Abstract
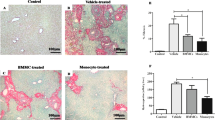
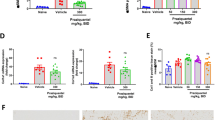
Hepatic fibrosis is a common outcome of chronic liver diseases. In schistosomiasis, chronic parasite egg-induced granuloma formation can lead to fibrosis, which is immunologically characterized by the dominant Th2 response. Recently, it has been shown that gene therapy is an attractive approach for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis. To investigate the antifibrotic effects of IL-18 gene transfer, a normal murine liver cell line BNL.CL2 was transfected with recombinant adenovirus encoding mouse IL-18, and then intrasplenically transplanted into mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum (S. japonicum). Our data show that IL-18 gene-modified hepatocytes intrasplenically transplanted into mice can effectively express IL-18 in the liver and in peripheral blood. Intrasplenic transplantation of IL-18 gene-modified hepatocytes into S. japonicum-infected mice could result in a significantly increased IFN-γ and IL-2 but decreased IL-4 and IL-10 concentration both in the liver and in the serum, suggesting that the dominant Th2 response in mice with schistosomiasis could be reversed by this intervention. Consistent with the changes in Th1 and Th2 cytokine production, mice intrasplenically transplanted with IL-18 gene-modified hepatocytes developed much less hepatic fibrosis at 20 weeks after infection, which was evaluated by liver content of hydroxyproline, collagens, and hepatic mRNA expression of procollagens. These data indicate that intrasplenic transplantation of IL-18 gene-modified hepatocytes can be a candidate for therapeutic intervention in hepatic fibrosis through induction of a dominant Th1 response.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman SL . Molecular mechanisms of hepatic fibrosis and principles of therapy J Gastroenterol 1997 32: 424–430
Rockey DC . Gene therapy for hepatic fibrosis-bringing treatment into the new millennium Hepatology 1999 30: 816–818
Qi Z et al. Blockade of type beta transforming growth factor signaling prevents liver fibrosis and dysfunction in the rat Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999 96: 2345–2349
Ueki T et al. Hepatocyte growth factor gene therapy of liver cirrhosis in rats Nat Med 1999 5: 226–230
McManus DP . The search for a vaccine against schistosomiasis – a difficult path but an achievable goal Immunol Rev 1999 171: 149–161
Wynn TA, Cheever AW . Cytokine regulation of granuloma formation in schistosomiasis Curr Opin Immunol 1995 7: 505–511
Wahl SM et al. Cytokine regulation of schistosome-induced granuloma and fibrosis Kidney Int 1997 51: 1370–1375
Farah IO et al. Repeated exposure induces periportal fibrosis in Schistosoma mansoni-infected baboons: role of TGF-beta and IL-4 J Immunol 2000 164: 5337–5343
Zhang L et al. IFN-gamma gene therapy by intrasplenic hepatocyte transplantation: a novel strategy for reversing hepatic fibrosis in Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice Parasite Immunol 2001 23: 11–17
Ninomiya T et al. Clinical significance of serum hyaluronic acid as a fibrosis marker in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with interferon-alpha: histological evaluation by a modified histological activity index scoring system J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1998 13: 68–74
Mallat A et al. Interferon alfa and gamma inhibit proliferation and collagen synthesis of human Ito cells in culture Hepatology 1995 21: 1003–1010
Lo Iacono O et al. Soluble adhesion molecules correlate with liver inflammation and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C treated with interferon-alpha Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1998 12: 1091–1099
Okamura H et al. Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN-gamma production by T cells Nature 1995 378: 88–91
Stoll S et al. Production of functional IL-18 by different subtypes of murine and human dendritic cells (DC): DC-derived IL-18 enhances IL-12-dependent Th1 development Eur J Immunol 1998 28: 3231–3239
Cao X et al. Augmentation of liver immune functions by intrasplenic transplantation of IL-2 gene-modified hepatocytes Natl Med J China 1996 76: 646–649
Zhang W et al. In vivo distribution and gene expression of genetically modified hepatocytes after intrasplenic transplantation Science China (Series C) 1997 40: 554–560
Okamura H et al. A novel costimulatory factor for gamma interferon induction found in the livers of mice causes endotoxic shock Infect Immun 1995 63: 3966–3972
Kremer L, Dupre L, Wolowczuk I, Locht C . In vivo immunomodulation following intradermal injection with DNA encoding IL-18 J Immunol 1999 163: 3226–3231
Gupta S . Hepatocyte transplantation: new strategies for hepatic reconstitution and gene therapy Indian J Gastroenterol 1994 13: 13–23
Ozawa CR, Springer ML, Blau HM . A novel means of drug delivery: myoblast-mediated gene therapy and regulatable retroviral vectors Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2000 40: 295–317
Fenjves ES, Schwartz PM, Blaese RM, Taichman LB . Keratinocyte gene therapy for adenosine deaminase deficiency: a model approach for inherited metabolic disorders Hum Gene Ther 1997 8: 911–917
Raper SE . Hepatocyte transplantation and gene therapy Clin Transplant 1995 9: 249–254
Chowdhury JR et al. Human hepatocyte transplantation: gene therapy and more? Pediatrics 1998 102: 647–648
Kobayashi N et al. Hepatocyte transplantation in rats with decompensated cirrhosis Hepatology 2000 31: 851–857
Matsusaka S et al. The role of oval cells in rat hepatocyte transplantation Transplantation 2000 70: 441–446
Calise F et al. Intrasplenic hepatocyte transplantation in the pig: new technical aspects Transplant Proc 1997 29: 1999–2001
Arkadopoulos N et al. Intrasplenic transplantation of allogeneic hepatocytes prolongs survival in anhepatic rats Hepatology 1998 28: 1365–1370
Kobayashi N et al. Transplantation of highly differentiated immortalized human hepatocytes to treat acute liver failure Transplantation 2000 69: 202–207
Benedetti E et al. Intrasplenic hepatocyte allotransplantation in dalmation dogs with and without cyclosporine immunosuppression Transplantation 1997 63: 1206–1209
Rosenthal RJ et al. Techniques for intrasplenic hepatocyte transplantation in the large animal model Surg Endosc 1996 10: 1075–1079
Vogels BA, Maas MA, Bosma A, Chamuleau RA . Significant improvement of survival by intrasplenic hepatocyte transplantation in totally hepatectomized rats Cell Transplant 1996 5: 369–378
Chiaramonte MG, Donaldson DD, Cheever AW, Wynn TA . An IL-13 inhibitor blocks the development of hepatic fibrosis during a T-helper type 2-dominated inflammatory response J Clin Invest 1999 104: 777–785
Kaplan MH, Whitfield JR, Boros DL, Grusby MJ . Th2 cells are required for the Schistosoma mansoni egg-induced granulomatous response J Immunol 1998 160: 1850–1856
Wynn TA et al. An IL-12-based vaccination method for preventing fibrosis induced by schistosome infection Nature 1995 376: 594–596
Wynn TA et al. Endogenous interleukin 12 (IL-12) regulates granuloma formation induced by eggs of Schistosoma mansoni and exogenous IL-12 both inhibits and prophylactically immunizes against egg pathology J Exp Med 1994 179: 1551–1561
Hoffmann KF, Cheever AW, Wynn TA . IL-10 and the dangers of immune polarization: excessive type 1 and type 2 cytokine responses induce distinct forms of lethal immunopathology in murine schistosomiasis J Immunol 2000 164: 6406–6416
Fallon PG, Richardson EJ, McKenzie GJ, McKenzie AN . Schistosome infection of transgenic mice defines distinct and contrasting pathogenic roles for IL-4 and IL-13: IL-13 is a profibrotic agent J Immunol 2000 164: 2585–2591
Dessein AJ et al. Severe hepatic fibrosis in Schistosoma mansoni infection is controlled by a major locus that is closely linked to the interferon-gamma receptor gene Am J Hum Genet 1999 65: 709–721
Hoffmann KF, Caspar P, Cheever AW, Wynn TA . IFN-gamma, IL-12, and TNF-alpha are required to maintain reduced liver pathology in mice vaccinated with Schistosoma mansoni eggs and IL-12 J Immunol 1998 161: 4201–4210
Sakaida I et al. Quantitative analysis of liver fibrosis and stellate cell changes in patients with chronic hepatitis C after interferon therapy Am J Gastroenterol 1999 94: 489–496
Garcia VE et al. IL-18 promotes type 1 cytokine production from NK cells and T cells in human intracellular infection J Immunol 1999 162: 6114–6121
Yoshimoto T et al. Interleukin 18 together with interleukin 12 inhibits IgE production by induction of interferon-gamma production from activated B cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 3948–3953
Munder M, Mallo M, Eichmann K, Modolell M . Murine macrophages secrete interferon gamma upon combined stimulation with interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-18: a novel pathway of autocrine macrophage activation J Exp Med 1998 187: 2103–2108
Tsukamoto H . Cytokine regulation of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis Alcohol Clin Exp Res 1999 23: 911–916
Ju DW et al. Interleukin-18 gene transfer increases antitumor effects of suicide gene therapy through efficient induction of antitumor immunity Gene Therapy 2000 7: 1672–1679
Bergman I, Loxyley R . Two improved and simplified methods for the spectrophotometric determination of hydroxyproline Anal Chem 1963 35: 1961–1965
Jimenez W et al. Measurement of fibrosis in needle liver biopsies: evaluation of a colorimetric method Hepatology 1985 5: 815–818
Sugama S et al. Tissue-specific expression of rat IL-18 gene and response to adrenocorticotropic hormone treatment J Immunol 2000 165: 6287–6292
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 39825123). We thank Dr H Hamada (Department of Molecular Medicine, Sapporo Medical University, Japan) for generously providing recombinant adenovirus encoding LacZ, and Prof H Yu for helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Pan, J., Yao, H. et al. Intrasplenic transplantation of IL-18 gene-modified hepatocytes: an effective approach to reverse hepatic fibrosis in schistosomiasis through induction of dominant Th1 response. Gene Ther 8, 1333–1342 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301524
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301524
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification of IFN-γ-producing innate B cells
Cell Research (2014)
-
TLR4 is essential for dendritic cell activation and anti-tumor T-cell response enhancement by DAMPs released from chemically stressed cancer cells
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2014)
-
Interleukin-18: Friend or Foe for Systemic Sclerosis?
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2011)
-
Response to “Interleukin-18: Friend or Foe for Systemic Sclerosis?”
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2011)
-
IL-18 Downregulates Collagen Production in Human Dermal Fibroblasts via the ERK Pathway
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2010)