Abstract
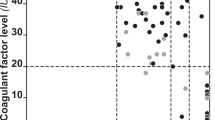
The most common inherited bleeding disorder in man, haemophilia A, is caused by defect in factor VIII, a component in the blood coagulation pathway. The X-chromosome-linked disease almost certainly stems from a heterogeneous collection of genetic lesions. Because, without proper treatment, haemophilia can be a fatal disease, new mutations are necessary to account for its constant frequency in the population1. In addition, haemophilia A displays a wide range of severity, and some 15% of haemophiliacs generate high levels of antibodies against factor VIII (‘inhibitor patients’). The present work elucidates the molecular genetic basis of haemophilia in some individuals. Using the recently cloned factor VIII gene as a probe2,3, we have identified two different nonsense point mutations in the factor VIII gene of haemophiliacs, as well as two different partial deletions of the gene. Our survey of 92 haemophiliacs indicates no firm correlation between antibody (inhibitor) production and gross gene defects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haldane, J. B. S. J. Genet. 31, 317–326 (1935).
Wood, W. I. et al. Nature 312, 330–337 (1984).
Gitschier, J. et al. Nature 312, 326–330 (1984).
Gitschier, J., Drayna, D., Tuddenham, E. G. D., White, R. L. & Lawn, R. M. Nature 314, 738–740 (1985).
Barker, D., Shafer, M. & White, R. Cell 36, 131–138 (1984).
Fulcher, C. A., Roberts, J. R. & Zimmerman, T. S. Blood 61, 807–811 (1983).
Vehar, G. A. et al. Nature 312, 337–342 (1984).
Breathnach, R. & Chambon, P. A. Rev. Biochem. 50, 349–383 (1981).
Schmid, C. W. & Jelinek, W. R. Science 216, 1065–1070 (1982).
Giannelli, F. et al. Nature 303, 181–182 (1983).
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F. & Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1982).
Taylor, J. M., Illmensee, R. & Summer, S. Biochim. biophys. Acta 442, 324–330 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gitschier, J., Wood, W., Tuddenham, E. et al. Detection and sequence of mutations in the factor VIII gene of haemophiliacs . Nature 315, 427–430 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/315427a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/315427a0
This article is cited by
-
Novel copy number variations within SYCE1 caused meiotic arrest and non-obstructive azoospermia
BMC Medical Genomics (2022)
-
Genetic analysis of haemophilia A in Bulgaria
BMC Hematology (2004)
-
Flipping the tip of the X
Nature Genetics (1993)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.