Abstract
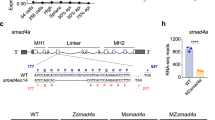
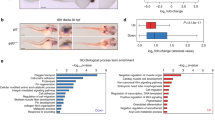
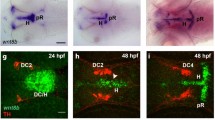
EARLY during its development, the vertebrate brain is subdivided into regions that have distinct fates and correlate with the expression domains of regulatory genes1,2, but little is known about the cell–cell interactions that establish this spatial pattern. Candidates for regulating such interactions are the Eph-related receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) which have spatially restricted expression in the developing brain2–6. These RTKs may mediate cell-contact-dependent signalling by interacting with membrane-bound ligands7, and have been implicated in axon repulsion8,9 and the segmental restriction of gene expression in the hindbrain10, but nothing is known regarding their function in the rostral neural epithelium. Here we use a dominant-negative approach in the zebrafish embryo to interfere with the function of Rtk1, an Eph-related RTK expressed in the developing diencephalon. We find that expression of a truncated receptor leads to expansion of the eye field into diencephalic territory and loss of diencephalic structures, indicating a role for Rtk1 in patterning the developing forebrain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rubenstein, J. L. R. & Puelles, L. in Current Topics in Developmental Biology Vol. 29 (ed. Pedersen, R. A.) 1–63 (Academic, London, 1994).
Macdonald, R. et al. Neuron 13, 1039–1053 (1994).
van der Geer, P., Hunter, T. & Lindberg, R. A. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 10, 251–337 (1994).
Lai, C. & Lemke, G. Neuron 6, 691–704 (1991).
Pasquale, E. B. et al. J. Neurosci. 12, 3956–3967 (1992).
Nieto, M. A. et al. Development 116, 1137–1150 (1992).
Pandey, A., Lindberg, R. A. & Dixit, V. M. Curr. Biol. 5, 986–989 (1995).
Cheng, H.-J. et al. Cell 82, 371–381 (1995).
Drescher, U. et al. Cell 82, 359–370 (1995).
Xu, Q. et al. Development 121, 4005–4016 (1995).
Irving, C. et al. Devl Biol. 173, 26–38 (1996).
Xu, Q. et al. Development 120, 287–299 (1994).
Hemmati-Brivanlou, A. & Melton, D. A. Nature 359, 609–614 (1992).
Graff, J. M. et al. Cell 79, 169–179 (1994).
Amaya, E., Musci, T. J. & Kirschner, M. W. Cell 66, 256–270 (1991).
Schmitt, E. A. & Dowling, J. E. J. comp. Neurol. 344, 532–542 (1994).
Allende, M. L. & Weinberg, E. S. Devl Biol. 166, 509–530 (1994).
Krauss, S. et al. EMBO J. 10, 3609–3619 (1991).
Figdor, M. C. & Stern, C. D. Nature 363, 630–634 (1993).
Papalopulu, N. Perspect. dev. Neurobiol. 3, 39–52 (1995).
Chung, S. H. & Cooke, J. Nature 258, 126–132 (1975).
Nakamura, H. et al. Cell Diff. Dev. 19, 187–193 (1986).
Alvarado-Mallart, R., Martinez, S. & Lance-Jones, C. Devl Biol. 139, 75–88 (1990).
Martinez, S., Wassef, M. & Alvarado-Mallart, R. M. Neuron 6, 971–981 (1991).
Woo, K. & Fraser, S. E. Development 121, 2595–2609 (1995).
Cheng, H.-J. & Flanagan, J. G. Cell 79, 157–168 (1994).
Bergemann, A. D. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 15, 4921–4929 (1995).
Macdonald, R. et al. Development 121, 3267–3277 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Alldus, G., Macdonald, R. et al. Function of the Eph-related kinase rtk1 in patterning of the zebrafish forebrain. Nature 381, 319–322 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/381319a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/381319a0
This article is cited by
-
Ephrins make eyes with planar cell polarity
Nature Cell Biology (2006)
-
Regulation of repulsion versus adhesion by different splice forms of an Eph receptor
Nature (2000)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.