Abstract
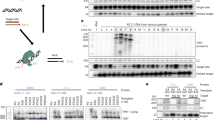
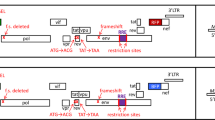
Sustained expression of recombinant proteins is a critical factor for the effectiveness of numerous applications in the biomedical sciences including the treatment of human disease by gene therapy, the large scale production of therapeutic proteins, as well as the investigation of gene function by transgenesis or cell type specific mutagenesis. Although much attention has been paid to the optimisation of regulatory sequences such as promoters, untranslated regions and polyadenylation signals, effective and sustained expression of recombinant genes in vivo is often difficult to achieve. Here we report that the creation of artificial exons, by insertion of two short heterologous introns into open reading frames, is not only compatible with functional expression, but also leads to a 30-fold enhancement of mRNA production for both green fluorescent protein and the bacteriophage P1-derived Cre recombinase. The levels of green fluorescence were increased five-fold in cell lines and sustained long-term expression at increased levels was observed in rat brain after transduction with a herpes simplex virus-based vector. The data presented identify a means by which the expression of recombinant genes can be enhanced considerably, in addition to and independently from the surrounding regulatory sequences. The method should help obtain sustained and effective expression of recombinant proteins in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palmiter RD et al. Heterologous introns can enhance expression of transgenes in mice Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991 88: 478–482
Evans MJ, Scarpulla RC . Introns in the 3′-untranslated region can inhibit chimeric CAT and beta-galactosidase gene expression Gene 1989 84: 135–142
Boyd AC et al. Insertion of natural intron 6a-6b into a human cDNA-derived gene therapy vector for cystic fibrosis improves plasmid stability and permits facile RNA/DNA discrimination J Gene Med 1999 1: 312–321
Kay MA et al. Evidence for gene transfer and expression of factor IX in haemophilia B patients treated with an AAV vector Nat Genet 2000 24: 257–261
Chalfie M et al. Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression Science 1994 263: 802–805
Cubitt AB et al. Understanding, improving and using green fluorescent proteins Trends Biochem Sci 1995 20: 448–455
Sauer B, Henderson N . Site-specific DNA recombination in mammalian cells by the Cre recombinase of bacteriophage P1 Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988 85: 5166–5170
Wang Y, Krushel LA, Edelman GM . Targeted DNA recombination in vivo using an adenovirus carrying the cre recombinase gene Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996 93: 3932–3936
Rajewsky K et al. Conditional gene targeting J Clin Invest 1996 98: 600–603
Palmer JA et al. Development and optimization of herpes simplex virus vectors for multiple long-term gene delivery to the peripheral nervous system J Virol 2000 74: 5604–5618
Deglon N et al. Self-inactivating lentiviral vectors with enhanced transgene expression as potential gene transfer system in Parkinson's disease Hum Gene Ther 2000 11: 179–190
Neel H, Weil D, Giansante C, Dautry F . In vivo cooperation between introns during pre-mRNA processing Genes Dev 1993 7: 2194–2205
Liu K, Sandgren EP, Palmiter RD, Stein A . Rat growth hormone gene introns stimulate nucleosome alignment in vitro and in transgenic mice Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 7724–7728
Beckmann JS, Trifonov EN . Splice junctions follow a 205-base ladder Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991 88: 2380–2383
Bestor TH . Gene silencing as a threat to the success of gene therapy J Clin Invest 2000 105: 409–411
Neuberger MS, Williams GT . The intron requirement for immunoglobulin gene expression is dependent upon the promoter Nucleic Acids Res 1988 16: 6713–6724
Enriquez-Harris P, Levitt N, Briggs D, Proudfoot NJ . A pause site for RNA polymerase II is associated with termination of transcription EMBO J 1991 10: 1833–1842
Chen CY, Shyu AB . Selective degradation of early-response-gene mRNAs: functional analyses of sequence features of the AU-rich elements Mol Cell Biol 1994 14: 8471–8482
Acknowledgements
Experiments on animals were carried out in accordance to the regulations under the Home Office (United Kingdom) Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986. ALH and RT contributed equally to this work. This work was supported by the Wellcome Trust grants 47608, 55287, 47273 the latter to J Savill, University of Edinburgh, whom we gratefully acknowledge for the support of ALH during the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lacy-Hulbert, A., Thomas, R., Li, XP. et al. Interruption of coding sequences by heterologous introns can enhance the functional expression of recombinant genes. Gene Ther 8, 649–653 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301440
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301440
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Expression vector cassette engineering for recombinant therapeutic production in mammalian cell systems
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2020)
-
In vivo measurements reveal a single 5′-intron is sufficient to increase protein expression level in Caenorhabditis elegans
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Development of a silicon limitation inducible expression system for recombinant protein production in the centric diatoms Thalassiosira pseudonana and Cyclotella cryptica
Microbial Cell Factories (2017)
-
Comparative study reveals better far-red fluorescent protein for whole body imaging
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
A Mini-intronic Plasmid (MIP): A Novel Robust Transgene Expression Vector In Vivo and In Vitro
Molecular Therapy (2013)