin A, Lawrence J, Kalsi G, Gurling H, Curtis D . No allelic association between bipolar affective disorder and the tryptophan hydroxylase gene Arch Gen Psychiatry 1999 56: 99–100
Vincent JB, Masellis M, Lawrence J, Choi V, Gurling HM, Parikh SV et al. Genetic association analysis of serotonin system genes in bipolar affective disorder Am J Psychiatry 1999 156: 136–138
Tsai SJ, Hong CJ, Wang YC . Tryptophan hydroxylase gene polymorphism (A218C) and suicidal behaviors Neuroreport 1999 10: 3773–3775
Rietschel M, Schorr A, Albus M, Franzek E, Kreiner R, Held T et al. Association study of the tryptophan hydroxylase gene and bipolar affective disorder using family-based internal controls Am J Med Genet 2000 96: 310–311
Ishiguro H, Saito T, Shibuya H, Toru M, Arinami T . The 5′ region of the tryptophan hydroxylase gene: mutation search and association study with alcoholism J Neural Transm 1999 106: 1017–1025
Han L, Nielsen DA, Rosenthal NE, Jefferson K, Kaye W, Murphy D et al. No coding variant of tryptophan hydroxylase gene detected in seasonal affective disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, anorexia nervosa, and alcoholism Biol Psychiatry 1999 45: 615–619
Rotondo A, Schuebel KE, Bergen AW, Aragon R, Virkkunen M, Linnoila M et al. Identification of four variants in the tryptophan hydroxylase promoter and association to behavior Mol Psychiatry 1999 4: 360–368
Frisch A, Michaelovsky E, Rockah R, Amir I, Hermesh H, Laor N et al. Association between obsessive-compulsive disorder and polymorphisms of genes encoding components of the serotonergic and dopaminergic pathways Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2000 10: 205–209
Nielsen DA, Goldman D, Virkkunen M, Tokola R, Rawlings R, Linnoila M . Suicidality and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid concentration associated with a tryptophan hydroxylase polymorphism Arch Gen Psychiatry 1994 51: 34–38
Mann JJ, Malone KM, Nielsen DA, Goldman D, Erdos J, Gelernter J . Possible association of a polymorphism of the tryptophan hydroxylase gene with suicidal behavior in depressed patients Am J Psychiatry 1997 154: 1451–1453
Abbar M, Courtet P, Amadeo S, Caer Y, Mallet J, Baldy-Moulinier M et al. Suicidal behaviors and the tryptophan hydroxylase gene Arch Gen Psychiatry 1995 52: 846–849
Bennett PJ, McMahon WM, Watabe J, Achilles J, Bacon M, Coon H et al. Tryptophan hydroxylase polymorphisms in suicide victims Psychiatr Genet 2000 10: 13–17
Paik I, Toh K, Kim J, Lee C . TPH gene may be associated with suicidal behavior, but not with schizophrenia in the Korean population Hum Hered 2000 50: 365–369
Geijer T, Frisch A, Persson ML, Wasserman D, Rockah R, Michaelovsky E et al. Search for association between suicide attempt and serotonergic polymorphisms Psychiatr Genet 2000 10: 19–26
Manuck SB, Flory JD, Ferrell RE, Dent KM, Mann JJ, Muldoon MF . Aggression and anger-related traits associated with a polymorphism of the tryptophan hydroxylase gene Biol Psychiatry 1999 45: 603–614
Evans J, Reeves B, Platt H, Leibenau A, Goldman D, Jefferson K et al. Impulsiveness, serotonin genes and repetition of deliberate self-harm (DSH) Psychol Med 2000 30: 1327–1334
Cohen J . Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ 1988
American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edn American Psychiatric Association: Washington DC 1994
Leckman JF, Sholomskas D, Thompson WD, Belanger A, Weissman MM . Best estimate of lifetime psychiatric diagnosis: a methodological study Arch Gen Psychiatry 1982 39: 879–883
Hamilton M . Development of a rating scale for primary depressive illness Br J Soc Clin Psychol 1967 6: 278–296
Bech P, Malt U, Dencker S, Ahlfors U, Elgen K, Lewander T et al. Scales for assessment of diagnosis and severity of mental disorders Acta Psychiatr Scand 1993 87 Suppl 372: 37–40
Bellini L, Gatti F, Gasperini M, Smeraldi E . A comparison between delusional and non-delusional depressives J Affect Disord 1992 25: 129–138
Sobin CA, Sackeim H . Psychomotor symptoms of depression Am J Psychiatry 1997 154: 4–17
Lucca A, Lucini V, Catalano M, Alfano M, Smeraldi E . Plasma tryptophan to large neutral amino acids ratio and therapeutic response to a selective serotonin uptake inhibitor Neuropsychobiology 1994 29: 108–111
Lahiri DK, Nurnberger JIJ . A rapid non-enzymatic method for the preparation of HMW DNA from blood for RFLP studies Nucleic Acid Res 1991 19: 5444
Gibbons RD, Hedeker D, Elkin I, Waternaux C, Kraemer HC, Greenhouse JB et al. Some conceptual and statistical issues in analysis of longitudinal psychiatric data. Application to the NIMH treatment of Depression Collaborative Research Program dataset Arch Gen Psychiatry 1993 50: 739–750
Elkin I, Gibbons RD, Shea MT, Sotsky SM, Watkins JT, Pilkonis PA et al. Initial severity and differential treatment outcome in the National Institute of Mental Health Treatment of Depression Collaborative Research Program J Consult Clin Psychol 1995 63: 841–847
Serretti A, Lattuada E, Zanardi R, Franchini L, Smeraldi E . Patterns of symptom improvement during antidepressant treatment of delusional depression Psychiatry Res 2000 94: 185–190
Hedeker D, Gibbons RD . MIXREG: a computer program for mixed-effects regression analysis with autocorrelated errors Comput Methods Programs Biomed 1996 49: 229–252
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Istituto Scientifico Ospedale. San Raffaele (grants M0975 and M2511). The authors acknowledge Cristina Lorenzi for her help with DNA analysis and Enrico Lattuada MD for collecting blood samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serretti, A., Zanardi, R., Rossini, D. et al. Influence of tryptophan hydroxylase and serotonin transporter genes on fluvoxamine antidepressant activity. Mol Psychiatry 6, 586–592 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000876
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000876
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of chiral cysteine-capped CdSe quantum dots for fluorometric differentiation and quantitation of tryptophan enantiomers
Microchimica Acta (2020)
-
Pharmacogenetics and Imaging–Pharmacogenetics of Antidepressant Response: Towards Translational Strategies
CNS Drugs (2016)
-
Review and meta-analysis of antidepressant pharmacogenetic findings in major depressive disorder
Molecular Psychiatry (2010)
-
Pharmacogenetics of antidepressant response: An update
Human Genomics (2008)
-
Interaction between TPH1 and GNB3 genotypes and electroconvulsive therapy in major depression
Journal of Neural Transmission (2007)