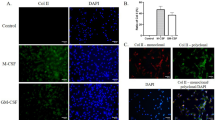
Abstract
There are two phenotypically distinct subpopulations of mast cells in rodents: connective tissue-type mast cells (CTMC) and mucosal mast cells (MMC). These populations differ in their location, cell size, staining characteristics, ultrastructure, mediator content and T-cell dependency1–3. Several investigators4–9 recently reported a further subclass of mast cells which arise when normal mouse haematopoietic cells are cultured with interleukin-3 (IL-3); IL-3 is an activity similar or identical to mast-cell growth factor, histamine-producing factor, or P-cell stimulating factor4–9. These cultured mast cells are in many ways similar to MMC; they stain with Alcian blue but not safranin, contain chondroitin sulphate E proteoglycan rather than heparin proteoglycan and have relatively low histamine content, as do MMC10–13. Although proliferation of MMC is known to be T-cell dependent in vivo and thought to be IL-3-dependent in vitro, the factors on which CTMC proliferation depends remain elusive. Here we show that mature CTMC purified from mouse peritoneal cells can proliferate in vitro in methylcellulose culture and maintain the appearance and function of CTMC. We also present evidence that mature CTMC cannot proliferate in the presence of pure IL-3 alone.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Enerback, L. Monogr. Allerg. 17, 222–232 (1981).
Bienenstock, J., Befus, A. D., Pearce, F., Denburg, J. & Goodacre, R. Allerg. din. Immun. 70, 407–412 (1982).
Galli, S. J., Dvorak, A. M. & Dvorak, H. F. Prog. Allerg. 34, 1–141 1984).
Nabel, G., Galli, S. J., Dvorak, A. M., Dvorak, H. F. & Cantor, H. Nature 291, 332–334 (1981).
Schrader, J. W., Lewis, S. J., Clarke-Lewis, I. & Culvenor, J. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 323–327 (1981).
Razin, E., Cordon-Cardo, C. & Good, R. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 2559–2561 1981).
Yung, Y. P., Eger, R., Tertian, G. & Moore, M. A. S. J. Immun. 127, 794–799 (1981).
Ihle, J. N. et al. J. Immun. 131, 282–287 (1983).
Yokota, T. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 1070–1074 (1984).
Haig, D. M., McKee, T. A., Jarrett, E. E., Woodbury, R., & Miller, H. R. P. Nature 300, 188–190 (1982).
Razin, E., Stevens, R. L., Akiyama, F., Schmidt, K. & Austen, K. J. biol. Chem. 257, 7229–7236 (1982).
Razin, E. et al. J. Immun. 132, 1479–1486 (1984).
Galli, S. J. et al. J. Cell Biol. 95, 435–444 (1982).
Kobayashi, T. et al. J. Immun. 136, 1378–1384 (1986).
Enerback, L. Histochemistry 42, 301–313 (1974).
Dimlich, R. V. M., Meineke, H. A., Reilly, F. D. & McCuskey, R. S. Stain Tech. 55, 217–223 (1980).
Nakano, T. et al. J. exp. Med. 162, 1025–1043 (1985).
Pretlow, T. G. & Gassady, I. M. Am. J. Path. 61, 323–338 (1970).
Nakahata, T. et al. Blood 65, 1010–1016 (1985).
Sonoda, T. et al. J. exp. Med. 160, 138–151 (1984).
Yung, Y. P., Wang, S. Y. & Moore, M. A. S. J. Immun. 130, 2843–2848 (1983).
Rennick, D. M. J. Immun. 134, 910–914 (1985).
Bland, C. E., Ginsburg, H., Silbert, J. E. & Metcalfe, D. D. J. biol Chem. 257, 8661–8666 (1982).
Levi-Schaffer, F. et al>. J. Immun. 135, 3454–3462 (1985).
Burgess, A. W., Camakaris, J. & Metcalf, D. J. biol. Chem. 252, 1998–2003 (1977).
Nicola, N. A., Metcalf, D., Matsumoto, M. & Johnson, G. R. J. biol. Chem. 258, 9017–9023 (1983).
Stanley, E. R. & Heard, B. M. J. biol. Chem. 252, 4305–4312 (1977).
Frei, K., Bodmer, S., Schwerdel, C. & Fontana, A. J. Immun. 135, 4044–4047 (1985).
Nakahata, T., Spicer, S. S., Cantey, J. R. & Ogawa, M. Blood 60, 352–361 (1982).
Nakahata, T. & Ogawa, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 3843–3847 (1982).
Spicer, S. S. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 8, 18–35 (1960).
Kubota, K., Mizoguchi, H., Miura, Y., Suda, T. & Takaku, F. Expl Hemat. 8, 339–344 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakahata, T., Kobayashi, T., Ishiguro, A. et al. Extensive proliferation of mature connective-tissue type mast cells in vitro. Nature 324, 65–67 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/324065a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/324065a0
This article is cited by
-
Molecular regulation of mast cell development and maturation
Molecular Biology Reports (2010)
-
Effects of FK506 and Cyclosporin a on proliferation, histamine release and phenotype of murine mast cells
Archives of Dermatological Research (1996)
-
Transforming growth factor ?1 inhibits IL-3- and IL-4-dependent mouse connective tissue-type mast cell proliferation
Archives of Dermatological Research (1995)
-
Tryptase and chymase, markers of distinct types of human mast cells
Immunologic Research (1989)
-
An ultrastructural study of the morphology and lectin-binding properties of human mast cell granules
The Histochemical Journal (1988)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.