Abstract
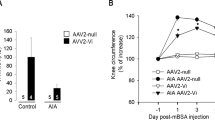
Plasmin is essential for metalloproteases activation, endothelial cell migration and degradation of the extracellular matrix. The process is common to neoangiogenesis pannus formation and cartilage degradation within arthritic joints. Since 80% of synovial cells express urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR), we investigated the inhibition of plasmin activation in a collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice model, by expressing a uPA/uPAR antagonist molecule (ATF) fused to human serum albumin (HSA) to extend its serum half-life. Overexpression was obtained with an adenoviral vector expressing the chimeric murine ATF-HSA. We showed that the genetic coupling did not significantly reduce the ability of the ATF moiety to interact with its receptor uPAR. The chimeric protein was detectable in the sera of injected mice 7 days following Ad-mATF-HSA injection, then decreased in parallel with the anti-HSA titer increase. Systemic Ad-mATF-HSA injection performed on day 25 following CIA induction decreased the incidence of arthritis and the severity of the disease. Moreover, synovial angiogenesis in arthritic paws was decreased after Ad-mATF-HSA gene transfer, as assessed by smooth muscle actin immunostaining. The preventive effect observed on arthritis was related to the decrease in angiogenesis, rather than inhibition of extracellular matrix degradation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koch A.E. . Review: angiogenesis: implications for rheumatoid arthritis Arthritis Rheum 1998 41: 951 951
Firestein G.S. . Starving the synovium: angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis J Clin Invest 1999 103: 3 3
Zhang Y. et al. Cell cycle inhibition by the anti-angiogenic agent TNP-470 is mediated by p53 and p21WAF1/CIP1 Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000 97: 6427 6427
Nagashima M. et al. Effects of combinations of anti-rheumatic drugs on the production of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in cultured synoviocytes and patients with rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 39: 1255 1255
Nagashima M., Asano G., Yoshino S. . Imbalance in production between vascular endothelial growth factor and endostatin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis J Rheumatol 2000 27: 2339 2339
Storgard C.M. et al. Decreased angiogenesis and arthritic disease in rabbits treated with an alphavbeta3 antagonist J Clin Invest 1999 103: 47 47
Peacock D.J., Banquerigo M.L., Brahn E. . Angiogenesis inhibition suppresses collagen arthritis J Exp Med 1992 175: 1135 1135
Oliver S.J. et al. Suppression of collagen-induced arthritis by an angiogenesis inhibitor, AGM-1470, in combination with cyclosporin: reduction of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) Cell Immunol 1995 166: 196 196
Lu J. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and regulation of murine collagen-induced arthritis J Immunol 2000 164: 5922 5922
Szekanecz Z., Haines G.K., Koch A.E. . Differential expression of the urokinase receptor (CD87) in arthritic and normal synovial tissues J Clin Pathol 1997 50: 314 314
Pollanen J., Stephens R.W., Vaheri A. . Directed plasminogen activation at the surface of normal and malignant cells Adv Cancer Res 1991 57: 273 273
Pepper M.S. et al. Upregulation of urokinase receptor expression on migrating endothelial cells J Cell Biol 1993 122: 673 673
Busso N. . Plasminogen activation in synovial tissues: differences between normal, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis joints Ann Rheum Dis 1997 56: 550 550
Kobayashi H. et al. Inhibitory effect of a conjugate between human urokinase and urinary trypsin inhibitor on tumor cell invasion in vitro J Biol Chem 1995 270: 8361 8361
Li H. et al. Adenovirus-mediated delivery of a uPA/uPAR antagonist suppresses angiogenesis-dependent tumor growth and dissemination in mice Gene Therapy 1998 5: 1105 1105
Li H. et al. Systemic delivery of antiangiogenic adenovirus AdmATF induces liver resistance to metastasis and prolongs survival of mice Hum Gene Ther 1999 10: 3045 3045
Min H.Y. et al. Urokinase receptor antagonists inhibit angiogenesis and primary tumor growth in syngeneic mice Cancer Res 1996 56: 2428 2428
Walsh D.A. . Angiogenesis and arthritis Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999 38: 103 103
Ronday H.K. et al. Tranexamic acid, an inhibitor of plasminogen activation, reduces urinary collagen cross-link excretion in both experimental and rheumatoid arthritis Br J Rheumatol 1998 37: 34 34
Van der Land W.H. et al. Cartilage degradation and invasion by rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts is inhibited by gene transfer of a cell surface-targeted plasmin inhibitor Arthritis Rheum 2000 43: 1710 1710
Stehle G. et al. Albumin-based drug carriers: comparison between serum albumins of different species on pharmacokinetics and tumor uptake of the conjugate Anticancer Drugs 1999 10: 785 785
Carter D.C., Ho J.X. . Structure of serum albumin Adv Protein Chem 1994 45: 153 153
Yeh P. et al. Design of yeast-secreted albumin derivatives for human therapy: biological and antiviral properties of a serum albumin-CD4 genetic conjugate Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992 89: 1904 1904
Worgall S. et al. Innate immune mechanisms dominate elimination of adenoviral vectors following in vivo administration Hum Gene Ther 1997 8: 37 37
Crouzet J. et al. Recombinational construction in Escherichia coli of infectious adenoviral genomes Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 1414 1414
Joosten L.A. et al. IL-1 alpha beta blockade prevents cartilage and bone destruction in murine type II collagen-induced arthritis, whereas TNF-alpha blockade only ameliorates joint inflammation J Immunol 1999 163: 5049 5049
Apparailly F. et al. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of viral IL-10 gene inhibits murine collagen-induced arthritis J Immunol 1998 160: 5213 5213
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Michèle Radal from the CRLC Val d'Aurelle in Montpellier for the preparation of histology sections, and the breast radiography group from Lapeyronie Hospital in Montpellier who performed the X-rays. We also acknowledge Elisabeth Connault from UMR1582/CNRS-IGR for performing immunohistogical technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Apparailly, F., Bouquet, C., Millet, V. et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of urokinase plasminogen inhibitor inhibits angiogenesis in experimental arthritis. Gene Ther 9, 192–200 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301628
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301628
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Molecular imaging of the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor: opportunities beyond cancer
EJNMMI Research (2020)
-
Apoptotic cell infusion treats ongoing collagen-induced arthritis, even in the presence of methotrexate, and is synergic with anti-TNF therapy
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2016)
-
A gene transfer comparative study of HSA-conjugated antiangiogenic factors in a transgenic mouse model of metastatic ocular cancer
Cancer Gene Therapy (2007)
-
Technology Insight: gene transfer and the design of novel treatments for rheumatoid arthritis
Nature Clinical Practice Rheumatology (2006)
-
Gene therapy works in animal models of rheumatoid arthritis so what!
Current Rheumatology Reports (2006)