Abstract
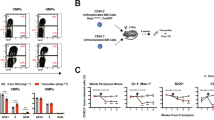
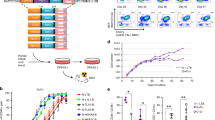
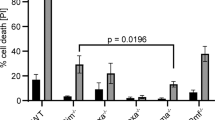
THE E2A–HLF (for hepatic leukaemia factor) fusion gene, formed by action of the t(17;19) (q22;p13) chromosomal translocation, drives the leukaemic transformation of early B-cell precursors1–4, but the mechanism of this activity remains unknown. Here we report that human leukaemia cells carrying the translocation t(17;19) rapidly died by apoptosis when programmed to express a dominant-negative suppressor of the fusion protein E2A–HLF, indicating that the chimaeric oncoprotein probably affects cell survival rather than cell growth. Moreover, when introduced into murine pro-B lymphocytes, the oncogenic E2A–HLF fusion protein reversed both interleukin-3-dependent and p53-mediated apoptosis. The close homology of the basic region/leucine zipper (bZIP) DNA-binding and dimerization domain of HLF to that of the CES-2 cell-death specification protein of Caenorhabditis elegans5 suggests a model of leukaemogenesis in which E2A–HLF blocks an early step within an evolutionarily conserved cell-death pathway6–9.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inaba, T. et al. Science 257, 531–534 (1992).
Hunger, S. P., Ohyashiki, K., Toyama, K. & Cleary, M. L. Genes Dev. 6, 1608–1620 (1992).
Inaba, T. et al. Molec. cell Biol. 14, 3403–3413 (1994).
Hunger, S. P., Brown, R. & Cleary, M. L. Molec. cell. Biol. 14, 5986–5996 (1994).
Metzstein, M. M., Hengartner, M. O., Tsung, N., Ellis, R. E. E. & Horvitz, H. R. Nature 382, 545–547 (1996).
Horvitz, H. R., Shaham, S. & Hengartner, M. O. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 59, 377–385 (1994).
Ellis, R. E. & Horvitz, H. R. Development 112, 591–603 (1991).
Ellis, R. E., Yuan, J. Y. & Horvitz, H. R. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 7, 663–698 (1991).
Wyllie, A. H. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 5, 97–104 (1995).
Aronheim, A., Shiran, R., Rosen, A. & Walker, M. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 8063–8067 (1993).
Quong, M. W., Massari, M. E., Zwart, R. & Murre, C. Molec. cell Biol. 13, 792–800 (1993).
Palacios, R. & Steinmetz, M. Cell 41, 727–734 (1985).
Canman, C. E., Gilmer, T. M., Coutts, S. B. & Kastan, M. B. Genes Dev. 9, 600–611 (1995).
Collins, M. K., Marvel, J., Malde, P. & Lopez-Rivas, A. J. exp. Med. 176, 1043–1051 (1992).
Hunger, S. P. Blood 87, 1211–1224 (1996).
Raff, M. C. Nature 356, 397–400 (1992).
Thompson, C. B. Science 267, 1456–1462 (1995).
Korsmeyer, S. J. Blood 80, 879–886 (1992).
Hockenbery, D., Nunez, G., Milliman, C., Schreiber, R. D. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Nature 348, 334 (1990).
Vaux, D. L., Cory, S. & Adams, J. M. Nature 335, 440–442 (1988).
Nunez, G., London, L., Hockenbery, D., Alexander, M., McKearn, J. P. & Korsmeyer, S. J. J. Immunol. 144, 3602–3610 (1990).
Hockenbery, D. M., Olivai, Z. N., Yin, X.-M., Milliman, S. J. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Cell 75, 241–251 (1993).
Squier, M. K. T., Sehnert, A. J. & Cohen, J. J. J. Leuk. Biol. 57, 2–10 (1995).
Nossal, G. J. Cell 76, 229–239 (1994).
Hengartner, M. O. & Horvitz, H. R. Cell 76, 665–676 (1994).
Miura, M., Zhu, H., Rotello, R., Hartwieg, E. A. & Yuan, J. Cell 75, 653–660 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inaba, T., Inukai, T., Yoshihara, T. et al. Reversal of apoptosis by the leukaemia-associated E2A–HLF chimaeric transcription factor. Nature 382, 541–544 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/382541a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/382541a0
This article is cited by
-
Harnessing function of EMT in cancer drug resistance: a metastasis regulator determines chemotherapy response
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2024)
-
Emerging roles of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hematological malignancies
Journal of Biomedical Science (2018)
-
Mutated Ptpn11 alters leukemic stem cell frequency and reduces the sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia cells to Mcl1 inhibition
Leukemia (2015)
-
Oncogenic fusion E2A-HLF sensitizes t(17;19)-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by upregulating the expression of death receptors
Leukemia (2012)
-
The E2A-HLF oncogenic fusion protein acts through Lmo2 and Bcl-2 to immortalize hematopoietic progenitors
Leukemia (2011)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.