Abstract
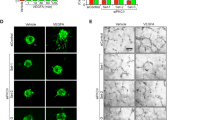
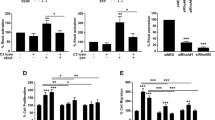
Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and its receptor (IGF-IR) are essential for normal ocular development and are expressed in numerous ocular cell types including lens epithelial cells, retinal pigment epithelial cells, Müller cells and endothelial cells. Endothelial cell proliferation is a common feature of proliferative retinopathies and involves abnormal growth of blood vessels within and on the surface of the retina. In an effort to inhibit the formation of these aberrant blood vessels, we cloned an IGF-IR ribozyme into an expression vector that limits expression of the ribozyme to proliferating endothelial cells. An endothelin enhancer and Cdc6 promoter chimera drives expression of the IGF-IR ribozyme. This promoter limited retinal expression of the reporter gene to proliferating endothelial cells in two mouse models of proliferative retinopathy. In addition, expression of the IGF-IR ribozyme by this promoter inhibited aberrant retinal angiogenesis in both models while preserving normal vessels. These results demonstrate the feasibility of IGF-IR ribozyme expression in a selective manner for safer treatment of abnormal angiogenesis associated with retinopathy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walker JL, Zhang L, Zhou J, Woolkalis MJ, Menko AS . Role for alpha 6 integrin during lens development: evidence for signaling through IGF-1R and ERK. Dev Dyn 2002; 223: 273–284.
Rosenthal R, Wohlleben H, Malek G, Schlichting L, Thieme H, Bowes Rickman C et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 contributes to neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004; 323: 1203–1208.
Zygar CA, Colbert S, Yang D, Fernald RD . IGF-1 produced by cone photoreceptors regulates rod progenitor proliferation in the teleost retina. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 2005; 154: 91–100.
Li F, Cao W, Steinberg RH, LaVail MM . Basic FGF-induced down-regulation of IGF-I mRNA in cultured rat Muller cells. Exp Eye Res 1999; 68: 19–27.
Smith LE, Shen W, Perruzzi C, Soker S, Kinose F, Xu X et al. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent retinal neovascularization by insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Nat Med 1999; 5: 1390–1395.
Hellstrom A, Carlsson B, Niklasson A, Segnestam K, Boguszewski M, de Lacerda L et al. IGF-I is critical for normal vascularization of the human retina. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 3413–3416.
Merimee TJ, Zapf J, Froesch ER . Insulin-like growth factors: studies in diabetics with and without retinopathy. N Engl J Med 1983; 309: 527–530.
Grant MB, Russell B, Fitzgerald C, Merimee TJ . Insulin-like growth factors in vitreous: studies in control and diabetic subjects with neovascularization. Diabetes 1986; 35: 416–420.
Dills DG, Moss SE, Klein R, Klein BE . Association of elevated IGF-I levels with increased retinopathy in late-onset diabetes. Diabetes 1991; 40: 1725–1730.
Hyer SL, Sharp PS, Brooks RA, Burrin JM, Kohner EM . A two-year follow-up study of serum insulinlike growth factor-I in diabetics with retinopathy. Metabolism 1989; 38: 586–589.
Chantelau E, Eggert H, Seppel T, Schonau E, Althaus C . Elevation of serum IGF-1 precedes proliferative diabetic retinopathy in Mauriac's syndrome. Br J Ophthalmol 1997; 81: 169–170.
Grant MB, Ellis EA, Caballero S . The role of insulin-like growth factor-I in proliferative diabetic retinopathy: a modulator of free radical derived oxidant generation. In: Shigeta Y, King GL (eds). Recent Advances in Endothelial Cell Dysfunction in Diabetes. Churchill Livingstone: Osaka, Japan, 1994, pp 265–280.
Meyer-Schwickerath R, Pfeiffer A, Blum WF, Freyberger H, Klein M, Losche C et al. Vitreous levels of the insulin-like growth factors I and II, and the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 2 and 3, increase in neovascular eye disease. Studies in nondiabetic and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest 1993; 92: 2620–2625.
Grant MB, Mames RN, Fitzgerald C, Ellis EA, Caballero S, Chegini N et al. Insulin-like growth factor I as an angiogenic agent. In vivo and in vitro studies. Ann NY Acad Sci 1993; 692: 230–242.
Shaw LC, Afzal A, Lewin AS, Timmers AM, Spoerri PE, Grant MB . Decreased expression of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor by ribozyme cleavage. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003; 44: 4105–4113.
Hellstrom A, Engstrom E, Hard AL, Albertsson-Wikland K, Carlsson B, Niklasson A et al. Postnatal serum insulin-like growth factor I deficiency is associated with retinopathy of prematurity and other complications of premature birth. Pediatrics 2003; 112: 1016–1020.
Szymanski P, Anwer K, Sullivan S . Prolliferating endothelium specific gene expression. J Gene Med 2006 (in press).
Anwer K, Kao G, Proctor B, Rolland A, Sullivan S . Optimization of cationic lipid/DNA complexes for systemic gene transfer to tumor lesions. J Drug Target 2000; 8: 125–135.
Anwer K, Meaney C, Kao G, Hussain N, Shelvin R, Earls RM et al. Cationic lipid-based delivery system for systemic cancer gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 2000; 7: 1156–1164.
Rhee J, Hoff PM . Angiogenesis inhibitors in the treatment of cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2005; 6: 1701–1711.
Wakelee HA, Schiller JH . Targeting angiogenesis with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor small-molecule inhibitors: novel agents with potential in lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 2005; 7 (Suppl 1): S31–S38.
Adamis AP, Miller JW, Bernal MT, DJ DA, Folkman J, Yeo TK et al. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the vitreous of eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 1994; 118: 445–450.
Simo R, Lecube A, Segura RM, Garcia Arumi J, Hernandez C . Free insulin growth factor-I and vascular endothelial growth factor in the vitreous fluid of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 2002; 134: 376–382.
Freyberger H, Brocker M, Yakut H, Hammer J, Effert R, Schifferdecker E et al. Increased levels of platelet-derived growth factor in vitreous fluid of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2000; 108: 106–109.
Tombran-Tink J, Chader GG, Johnson LV . PEDF: a pigment epithelium-derived factor with potent neuronal differentiative activity. Exp Eye Res 1991; 53: 411–414.
Kommonen B, Dawson WW, Parmer R . Pigment epithelial function in canine retina. Am J Vet Res 1991; 52: 1341–1344.
Mori M, Ghyselinck NB, Chambon P, Mark M . Systematic immunolocalization of retinoid receptors in developing and adult mouse eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2001; 42: 1312–1318.
Mori K, Gehlbach P, Ando A, Dyer G, Lipinsky E, Chaudhry AG et al. Retina-specific expression of PDGF-B versus PDGF-A: vascular versus nonvascular proliferative retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2002; 43: 2001–2006.
Gehlbach P, Demetriades AM, Yamamoto S, Deering T, Duh EJ, Yang HS et al. Periocular injection of an adenoviral vector encoding pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits choroidal neovascularization. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 637–646.
Rasmussen H, Chu KW, Campochiaro P, Gehlbach PL, Haller JA, Handa JT et al. Clinical protocol. An open-label, phase I, single administration, dose-escalation study of ADGVPEDF.11D (ADPEDF) in neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Hum Gene Ther 2001; 12: 2029–2032.
Krzystolik MG, Afshari MA, Adamis AP, Gaudreault J, Gragoudas ES, Michaud NA et al. Prevention of experimental choroidal neovascularization with intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody fragment. Arch Ophthalmol 2002; 120: 338–346.
Hofmann F, Garcia-Echeverria C . Blocking the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor as a strategy for targeting cancer. Drug Discov Today 2005; 10: 1041–1047.
Wang Y, Sun Y . Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 as an anti-cancer target: blocking transformation and inducing apoptosis. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2002; 2: 191–207.
Baserga R . The contradictions of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Oncogene 2000; 19: 5574–5581.
Baserga R . The IGF-I receptor in cancer research. Exp Cell Res 1999; 253: 1–6.
Arteaga CL, Osborne CK . Growth inhibition of human breast cancer cells in vitro with an antibody against the type I somatomedin receptor. Cancer Res 1989; 49: 6237–6241.
Khalili K, Del Valle L, Wang JY, Darbinian N, Lassak A, Safak M et al. T-antigen of human polyomavirus JC cooperates with IGF-IR signaling system in cerebellar tumors of the childhood-medulloblastomas. Anticancer Res 2003; 23: 2035–2041.
Min Y, Adachi Y, Yamamoto H, Ito H, Itoh F, Lee CT et al. Genetic blockade of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor: a promising strategy for human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 6432–6441.
Furstenberger G, Morant R, Bolliger B, Senn HJ . Serum levels of IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 during adjuvant chemotherapy for primary breast cancer. Breast 2003; 12 (Suppl 1): S31.
Maloney EK, McLaughlin JL, Dagdigian NE, Garrett LM, Connors KM, Zhou XM et al. An anti-insulin-like growth factor I receptor antibody that is a potent inhibitor of cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 5073–5083.
Wu JD, Odman A, Higgins LM, Haugk K, Vessella R, Ludwig DL et al. In vivo effects of the human type I insulin-like growth factor receptor antibody A12 on androgen-dependent and androgen-independent xenograft human prostate tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 3065–3074.
Cohen BD, Baker DA, Soderstrom C, Tkalcevic G, Rossi AM, Miller PE et al. Combination therapy enhances the inhibition of tumor growth with the fully human anti-type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 2063–2073.
Wang Y, Malkowski M, Hailey J, Turek-Etienne T, Tripodi T, Pachter JA . Screening for small molecule inhibitors of insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) kinase: comparison of homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence and 33P-ATP plate assay formats. J Exp Ther Oncol 2004; 4: 111–119.
Ludwig DL, Witte L, Hicklin DJ, Prewett M, Bassi R, Burtrum D et al. Conservation of receptor antagonist anti-tumor activity by epidermal growth factor receptor antibody expressed in transgenic corn seed. Hum Antibodies 2004; 13: 81–90.
Li W, Favelyukis S, Yang J, Zeng Y, Yu J, Gangjee A et al. Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor I receptor autophosphorylation by novel 6-5 ring-fused compounds. Biochem Pharmacol 2004; 68: 145–154.
Warshamana-Greene GS, Litz J, Buchdunger E, Hofmann F, Garcia-Echeverria C, Krystal GW . The insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor kinase inhibitor NVP-ADW742, in combination with STI571, delineates a spectrum of dependence of small cell lung cancer on IGF-I and stem cell factor signaling. Mol Cancer Ther 2004; 3: 527–535.
Byron SA, Yee D . Potential therapeutic strategies to interrupt insulin-like growth factor signaling in breast cancer. Semin Oncol 2003; 30: 125–132.
Vasilcanu D, Girnita A, Girnita L, Vasilcanu R, Axelson M, Larsson O . The cyclolignan PPP induces activation loop-specific inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Link to the phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase/Akt apoptotic pathway. Oncogene 2004; 23: 7854–7862.
Ye JJ, Liang SJ, Guo N, Li SL, Wu AM, Giannini S et al. Combined effects of tamoxifen and a chimeric humanized single chain antibody against the type I IGF receptor on breast tumor growth in vivo. Horm Metab Res 2003; 35: 836–842.
Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE . Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 505–518.
Zhang H, Yee D . The therapeutic potential of agents targeting the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2004; 13: 1569–1577.
Smith LE, Kopchick JJ, Chen W, Knapp J, Kinose F, Daley D et al. Essential role of growth hormone in ischemia-induced retinal neovascularization. Science 1997; 276: 1706–1709.
Grant MG, Guay C . Plasminogen activator production by human retinal endothelial cells of nondiabetic and diabetic origin. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1991; 32: 53–64.
Ohki EC, Tilkins ML, Ciccarone VC, Price PJ . Improving the transfection efficiency of post-mitotic neurons. J Neurosci Methods 2001; 112: 95–99.
Smith LE, Wesolowski E, McLellan A, Kostyk SK, D'Amato R, Sullivan R et al. Oxygen-induced retinopathy in the mouse. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1994; 35: 101–111.
Grant MB, May WS, Caballero S, Brown GA, Guthrie SM, Mames RN et al. Adult hematopoietic stem cells provide functional hemangioblast activity during retinal neovascularization. Nat Med 2002; 8: 607–612.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Gene Therapy website (http://www.nature.com/gt).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaw, L., Pan, H., Afzal, A. et al. Proliferating endothelial cell-specific expression of IGF-I receptor ribozyme inhibits retinal neovascularization. Gene Ther 13, 752–760 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302718
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302718
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
IGF-1R Regulates the Extracellular Level of Active MMP-2, Pathological Neovascularization, and Functionality in Retinas of OIR Mouse Model
Molecular Neurobiology (2018)
-
Novel endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors and their therapeutic potential
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2015)
-
Construction of a novel expression cassette for increasing transgene expression in vivo in endothelial cells of large blood vessels
Gene Therapy (2011)
-
In Vivo Anti-Tumor Effect of Expressing p14ARF-TAT Using a FGF2-Targeted Cationic Lipid Vector
Pharmaceutical Research (2011)
-
Prediction of cis-regulatory elements controlling genes differentially expressed by retinal and choroidal vascular endothelial cells
Journal of Ocular Biology, Diseases, and Informatics (2008)