Abstract
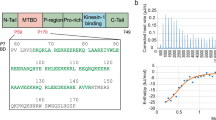
KINESIN is a microtubule (MT)-associated 'motor' molecule fundamental to organelle transport1,2. Recently, various kinesin superfamily members (KIFs) have also been identified and suggested as being responsible for the transport of specific organelles3¤-5. Kinesin is a heterotetramer composed of two heavy chains and two light chains. The heavy chains form two globular heads, a rod and a fan-like tail completed by the light chains6,7. The globular head, which is composed of approximately 340 amino-terminal residues of the heavy chain, includes both ATP-binding and MT-binding domains, and its recombinant protein also has these properties8. To improve the understanding of the mechanism offeree generation by an MT-based molecular motor, kinesin, we report here the three-dimensional structure of the complex of a recombinant kinesin head and MTs, as revealed by helical reconstruction from cryo-electron micrographs. A kinesin head is a globular teardrop-like structure binding to the ridge of one protofilament of MTs. We have determined the polarity of the structure of the complex of MTs and the kinesin head in relation to MT polarity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vale, R. in Guidebook to the Cytoskeletal and Motor Proteins (eds Thomas, K. & Vale, R.) 175–212 (Oxford Univ. Press, 1993).
Brady, S. T. Neuron 7, 521–533 (1991).
Hirokawa, N. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 3, 724–731 (1993).
Nangaku, M. et al. Cell 79, 1209–1220 (1994).
Okada, Y., Yamazaki, H., Sekine, Y. & Hirokawa, N. Cell 81, 769–780 (1995).
Hirokawa, N. et al. Cell 56, 867–878 (1989).
Scholey, J., Heuser, J., Yang, J. & Goldstein, L. Nature 338, 355–357 (1989).
Yang, J. T., Saxton, W. M., Stewart, R. J., Raff, E. C. & Goldstein, L. S. Science 249, 42–47 (1990).
Kikkawa, M., Ishikawa, T., Nakata, T., Wakabayashi, T. & Hirokawa, N. J. Cell Biol. 127, 1965–1971 (1994).
Kato, K. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2, 704–711 (1991).
Song, Y. & Mandelkow, E. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 1671–1675 (1993).
Harrison, B. et al. Nature 362, 73–75 (1993).
Chrétien, D. & Wade, R. Biol. Cell 71, 161–174 (1991).
Ray, S., Meyhofer, E., Milligan, R. & Howard, J. J. Cell Biol. 121, 1083–1093 (1993).
Mandelkow, E. & Mandelkow, E. J. molec. Biol. 181, 123–135 (1985).
Hirokawa, N. J. Cell Biol. 94, 129–142 (1982).
Mandelkow, E., Schultheiss, R., Rapp, R., Muller, M. & Mandelkow, E. J. Cell Biol. 102, 1067–1073 (1986).
Beese, L., Stubbs, G. & Cohen, C. J. molec. Biol. 194, 257–264 (1987).
Song, Y. H. & Mandelkow, E. J. Cell Biol. 128, 81–94 (1995).
Berliner, E., Young, E. C., Anderson, K., Mahtani, H. K. & Gelles, J. Nature 373, 718–721 (1995).
Unwin, N. Nature 373, 37–43 (1995).
Shelanski, M., Gaskin, F. & Cantor, C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70, 765–768 (1973).
Herzog, W. & Weber, K. Eur. J. Biochem. 92, 1–8 (1978).
Dubochet, J. et al. Q. Rev. Biophys. 21, 129–228 (1988).
Ishikawa, T. & Wakabayashi, T. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 203, 951–958 (1994).
Egelman, E. H. Ultramicroscopy 19, 367–373 (1986).
DeRosier, D. & Moore, P. J. molec. Biol. 52, 355–369 (1970).
Wakabayashi, T., Huxley, H. E., Amos, L. A. & Klug, A. J. molec. Biol. 93, 477–497 (1975).
Amos, L. A. & Klug, A. J. molec. Biol. 99, 51–64 (1975).
Witman, G. B. Meth. Enzym. 134, 280–290 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kikkawa, M., Ishikawa, T., Wakabayashi, T. et al. Three-dimensional structure of the kinesin headá¤-microtubule complex. Nature 376, 274–277 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/376274a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/376274a0
This article is cited by
-
Overview of the mechanism of cytoskeletal motors based on structure
Biophysical Reviews (2018)
-
A molecular motor finds its track
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2013)
-
Structuring movement
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2010)
-
Spatial organization of intracellular communication: insights from imaging
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2010)
-
The yeast DASH complex forms closed rings on microtubules
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2005)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.