Abstract
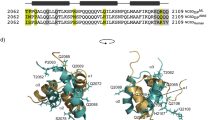
STEROID hormone receptors control gene expression through binding, as dimers, to short palindromic response elements located upstream of the genes they regulate1–3. An independent domain of ∼70 amino acids directs this sequence-specific DNA binding and is highly conserved between different receptor proteins and related transcription factors4–6. This domain contains two zinc-binding Cys2–Cys2 sequence motifs, which loosely resemble the 'zinc-finger' motifs of TFIIIA7–10. Here we describe the structure of the DNA-binding domain from the oestrogen receptor, as determined by two-dimensional 1H NMR techniques. The two 'zinc-finger'-like motifs fold to form a single structural domain and are thus distinct from the independently folded units of the TFIIIA-type zinc fingers11–13. The structure consists of two helices perpendicular to each other. A zinc ion, coordinated by four conserved cysteines, holds the base of a loop at the N terminus of each helix. This novel structural domain seems to be a general structure for protein-DNA recognition.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamamoto, K. R. A. Rev. Genet. 19, 209–252 (1985).
Green, S. & Chambon, P. Trends Genet. 4, 309–314 (1988).
Evans, R. M. Science 240, 889–895 (1988).
Green, S. & Chambon, P. Nature 325, 75–78 (1987).
Kumar, V. et al. Cell 51, 941–951 (1987).
Kumar, V. & Chambon, P. Cell 55, 145–156 (1988).
Klug, A. & Rhodes, D. Trends biochem. Sci. 12, 464–469 (1987).
Evans, R. M. & Hollenberg, S. M. Cell 52, 1–3 (1988).
Freedman, L. P. et al. Nature 334, 543–546 (1988).
Berg, J. M. Cell 57, 1065–1068 (1989).
Lee, M. S. et al. Science 245, 635–637 (1989).
Klevit, R. E., Herriott, J. R. & Horvath, S. J. Proteins 7, 215–226 (1990).
Neuhaus, D., Nakeseko, Y., Nagai, K. & Klug, A. FEBS lett. 262, 179–184 (1990).
Picard, D. & Yamamoto, K. R. EMBO J. 6, 3333–3340 (1987).
Studier, F. W. & Moffatt, B. A. J. molec. Biol. 189, 113–130 (1986).
Wüthrich, K. NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids (Wiley, New York, 1986).
Clore, G. M. & Gronenborn, A. M. Crit. Rev. biochem. molec. Biol. 24, 479–564 (1989).
Severne, Y., Wieland, S., Schaffner, W. & Rusconi, S. EMBO J. 7, 2503–2508 (1988).
Hollenberg, S. M. & Evans, R. M. Cell 55, 899–906 (1988).
Nilges, M. in Brünger, A. T. in X-PLOR Version 2.1. User Manual (Yale University Press, 1990).
Brünger, A. T. X-PLOR Manual (Yale University Press, 1988).
Mader, S., Kumar, V., de Verneuil, H. & Chambon, P. Nature 338, 271–274 (1989).
Umesono, K. & Evans, R. M. Cell 57, 1139–1146 (1989).
Danielsen, M., Hinck, L. & Ringold, G. M. Cell 57, 1131–1138 (1989).
Härd, T. et al. Science 249, 157–160 (1990).
Shaka, A. J., Lee, C. J. & Pines, A. J. magn. Reson. 77, 274–293 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwabe, J., Neuhaus, D. & Rhodes, D. Solution structure of the DMA-binding domain of the oestrogen receptor. Nature 348, 458–461 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/348458a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/348458a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.