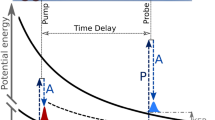
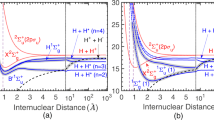
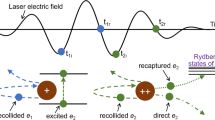
Abstract
Electronic correlations govern the dynamics of many phenomena in nature, such as chemical reactions and solid state effects, including superconductivity. Such correlation effects can be most clearly investigated in processes involving single atoms. In particular, the emission of two electrons from an atom—induced by the impact of a single photon1, a charged particle2 or by a short laser pulse3—has become the standard process for studies of dynamical electron correlations. Atoms and molecules exposed to laser fields that are comparable in intensity to the nuclear fields have extremely high probabilities for double ionization4,5; this has been attributed to electron–electron interaction3. Here we report a strong correlation between the magnitude and the direction of the momentum of two electrons that are emitted from an argon atom, driven by a femtosecond laser pulse (at 38 TW cm-2). Increasing the laser intensity causes the momentum correlation between the electrons to be lost, implying that a transition in the laser–atom coupling mechanism takes place.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Briggs, J. S. & Schmidt, V. Differential cross sections for photo-double-ionization of the helium atom. J. Phys. B 33, R1–R48 (2000).
Moshammer, R. et al. Double ionization of helium and neon for fast heavy-ion impact: Correlated motion of electrons from bound to continuum states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 1242–1245 (1996).
Lambropoulos, P., Maragakis, P. & Zhang, J. Two-electron atoms in strong fields. Phys. Rep. 305, 203–293 ( 1998).
Fittinghoff, D. N., Bolton, P. R., Chang, B. & Kulander, K. C. Observation of nonsequential double ionization of helium with optical tunneling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 2642–2645 (1992).
Walker, B. et al. Precision measurement of strong field double ionization of helium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 1227– 1231 (1994).
Corkum, P. B. Plasma perspective on strong field multiphoton ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 1994–1997 (1993).
Kulander, K. C., Cooper, J. & Schafer, K. J. Laser-assisted inelastic rescattering during above threshold ionization. Phys. Rev. A 51, 561 –568 (1995).
Liu, W. C., Eberly, J. H., Haan, S. L. & Grobe, R. Correlation effects in two-electron model atoms in intense laser fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 520–523 (1999).
Watson, J. B., Sanpera, A., Lappas, D. G., Knight, P. L. & Burnett, K. Nonsequential double ionization of helium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1884– 1887 (1997).
Lappas, D. G. & van Leeuwen, R. Electron correlation effects in the double ionization of He. J. Phys. B 31, L249– 256 (1998).
LaGattuta, K. J. & Cohen, J. S. Quasiclassical modelling of helium double photoionisation. J. Phys. B 31, 5281–5291 (1998).
Becker, A. & Faisal, F. H. M. Mechanism of laser-induced double ionization of helium. J. Phys. B 29, L197–202 (1996).
Becker, A. & Faisal, F. H. M. S-matrix analysis of ionization yields of noble gas atoms at the focus of Ti:sapphire laser pulses. J. Phys. B 32, L335–L343 (1999).
Schafer, K. J., Yang, B., DiMauro, L. F. & Kulander, K. C. Above threshold ionization beyond the high harmonic cutoff. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1599–1602 (1993).
Fittinghoff, D. N., Bolton, P. R., Chang, B. & Kulander, K. C. Polarization dependence of tunneling ionization of helium and neon by 120-fs pulses at 614 nm. Phys. Rev. A 49, 2174– 2177 (1994).
Sheehy, B., Lafon, R., Widmer, M., Walker, B. & DiMauro, L. F. Single- and multiple-electron dynamics in the strong-field tunneling limit. Phys. Rev. A 58, 3942– 3952 (1998).
Becker, A. & Faisal, F. H. M. Interplay of electron correlation and intense field dynamics in the double ionization of helium. Phys. Rev. A 59, R1742–R1745 (1999).
Weber, T. et al. Recoil-ion momentum distributions for single and double ionization of helium in strong laser fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 443–446 (2000).
Weber, T. et al. Sequential and nonsequential contributions to double ionization in strong laser fields. J. Phys. B 33, L128– L133 (2000).
Moshammer, R. et al. Momentum distributions of Ne ions created by an intense ultrashort laser pulse. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 447– 450 (2000).
Dörner, R. et al. Cold target recoil ion momentum spectroscopy. Phys. Rep. 330, 95–192 ( 2000).
Ullrich, J. et al. Cold target recoil ion momentum spectroscopy. J. Phys. B 30, 2917–2974 (1997).
Dörner, R. et al. Photo double ionization of He: Fully differential and absolute electronic and ionic momentum distributions. Phys. Rev. A 57, 1074–1090 (1998).
DiMauro, L. F. & Agostini, P. in Advances in Atomic and Molecular Physics 79–120 (Academic, New York, 1995).
Larochelle, S., Talebpour, A. & Chin, S. L. Non-sequential multiple ionization of rare gas atoms in a Ti:Sapphire laser field. J. Phys. B 31, 1201–1214 (1998).
Becker, A. & Faisal, F. H. M. Interpretation of momentum distribution of recoil ions from laser induced non-sequential double ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 3546– 3549 (2000).
Dörner, R. et al. Fully differential cross sections for double photoionization of He near threshold measured by recoil ion momentum spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 1024–1027 (1996).
Taylor, K. T., Parker, J. S., Dundas, D., Smyth, E. & Vitirito, S. Laser driven helium in full-dimensionality. Laser Phys. 9, 98–116 (1999).
Lein, M., Gross, E. K. U. & Engel, V. On the mechanism of strong-field double photoionisation in the helium atom. J. Phys. B 33, 433– 442 (2000).
Dörr, M. Double ionization in a one-cycle laser pulse. Optics Express 6, 111–116 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank H. Schmidt-Böcking for enthusiastic support, and R. Moshammer and J. Ullrich for helpful discussons. Our analysis of the influence of the laser field on the final state momenta emerged after fruitful discussion with A. Becker and F. H. M. Faisal. We are grateful to W. W. Rühle for continuous support and thank Roentdek GmbH for providing the position sensitive detectors. This work is supported by DFG, BMBF, GSI and DAAD. R.D. is supported by the Heisenberg Programme of the DFG. The Marburg group thanks the Land Hessen and the DFG for support through the SFB383 and their Graduiertenkolleg ‘Optoelektronik mesoskopischer Halbleiter’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weber, T., Giessen, H., Weckenbrock, M. et al. Correlated electron emission in multiphoton double ionization. Nature 405, 658–661 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35015033
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35015033
This article is cited by
-
Multiphoton electron emission with non-classical light
Nature Physics (2024)
-
Shepherd electron effects in multiple ionization of rubidium by circularly polarized intense laser fields
Communications Physics (2023)
-
Simulation of laser-induced tunnel ionization based on a curved waveguide
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Few-electron correlations after ultrafast photoemission from nanometric needle tips
Nature Physics (2023)
-
Entanglement of orbital angular momentum in non-sequential double ionization
Nature Communications (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.