Abstract
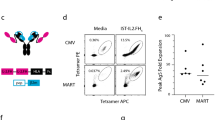
The clinical benefit of adoptive transfer of MHC-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes(CTL) for the treatment of cancer is hampered by the low success rate to generate antitumor CTLs. To bypass the need for tumor-specific CTL, we developed a strategy that allows for grafting of human T lymphocytes with MHC-restricted antigen specificity using in vitro selected human Fab fragments fused to the Fc(ɛ)RI-γ signaling molecule. Retroviral introduction of a Fab-based chimeric receptor specific for MAGE-A1/HLA-A1 into primary human T lymphocytes resulted in binding of relevant peptide/MHC complexes. Transduced T lymphocytes responded to native MAGE-A1/HLA-A1POS target cells by specific cytokine production and cytolysis. Therefore, peptide/MHC-specific Fab fragments represent new alternatives to TCR to confer human T lymphocytes with tumor specificity, which provides a promising rationale for developing immunogene therapies. Gene Therapy (2001) 8, 000-000.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meuer SC . Identification of the receptor for antigen and major histocompatibility complex on human inducer T lymphocytes Science 1983 4629: 1239–1242
Borst JA . T-cell receptor gamma/CD3 complex found on cloned functional lymphocytes Nature 1987 6106: 683–688
Davis MM, Bjorkman PJ . T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition Nature 1988 334: 395–402
Klausner RD, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Bonifacio JS . The T cell antigen receptor: insight into organelle biology Ann Rev Cell Biol 1990 6: 403–431
Riddell SR . Restoration of viral immunity in immunodeficient humans by adoptive transfer of T cell clones Science 1992 257: 238–241
Rosenberg SA . Treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma with autologous tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and interleukin 2 J Natl Cancer Inst 1994 86: 1159–1166
Van der Bruggen P . A gene encoding an antigen recognized by cytolytic T lymphocytes on a human melanoma Science 1991 254: 1643–1647
Boon T, van der Bruggen P . Human tumor antigens recognized by T lymphocytes J Exp Med 1996 183: 725–729
Heemels MT, Ploegh H . Generation, translocation, and presentation of MHC class I-restricted peptides Annu Rev Biochem 1995 64: 463–491
Madden DR, Gorga JC, Strominger JL, Wiley DC . The structure of HLA-B27 reveals nonamer self-peptides bound in an extended conformation Nature 1995 353: 321–325
Rammensee HG, Falk K, Rotzschke O . Peptides naturally presented by MHC class I molecules Annu Rev Immunol 1993 11: 213–244
Garboczi DN . Structure of the complex between human T-cell receptor, viral peptide and HLA-A2 Nature 1996 384: 134–141
Rosenberg SA . Cancer vaccines based on the identification of genes encoding cancer regression antigens Immunol Today 1997 4: 75–182
Rosenberg SA . Immunologic and therapeutic evaluation of a synthetic peptide vaccine for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma Nat Med 1998 4: 321–327
Nestle FO . Vaccination of melanoma patients with peptide- or tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cells Nat Med 1998 4: 328–332
Yee C . Isolation of high avidity melanoma-reactive CTL from heterogeneous populations using peptide-MHC tetramers J Immunol 1999 162: 2227–2234
Zaks TZ, Rosenberg ST . Immunization with a peptide epitope from HER-2/neu leads to peptide-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes that fail to recognize HER-2/neu+ tumors Cancer Res 1998 58: 4902–4908
Rivoltini L . Induction of tumor-reactive CTL from peripheral blood and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes of melanoma patients by in vitro stimulation with an immunodominant peptide of the human melanoma antigen MART-1 J Immunol 1995 54: 2257–2265
Bolhuis RLH, Gratama JW . Genetic re-targeting of T lymphocyte specificity Gene Therapy 1998 5: 1153–1155
Bolhuis RLH, Willemsen RA, Gratama JW . Clinical applications of redirected cytotoxicity Cytotoxic Cells: Basic Mechanisms and Medical Applications Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2000 423–440
Hwu P . Lysis of ovarian cancer cells by human lymphocytes redirected with a chimeric gene composed of an antibody variable region and the Fc receptor gamma chain J Exp Med 1993 178: 361–366
Weijtens MEM . Single chain Ig/γ gene-redirected human T lymphocytes produce cytokines, specifically lyse tumor cells, and recycle lytic capacity J Immunol 1996 157: 836–843
Weijtens MEM, Willemsen RA, Hart EH, Bolhuis RLH . A retroviral vector system ‘STITCH’ in combination with an optimized single chain antibody chimeric receptor gene structure allows efficient gene transduction and expression in human T lymphocytes Gene Therapy 1998 9: 1195–1203
Roberts MR . Targeting of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells by CD8+ T lymphocytes armed with universal T-cell receptors Blood 1994 9: 2878–2889
Weijtens MEM, Willemsen RA, Van Krimpen BA, Bolhuis RLH . Chimeric scFv/γreceptor-mediated T cell lysis of tumor cells is co-regulated by adhesion and accessory molecules Int J Cancer 1998 77: 181–187
Willemsen RA . Grafting primary human T lymphocytes with cancer specific chimeric single chain and two chain TCR Gene Therapy 2000 7: 1369–1377
Kieke MC . Selection of functional T cell receptor mutants from a yeast surface-display library Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999 96: 5651–5656
Holler PD . In vitro evolution of a T cell receptor with high affinity for peptide/MHC Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000 10: 5387–5392
Weidanz JA . Display of functional alpha beta single-chain T cell receptor molecules on the surface of bacteriophage J Immunol Meth 1998 221: 59–76
Wulfing C, Pluckthun A . Correctly folded T-cell receptor fragments in the periplasm of Escherischia coli. Influence of folding catalysis J Mol Biol 1994 5: 655–669
O'Herrin SM . Analysis of the expression of peptide-major histocompatibility complexes using high affinity soluble divalent T cell receptors J Exp Med 1997 8: 1333–1345
Day PM . Direct delivery of exogenous MHC class I molecule-binding oligopeptides to the endoplasmic reticulum of viable cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 15: 8064–8069
Zhong G, Reis E, Sousa C, Germain RN . Production, specificity, and functionality of monoclonal antibodies to specific peptide-major histocompatibility complex class II complexes formed by processing of exogenous protein Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 13856–13861
Reiter Y . Peptide-specific killing of antigen-presenting cells by a recombinant antibody-toxin fusion protein targeted to major histocompatibility complex/peptide class I complexes with T cell receptor-like specificity Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 9: 4631–4636
Tamminen WL, Wraith D, Barber BH . Searching for MHC-restricted anti-viral antibodies: antibodies recognizing the nucleoprotein of influenza virus dominate the serological response of C57BL/6 mice to syngeneic influenza-infected cells Eur J Immunol 1987 7: 999–1006
Chames P . Direct selection of a human antibody fragment directed against the tumor T-cell epitope HLA-A1/MAGE-A1 from a non-immunized phage-Fab library Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000 97: 7969–7974
Kolb HJ, Holler E . Adoptive immunotherapy with donor lymphocyte transfusions Curr Opin Oncol 1997 9: 139–145
Garboczi DN, Hung DT, Wiley DC . HLA-A2-peptide complexes: refolding and crystallization of molecules expressed in Escherichia coli and complexed with single antigenic peptides Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992 89: 3429–3433
DuBridge RB . Analysis of mutation in human cells by using an Epstein–Barr virus shuttle system Mol Cell Biol 1987 7: 379–387
Van de Griend RJ . Rapid expansion of human cytotoxic T cell clones: growth promotion by a heat-labile serum component and by various types of feeder cells J Immunol Meth 1984 66: 285–298
Van de Griend RJ, Bolhuis RLH . Rapid expansion of allospecific cytotoxic T cell clones using nonspecific feeder cell lines without further addition of exogenous IL2 Transplantation 1984 38: 401–406
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by EU grant BIO4-CT97-2196 to PC and HRH, EU grant No. QLK3-1999-01262 and a grant from the Dutch Technology Foundation STW (project RGN44.3498) to RLHB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Willemsen, R., Debets, R., Hart, E. et al. A phage display selected Fab fragment with MHC class I-restricted specificity for MAGE-A1 allows for retargeting of primary human T lymphocytes. Gene Ther 8, 1601–1608 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301570
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301570
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Chimeric antigen receptor T cells therapy in solid tumors
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2023)
-
TCR-like CARs and TCR-CARs targeting neoepitopes: an emerging potential
Cancer Gene Therapy (2021)
-
TCR-like antibodies in cancer immunotherapy
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2019)
-
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for solid tumors
Molecular Therapy - Oncolytics (2016)
-
Affinity maturation of T-cell receptor-like antibodies for Wilms tumor 1 peptide greatly enhances therapeutic potential
Leukemia (2015)