Abstract
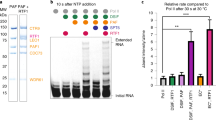
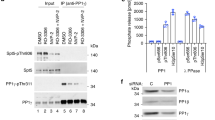
PHOSPHORYLATION of the heptapeptide repeats in the C-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II has been widely proposed as an essential step in transcription initiation1–8 on the basis of findings indicating (1) that the CTDs of RNA polymerase II molecules actively engaged in transcription are highly phosphorylated4,9,10; (2) that polymerase molecules containing non-phosphorylated CTDs preferentially enter the preinitiation complex3,11,12 where they are subsequently phosphorylated3,13; and (3) that essential initiation factors b from yeast14–16, δ from rat17,18, and BTF2(TFIIH) from human cells19–21 have closely associated CTD-kinase activities. Here we take advantage of a highly purified enzyme system which supports both CTD phosphorylation and basal transcription to test this hypothesis directly. Using the isoquinoline sulphonamide derivative H-8, which is a potent inhibitor of CTD kinase, we show that basal transcription occurs in the absence of CTD phosphorylation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young, R. A. A. Rev. Biochem. 60, 689–715 (1991).
Corden, J. L. Trends biochem. Sci. 15, 383–387 (1990).
Laybourn, P. J. & Dahmus, M. E. J. biol. Chem. 265, 13165–13173 (1990).
Payne, J. M., Laybourn, P. J. & Dahmus, M. E. J. biol. Chem. 264, 19621–19629 (1989).
Laybourn, P. J. & Dahmus, M. E. J. biol. Chem. 264, 6693–6698 (1989).
Sigler, P. B. Nature 333, 210–212 (1988).
Usheva, A. et al. Cell. 69, 871–881 (1992).
Peterson, M. G. & Tjian, R. Nature 358, 620–621 (1992).
Cadena, D. L. & Dahmus, M. E. J. biol. Chem. 262, 12468–12474 (1987).
Bartholomew, B., Dahmus, M. E. & Meares, C. F. J. biol. Chem. 261, 14226–14231 (1986).
Chesnut, J. D., Stephens, J. H. & Dahmus, M. E. J. biol. Chem. 267, 10500–10506 (1992).
Lu, H., Flores, O., Weinmann, R. & Reinberg, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 10004–10008 (1991).
Arias, J. A., Peterson, S. R. & Dynan, W. S. J. biol. Chem. 266, 8055–8061 (1991).
Feaver, W. J., Gileadi, O., Li, Y. & Kornberg, R. D. Cell 67, 1223–1230 (1991).
Feaver, W. J., Gileadi, O. & Kornberg, R. D. J. biol. Chem. 266, 19000–19005 (1991).
Gileadi, O., Feaver, W. J. & Kornberg, R. D. Science 257, 1389–1392 (1992).
Serizawa, H., Conaway, R. C. & Conaway, J. W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 7476–7480 (1992).
Conaway, R. C. & Conaway, J. W. Proc. natn. Acad Sci. U.S.A. 86, 7356–7360 (1989).
Gerard, M. et al. J. biol. Chem. 266, 20940–20945 (1991).
Fischer, L. et al. Science 257, 1392–1395 (1992).
Lu, H., Zawel, L., Fischer, L., Egly, J. M. & Reinberg, D. Nature 358, 641–645 (1992).
Conaway, R. C., Garrett, K. P., Hanley, J. P. & Conaway, J. W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 88, 6205–6209 (1991).
Conaway, R. C., Bradsher, J. N. & Conaway, J. W. J. biol. Chem. 267, 8464–8467 (1992).
Conaway, J. W. & Conaway, R. C. J. biol. Chem. 266, 17721–17724 (1991).
Hidaka, H., Masaki, I., Kawamoto, S. & Sasaki, Y. Biochemistry 23, 5036–5041 (1984).
Conaway, R. C. & Conaway, J. W. J. biol. Chem. 265, 7559–7563 (1990).
Thompson, N. E., Steinberg, T. H., Aronson, D. B. & Burgess, R. R. J. biol. Chem. 264, 11511–11520 (1989).
Thompson, N. E., Aronson, D. B. & Burgess, R. R. J. biol. Chem. 265, 7069–7077 (1990).
Conaway, J. W., Bradsher, J. N. & Conaway, R. C. J. biol. Chem. 267, 10142–10148 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serizawa, H., Conaway, J. & Conaway, R. Phosphorylation of C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II is not required in basal transcription. Nature 363, 371–374 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/363371a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/363371a0
This article is cited by
-
Selective inhibition of CDK9 in triple negative breast cancer
Oncogene (2024)
-
CTD-dependent and -independent mechanisms govern co-transcriptional capping of Pol II transcripts
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Structures of transcription pre-initiation complex with TFIIH and Mediator
Nature (2017)
-
TFIIH: when transcription met DNA repair
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2012)
-
Wogonin and related natural flavones are inhibitors of CDK9 that induce apoptosis in cancer cells by transcriptional suppression of Mcl-1
Cell Death & Disease (2011)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.