Abstract
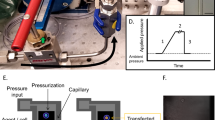
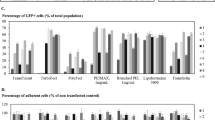
The nonreplicating vaccinia virus MVA/T7 RNA polymerase hybrid system was tested with Petri dish electroporation for ectopic gene expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). A range of voltages (150–450 V), pulse times (10–40 ms), DNA concentrations (0–20 μg/ml) and infection levels (0–15 multiplicities of infection) were tested for effects on T7 promoter-directed chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) activity after MVA/T7RP infection. MVA/T7RP-directed expression was transient and at least 10 000-fold in excess of nonviral, cytomegalovirus enhancer-directed expression. Use of a Petri dish electrode with the MVA/T7RP system showed increased viability compared with a cuvette electrode. Overexpression of interleukin-2 alpha subunit (IL2Rα) pro- tein followed by anti-IL2Rα-directed magnetic immunoaffinity cell sorting allowed isolation of the transfected population. The high fidelity of cellular sorting was shown by segregation of CAT activity in the IL2Rα-sorted population after transfection of T7 promoter-directed bicistronic IL2Rα/CAT DNA. Expression of a panel of proteins including the fluorophore green fluorescent protein as detected by fluorescence microscopy and p21cip1, p27kip1, pp60c-src, FGF-1, pRb, p107 and pRb2/p130 proteins was also achieved. Thus, use of the nonreplicating vaccinia virus/T7 RNA polymerase expression system with Petri dish electroporation is feasible for certain applications for the manipulation of HUVECs by gene transfer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwachtgen J-L, Ferreira V, Meyer D, Kerbiriou-Nabias D . Optimization of the transfection of human endothelial cells by electroporation BioTechniques 1994 17: 882–887
Tanner FC, Carr DP, Nabel GJ, Nabel EG . Transfection of human endothelial cells Cardiovascular Res 1997 35: 522–528
Teifel M, Heine L-T, Milbredt S, Friedl P . Optimization of transfection of human endothelial cells Endothelium 1997 5: 21–35
Edgell C-JS, Curiel DT, Hu P-C, Marr HS . Efficient gene transfer to human endothelial cells using DNA complexed to adenovirus particles BioTechniques 1998 25: 264–272
Fife K et al. Endothelial cell transfection with cationic liposomes and herpes simplex-thymidine kinase mediated killing Gene Therapy 1998 5: 614–620
Wilson DB, Dorfman DM, Orkin SH . A nonerythroid GATA-binding protein is required for function of the human preproendothelin-1 promoter in endothelial cells Mol Cell Biol 1992 10: 4854–4862
Nabel EG, Nabel GJ . Complex models for the study of gene function in cardiovascular biology Ann Rev Physiol 1994 56: 741–761
Inaba M et al. Retroviral gene transfer: effects on endothelial cell phenotype J Surg Res 1998 78: 31–36
de Martin R, Raidl M, Hofer E, Binder BR . Adenovirus-mediated expression of green fluorescent protein Gene Therapy 1997 4: 493–495
Riccioni T et al. Adenovirus-mediated wild-type p53 overexpression inhibits endothelial cell differentiation in vitro and angiogenesis in vivo Gene Therapy 1998 5: 747–754
Engleka KA, Lewis EW, Howard BH . Mechanisms of replication-deficient vaccinia virus/T7 RNA polymerase hybrid expression; effect of T7 RNA polymerase levels and alpha-amanitin Virology 1998 243: 331–339
Sutter G, Moss B . Nonreplicating vaccinia vector efficiently expresses recombinant genes Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992 89: 10847–10851
Sutter G, Olmann M, Erfle V . Non-replicating vaccinia vector efficiently expresses bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase FEBS Lett 1995 371: 9–12
Wyatt LS, Moss B, Rozenblatt S . Replication-deficient vaccinia virus encoding bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase for transient gene expression in mammalian cells Virology 1995 210: 202–205
Moss B et al. New mammalian expression vectors Nature 1990 348: 91–92
Muramatsu T, Nakamura A, Park H-M . In vivo electroporation: a powerful and convenient means of nonviral gene transfer to tissues of living animals Int J Mol Med 1998 1: 55–62
Nathwani AC et al. Efficient gene transfer into human umbilical vein endothelial cells allows functional analysis of the human tissue factor gene promoter Br J Haematol 1994 88: 122–128
Elroy-Stein O, Moss B . Cytoplasmic expression system based on constitutive synthesis of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase in mammalian cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990 87: 6743–6747
Giordano T et al. Isolation of a population of transiently transfected quiescent and senescent cells by magnetic affinity cell sorting Exp Cell Res 1991 192: 193–197
Padmanabhan R et al. Purification of transiently transfected cells by magnetic affinity cell sorting Anal Biochem 1988 170: 341–348
Prasher DC et al. Primary structure of the Aequorea victoria green-fluorescent protein Gene 1992 111: 229–233
Harper JW et al. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases Cell 1993 75: 805–816
Jaye M et al. Human endothelial cell growth factor: cloning, nucleotide sequence, and chromosome localization Science 1986 233: 541–545
DeCaprio JA et al. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene Cell 1988 54: 275–283
Ewen ME, Xing Y, Lawrence JB, Livingston D . Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping, and expression of the cDNA for p107, a retinoblastoma gene product-related protein Cell 1991 66: 1155–1164
Mayol X et al. Cloning of a new member of the retinoblastoma gene family (pRb2) which binds to the E1A transforming domain Oncogene 1993 8: 2561–2566
Tanaka A et al. DNA sequence encoding the amino-terminal region of the human c-src protein: implications of sequence divergence among src-type kinase oncogenes Mol Cell Biol 1987 7: 1978–1983
Polyak K et al. Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals Cell 1994 78: 59–66
Moss B et al. Host range restricted, non-replicating vaccinia virus vectors as vaccine candidates Adv Exp Med Biol 1996 397: 7–13
Bender BS et al. Oral immunization with a replication-deficient recombinant vaccinia virus protects mice against influenza J Virol 1996 70: 6418–6424
Sutter G et al. A recombinant vector derived from the host range-restricted and highly attenuated MVA strain of vaccinia virus stimulates protective immunity in mice to influenza virus Vaccine 1994 12: 1032–1040
Schneider J et al. Enhanced immunogenicity for CD8+ T cell induction and complete protective efficacy of malaria DNA vaccination by boosting with modified vaccinia virus Ankara Nature Med 1998 4: 397–402
Hanke T et al. Immunogenicities of intravenous and intramuscular administrations of modified vaccinia virus Ankara-based multi-CTL epitope vaccine for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in mice J Gen Virol 1998 79: 83–90
Mayr A, Hochstein-Mintzel V, Stickl H . Passage history, properties, and applicability of the attenuated vaccinia virus strain MVA Infection 1973 3: 6–14
van den Hoff MJB, Moorman AFM, Lamers WH . Electroporation in ‘intracellular’ buffer increases cell survival Nucleic Acids Res 1992 20: 2902
Zabner J et al. Cellular and molecular barriers to gene transfer by a cationic lipid J Biol Chem 1995 270: 18997–19007
Jaffe EA, Nachman RL, Becker CG, Minick CR . Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins J Clin Invest 1973 52: 2745–2746
Vuento M, Vaheri A . Purification of fibronectin from human plasma by affinity chromatography under non-denaturing conditions Biochem J 1979 183: 331–337
Regnault V, Rifat C, Stoltz JF . Affinity purification of human plasma fibronectin on immobilized gelation J Chromatogr 1988 432: 93–102
Maciag T, Weinstein R . Preparation of endothelial cell growth factor In: Barnes DW, Sirbasku DA, Sato GH (eds) . Methods for Preparation of Media, Supplements, and Substrata for Serum-free Animal Cell Culture Alan R Liss: New York 1984 pp 195–205
Elroy-Stein O, Fuerst TR, Moss B . Cap-independent translation of mRNA conferred by encephalomyocarditis virus 5′ sequence improves the performance of the vaccinia virus/bacteriophage T7 hybrid expression system Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989 86: 6126–6130
Malone RW, Felgner PL, Verma IM . Cationic liposome-mediated RNA transfection Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989 86: 6077–6081
Gorman CM, Moffat LF, Howard BH . Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells Mol Cell Biol 1982 2: 1044–1051
Leonard WJ et al. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs for the human interleukin-2 receptor Nature 1984 311: 626–631
Goldstein S, Fordis CM, Howard BH . Enhanced transfection efficiency and improved cell survival after electroporation of G2/M-synchronized cells and treatment with sodium butyrate Nucleic Acids Res 1989 17: 3959–3971
Fordis CM, Howard BH . Use of the CAT reporter gene for optimization of gene transfer into eukaryotic cells Meth Enzymol 1987 151: 382–397
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a National Research Council Research Associateship to Kurt A Engleka while a postdoctoral fellow at the National Institutes of Health, institutional support from Thomas Jefferson University and by a grant from the American Heart Association. The authors would like to thank Donald J Fujita, University of Calgary, Vasily V Ogryzko, National Institutes of Health, and Antonio Giordano, Thomas Jefferson University for supplying plasmids, Linda S Wyatt and Bernard Moss, National Institutes of Health, for MVA/T7RP recombinant virus, Marilyn Woolkalis, Thomas Jefferson University for HUVECs and P Macke Consigny, Thomas Jefferson University for the use of a fluorescence microscope and imaging system and rabbit microvascular endothelial cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewis, E., Rudo, T., St John, M. et al. Endothelial cell DNA transfer and expression using Petri dish electroporation and the nonreplicating vaccinia virus/T7 RNA polymerase hybrid system. Gene Ther 6, 1617–1625 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300977
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300977