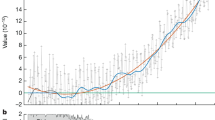
Abstract
THE rotation of the Sun is not that of a rigid body; at its surface, the gas near the poles has a lower angular velocity than that near the equator1. This latitudinal variation persists to the base of the convection zone, below which the angular velocity becomes approximately uniform2,3. Any variations of angular velocity at much greater depths are, however, poorly constrained4–10. Observations of solar oscillation modes have been used to probe density variations in the Sun; rotational splitting of degenerate modes, although difficult to resolve, provides important constraints on the dynamical structure11. Here we report observations of rotationally split modes made over a three-year period with the Birmingham Solar Oscillations Network. Our results indicate that there is a substantial region inside the Sun that is rotating more slowly than the surface. This situation seems likely to be transient—the minimum-energy state would have all the deeper regions rotating with the same angular velocity—and is at variance with our current ideas about the rotational evolution of main-sequence stars12. We have no solution to the dynamical problem this poses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snodgrass, H. B. Solar Phys. 94, 13–31 (1984).
Christensen-Dalsgaard, J. & Schou, J. Selsmology of the Sun and Sun-like Stars 149–153 (ESA SP-286 European Space Agency, Noordwijk, 1988).
Brown, T. M. et al. Astrophys. J. 343, 526–546 (1989).
Claverie, A. et al. Nature 293, 443–445 (1981).
Isaak, G. R. Selsmology of the Sun and the Distant Stars (ed. Gough, D. O.) 275–280 (NATO ASI Ser. C 169, Reidel, Dordrecht, 1986).
Loudagh, S. et al. Astr. Astrophys. 275, L25–L28 (1993).
Jiménez, A. et al. Astr. Astrophys. J. 435, 874–880 (1994).
Toutain, T. & Kosovichev, A. G. Astr. Astrophys. 284, 265–268 (1994).
Appourchaux, T. et al. Astr. Astrophys. 294, L13–L16 (1995).
Elsworth, Y. et al. GONG 1994: Helio- and Asteroseismology (eds Ulrich, R. K., Rhodes, E. J. Jr & Däppen, W.) 43–46 (Conf. Ser. 76, Astr. Soc. Pacific, San Francisco, 1995).
Gough, D. O. & Toomre, J. A. Rev. Astr. Astrophys. 29, 627–684 (1991).
Pinsonneault, M. H., Kawaler, S. D., Sofia, S. & Demarque, P. Astrophys. J. 338, 424–452 (1989).
Rhodes, E. J. Jr et al. Astrophys. J. 351, 687–700 (1990).
Gough, D. O. Future Missions in Solar, Heliospheric and Space Plasma Physics 183–197 (ESA SP-235, European Space Agency, Noordwijk, 1985).
Dziembowski, W. A. & Goode, P. R. GONG 1992: Seismic Investigation of the Sun and Stars (ed. Brown, T. M.) 225–227 (Conf. Ser. 42, Astr. Soc. Pacific, San Francisco, 1993).
Brookes, J. R., Isaak, G. R. & van der Raay, H. B. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 185, 1–17 (1978).
Elsworth, Y. et al. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 265, 888–898 (1993).
Christensen-Dalsgaard, J. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 239, 977–994 (1989).
Duvall, T. Jr et al. Nature 310, 22–25 (1984).
Cowling, T. G. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 101, 367–373 (1941).
Gough, D. O. et al. Inside the Stars (eds Weiss, W. W. & Baglin, A.) 93–96 (Conf. Ser. 40, Astr. Soc. Pacific, San Francisco, 1993).
Goode, P. R. & Dziembowsi, W. A. GONG 1992: Seismic Investigation of the Sun and Stars (ed. Brown, T. M.) 217 (Conf. Ser. 42, Astr. Soc. Pacific, San Francisco, 1993).
Tomczyk, S., Schou, J. & Thompson, M. J. Astrophys. J. Lett. (in the press).
Elsworth, Y. et al. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 242, 135–140 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elsworth, Y., Howe, R., Isaak, G. et al. Slow rotation of the Sun's interior. Nature 376, 669–672 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/376669a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/376669a0
This article is cited by
-
Asteroseismology of solar-type stars
Living Reviews in Solar Physics (2019)
-
The Life and Times of a Dissident Scientist
Solar Physics (2017)
-
Comparative Analyses of Brookhaven National Laboratory Nuclear Decay Measurements and Super-Kamiokande Solar Neutrino Measurements: Neutrinos and Neutrino-Induced Beta-Decays as Probes of the Deep Solar Interior
Solar Physics (2016)
-
Some Glimpses from Helioseismology at the Dynamics of the Deep Solar Interior
Space Science Reviews (2015)
-
What Have We Learned from Helioseismology, What Have We Really Learned, and What Do We Aspire to Learn?
Solar Physics (2013)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.