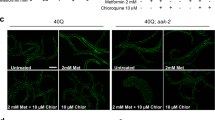
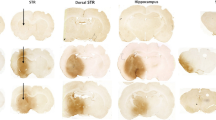
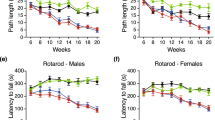
Abstract
Huntington's disease (HD) is an autosomal dominant neurological disorder characterized by progressive chorea, cognitive impairment and emotional disturbance1. The disease usually occurs in midlife and symptoms progress inexorably to mental and physical incapacitation. It has been postulated that an excitotoxin is involved in the pathogenesis of HD2,3. Schwarcz and colleagues have shown that quinolinic acid (QA) can produce axon-sparing lesions similar to those observed in HD4–7. The lesions result in a depletion of neurotransmitters contained within striatal spiny neurones, for example γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), while dopamine is unaffected. Recently, we and others have demonstrated that in HD striatum there is a paradoxical 3–5-fold increase in both somatostatin and neuropeptide Y which is attributable to selective preservation of a subclass of striatal aspiny neurones in which these peptides are co-localized8–12. In the present study we demonstrate that lesions due to quinolinic acid closely resemble those of HD as they result in marked depletions of both GABA and substance P, with selective sparing of somatostatin/neuropeptide Y neurones. Lesions produced by kainic acid (KA), ibotenic acid (IA) and N-methyl-D-aspartate (MeAsp) were unlike those produced by QA, as they affected all cell types without sparing somatostatin/neuropeptide Y neurones. These results suggest that QA or a similar compound could be responsible for neuronal degeneration in HD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin, J. B. Neurology 34, 1059–1072 (1984).
Coyle, J. T. & Schwarcz, R. Nature 263, 244–246 (1976).
McGeer, E. G. & McGeer, P. L. Nature 263, 517–519 (1976).
Schwarcz, R., Whetsell, W. O. & Mangano, R. M. Science 219, 316–319 (1983).
Schwarcz, R. et al. Life Sci. 35, 19–32 (1984).
Wolfensberger, M. et al. Neurosci. Lett. 41, 247–252 (1983).
Kohler, C., Okuno, E. & Schwarcz, R. Neurosci. Abstr. 11, 820 (1985).
Aronin, N. et al. Ann. Neural. 13, 519–526 (1983).
Beal, M. F. et al. Neurology 34, 663–666 (1984).
Nemeroff, C. B. et al. Science 221, 972–975 (1983).
Ferrante, R. J. et al. Science 230, 561–563 (1985).
Dawbarn, D., Dequidt, M. E. & Emson, P. C. Brain Res. 340, 251–260 (1985).
Gusella, J. F. et al. Nature 306, 234–238 (1983).
Beal, M. F. & Martin, J. B. Brain Res. 266, 67–73 (1983).
Beal, M. F. et al. Brain Res. 361, 135–145 (1985).
Allen, Y. S. et al. Neurosci. Abstr. 10, 813 (1984).
Konig, J. F. R. & Klippel, R. A. The Rat Brain (Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1963).
Beal, M. F. & Martin, J. B. Neurosci. Lett. 44, 271–276 (1984).
Lasley, S. M., Greenland, R. D. & Michaelson, I. A. Life Sci. 35, 1921–1930 (1984).
Arnold, M. A. et al. J. Neurosci. 2, 674–680 (1982).
Beal, M. F. et al. Neurosci. Lett. (in the press).
Mroz, E. A. & Leeman, S. A. in Methods of Hormone Radioimmunoassay (eds Jafee, B. & Behrman, J.) 121–137 (Academic, New York, 1978).
Kasting, N. W. et al. Can. J. Physiol Pharmac. 61, 427–431 (1983).
Bohlen, P. et al. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 155, 213–220 (1973).
Beal, M. F., Domesick, V. B. & Martin, J. B. Brain Res. 278, 103–108 (1983).
Beal, M. F., Domesick, V. B. & Martin, J. B. Brain Res. 330, 309–316 (1985).
Sperk, G. & Widmann, R. J. Neurochem. 45, 1441–1447 (1985).
Kowall, N. W., Beal, M. F., Ferrante, R. J. & Martin, J. B. Neurosci. Lett. 59, 61–66 (1985).
Vincent, S. R. et al. Neurosci. Lett. 35, 111–114 (1983).
Vincent, S. R. et al. J. comp. Neurol. 217, 252–263 (1983).
Kowall, N. W., Ferrante, R. J., Beal, M. F. & Martin, J. B. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 11, 209 (1985).
Araki, M., McGeer, P. L. & McGeer, E. G. Neurosci. Lett. 53, 197–202 (1985).
Henderson, L. M. & Hirsch, H. M. J. biol. Chem. 181, 669–675 (1949).
Henderson, L. M. & Ramasarma, G. B. J. biol. Chem. 181, 687–692 (1949).
Gholson, R. K. et al. J. biol. Chem. 239, 1208–1214 (1964).
Vonsattel, J. P. et al. J. Neuropath, exp. Neurol. 44, 559–577 (1985).
McCaughey, W. T. E. J. nerv. ment. Dis. 133, 91–103 (1961).
Foster, A. C., Vezzani, A., French, E. D. & Schwarcz, R. Neurosci. Lett. 48, 273–278 (1984).
Perkins, M. N. & Stone, T. W. Expl Neurol. 88, 570–579 (1985).
Thomas, E. & Pearse, A. G. E. Acta neuropath. 3, 238–249 (1964).
Schwarcz, R. & Meldrum, B. Lancet ii, 140–143 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beal, M., Kowall, N., Ellison, D. et al. Replication of the neurochemical characteristics of Huntington's disease by quinolinic acid. Nature 321, 168–171 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/321168a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/321168a0
This article is cited by
-
Exploring the neuroprotective effects of montelukast on brain inflammation and metabolism in a rat model of quinolinic acid-induced striatal neurotoxicity
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2023)
-
Toll-Like Receptor 4 Plays a Significant Role in the Biochemical and Neurological Alterations Observed in Two Distinct Mice Models of Huntington’s Disease
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Krankheitsmodifizierende Therapieansätze bei der Huntington-Krankheit
Der Nervenarzt (2022)
-
Effects of Quinolinate-Induced Lesion of the Medial Prefrontal Cortex on Prefrontal and Striatal Concentrations of d-Serine in the Rat
Neurochemical Research (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.