Abstract
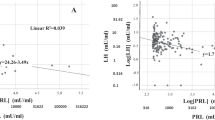
Prominent diseases of the endocrine system, such as diabetes mellitus, hypogonadism, and hyperprolactinemia, may cause erectile dysfunction (ED). ED affects about 50% of male diabetic patients possibly due to the vascular and neuropathic complications. Metabolic control and selective phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors are therapies of choice for controlling ED. By correcting hypogonadism, testosterone levels are restored. This, and the use of dopaminergic drugs, which normalize prolactin levels in male hyperprolactinemia, may be effective in reversing ED in these endocrine disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lue TF . Erectile dysfunction. N Engl J Med 2000; 342: 1802–1813.
Koya D, King GL . Protein kinase C activation and the development of diabetic complications. Diabetes 1998; 47: 859–866.
Koppiker N, Boolell M, Price D . Recent advances in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus. Endocr Pract 2003; 9: 52–63.
Seftel AD et al. Advanced glycation end products in human penis: elevation in diabetic tissue, site of deposition, and possible effect through iNOS or eNOS. Urology 1997; 50: 1016–1026.
Cameron NE, Eaton SE, Cotter MA, Tesfaye S . Vascular factors and metabolic interactions in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia 2001; 44: 1973–1988.
Burns-Cox N, Gingell C . The andropause: fact or fiction? Postgrad Med J 1997; 73: 553–556.
Harman SM et al. Longitudinal effects of aging on serum total and free testosterone levels in healthy men. Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 724–731.
Bhasin S, Buckwalter JG . Testosterone supplementation in older men: a rational idea whose time has not yet come. J Androl 2001; 22: 718–731.
Basaria S, Dobs AS . Hypogonadism and androgen replacement therapy in elderly men. Am J Med 2001; 110: 563–572.
Tsujimura A et al. The clinical studies of sildenafil for the ageing male. Int J Androl 2002; 25: 28–33.
Buvat J . Hyperprolactinemia and sexual function in men: a short review. Int J Impot Res 2003; 15: 373–377.
Carani C, Granata AR, Fustini MF, Marrama P . Prolactin and testosterone: their role in male sexual function. Int J Androl 1996; 19: 48–54.
De Rosa M et al. Hyperprolactinemia in men: clinical and biochemical features and response to treatment. Endocrine 2003; 20: 75–82.
Wortsman J, Rosner W, Dufau ML . Abnormal testicular function in men with primary hypothyroidism. Am J Med 1987; 82: 207–212.
Naya Y et al. Significant decrease of the International Index of Erectile Function in male renal failure patients treated with hemodialysis. Int J Impot Res 2002; 14: 172–177.
Rendell MS et al. Sildenafil for treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes. JAMA 1999; 281: 421–426.
Boulton AJ, Selam JL, Sweeney M, Ziegler D . Sildenafil citrate for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2001; 44: 1296–1301.
Stuckey BG et al. Sildenafil citrate for treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with type 1 diabetes: results of a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 279–284.
Tran D, Howes L . Cardiovascular safety of sildenafil. Drug Saf 2003; 26: 453–460.
Eardley I, Cartledge J . Tadalafil (Cialis) for men with erectile dysfunction. Int J Clin Pract 2002; 56: 300–304.
Hellstrom WJ et al. Vardenafil for treatment of men with erectile dysfunction: efficacy and safety in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Androl 2002; 23: 763–771.
Saenz De Tejada I, Anglin G, Knight JR, Emmick JT . Effects of tadalafil on erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002; 25: 2159–2164.
Goldstein I, Young J, Fischer J . Vardenafil, a new highly selective PDE5 inhibitor, improves erectile function in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 2001; 50: 114.
Montorsi F . Podium Session 2PS-2 Pharmacotherapy. Monday, November 17, 2003, 09:00-10:30D. Hatzichristou, Greece; F. Montorsi, Italy. Int J Impot Res 2003; 15: S3–S4.
Wessells H et al. Effect of an alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone analog on penile erection and sexual desire in men with organic erectile dysfunction. Urology 2000; 56: 641–646.
Heaton JP et al. Intracavernosal alprostadil is effective for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in diabetic men. Int J Impot Res 2001; 13: 317–321.
Snyder PJ et al. Effects of testosterone replacement in hypogonadal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 2670–2677.
Wang C et al. Transdermal testosterone gel improves sexual function, mood, muscle strength, and body composition parameters in hypogonadal men. Testosterone Gel Study Group. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 2839–2853.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miralles-García, J., García-Díez, L. Specific aspects of erectile dysfunction in endocrinology. Int J Impot Res 16 (Suppl 2), S10–S12 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901237
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901237
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Potential differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cell transplanted in rat corpus cavernosum toward endothelial or smooth muscle cells
International Journal of Impotence Research (2007)
-
The sexual and reproductive health in men with generalized epilepsy: a multidisciplinary evaluation
International Journal of Impotence Research (2006)