Abstract
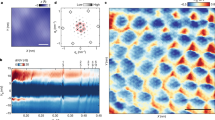
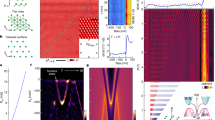
A SERIOUS impediment to many potential applications of the high-transition-temperature (high-Tc) copper oxide superconductors is the relative ease with which magnetic flux lines move within these materials, thereby producing finite electrical resistance1,2. To devise methods for rigidly fixing flux lines in these materials, which is necessary to achieve a truly superconducting (zero resistance) state, requires an understanding of their fundamental properties. In clean, conventional type II superconductors, flux lines or vortices can be modelled well as rigid objects that pass straight through a sample. In the high-Tc materials, however, comparatively short coherence lengths, large anisotropies and large accessible thermal energies lead to more complex and fascinating behaviour, giving for example entangled flux lines and two-dimensional pancake vortices3–5. Some detail of the vortex lattice has been resolved previously6–13, although it is not clear how vortices pass through these materials. Here we address this critical issue by simultaneously decorating the positions of flux lines at opposite sides of single-crystal Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8 (BSCCO) high-Tc superconductors using the Bitter technique14,15. These new data enable us to quantify the wandering of vortices as they pass through the BSCCO high-Tc materials and address the elasticity of the vortex lattice. This information will be useful for devising effective strategies for pinning flux lines to the crystal lattice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop, D. J., Gammel, P. L., Huse, D. A. & Murray, C. A. Science 255, 165–172 (1992).
Huse, D. A., Fisher, M. P. A. & Fisher, D. S. Nature 358, 553–559 (1992).
Nelson, D. R. & Seung, H. S. Phys. Rev. B39, 9153–9174 (1989).
Brandt, E. H. J. Supercond. 6, 201–217 (1993).
Clem, J. R. Phys. Rev. B 43, 7837–7846 (1991).
Dolan, G. J., Chandrashekhar, G. V., Dinger, T. R., Feild, C. & Holtzberg, F. Phys. Rev. Lett. 62, 827–830 (1989).
Grier, D. G. et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 2270–2273 (1991).
Bolle, C. A. et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 112–115 (1991).
Dai, H., Liu, J. & Lieber, C. M. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 748–751 (1994).
Yoon, S., Dai, H., Liu, J. & Lieber, C. M. Science 265, 215–218 (1994).
Cubitt, R. et al. Nature 365, 407–411 (1993).
Yethiraj, M. et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 857–860 (1993).
Harada, K. et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 3371–3374 (1993).
Essman, U. & Träuble, H. Phys. Status Solidi 18, 813–828 (1966).
Huebner, R. P. Magnetic Flux Structures in Superconductors (Springer, Berlin, 1979).
Huse, D. A. Phys. Rev. B46, 8621–8623 (1992).
Nelson, D. R. in Phenomenology and Applications of High-Temperature Superconductors (eds Bedell, K. S., Inui, M., Meltzer, D., Schrieffer, J. R. & Doniach, S.) 187–242 (Addison-Wesley, New York, 1992).
Marchetti, M. C. & Nelson, D. R. Phys. Rev. B47, 12214–12223 (1993).
Nelson, D. R. & Le Doussal, P. Phys. Rev. B42, 10113–10129 (1990).
Fisher, D. S. in Phenomenology and Applications of High-Tempeature Superconductors (eds Bedell, K. S., Inui, M., Meltzer, D., Schrieffer, J. R. & Doniach, S.) 287–327 (Addison-Wesley, New York, 1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Z., Yoon, S., Dai, H. et al. Path of magnetic flux lines through high-Tc copper oxide superconductors. Nature 371, 777–779 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/371777a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/371777a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.