Abstract
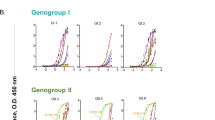
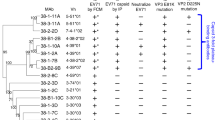
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1, HTLV-III/LAV), the retrovirus responsible for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), shows a high degree of genetic polymorphism, particularly in the env gene1–6. We have examined sera from rabbits and guinea pigs immunized with gpl30, a recombinant env glycoprotein7, and sera from HIV-1-infected subjects8, to test their capacity to neutralize a panel of genetically divergent HIV-1 isolates. The sera raised against recombinant antigen specifically neutralized the virus strain from which the env gene was cloned (HTLV-IIIB), but not an independent isolate (HTLV-IIIRF). One rabbit serum tested on seven isolates cross-neutralized two at lower titres. In contrast, human sera from Britain and Uganda, chosen for ability to neutralize HTLV-IIIRF, cross-neutralized six other HIV-1 isolates. When serum and isolate were derived from the same subject, the serum was in some cases effective at slightly lower concentrations (higher titres). Human complement did not affect neutralization titres. These findings indicate that genetically diverse HIV-1 isolates carry both variable and widely conserved antigenic epitopes for neutralizing antibodies. The identification of shared epitopes may help the development of protective vaccines.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong-Staal, F. et al. Science 229, 759–762 (1985).
Benn, S. et al. Science 230, 949–951 (1985).
Hahn, B. H. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 4813–4817 (1985).
Starcich, B. R. et al. Cell 45, 637–648 (1986).
Alizon, M., Wain-Hobson, S., Montagnier, L. & Sonigo, P. Cell 46, 63–74 (1986).
Coffin, J. M. Cell 46, 1–4 (1986).
Lasky, L. A. et al. Science 233, 209–212 (1986).
Weiss, R. A. et al. Nature 316, 69–72 (1985).
Serwadda, D. et al. Lancet ii, 849–852 (1985).
Webster, A. D. B. et al. Lancet i, 581–583 (1985).
Haase, A. Nature 322, 130–136 (1986).
Hahn, B. H. et al. Science 232, 1548–1553 (1986).
Clapham, P. R., Nagy, K. & Weiss, R. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 2886–2889 (1984).
Hoshino, H. et al. Int. J. Cancer 36, 671–675 (1985).
Ishizaki, R. & Vogt, P. K. Virology 30, 375–387 (1966).
Weiss, R. A. & Biggs, P. M. J. natn. Cancer Inst. 49, 1713–1725 (1972).
Bruck, C., Portetelle, D., Mammerickx, M., Mathot, S. & Burny, A. Leukemia Res. 8, 315–321 (1984).
Dalgleish, A. G. et al. Nature 312, 763–767 (1984).
Klatzmann, D. et al. Nature 312, 767–769 (1984).
McDougal, J. S. et al. Science 231, 382–385 (1986).
Matthews, T. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiss, R., Clapham, P., Weber, J. et al. Variable and conserved neutralization antigens of human immunodeficiency virus. Nature 324, 572–575 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/324572a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/324572a0
This article is cited by
-
The expanding array of HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies
Retrovirology (2018)
-
Analysis of HIV-1 envelope evolution suggests antibody-mediated selection of common epitopes among Chinese former plasma donors from a narrow-source outbreak
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Promise and problems associated with the use of recombinant AAV for the delivery of anti-HIV antibodies
Molecular Therapy - Methods & Clinical Development (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.