Abstract
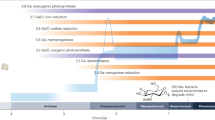
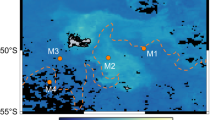
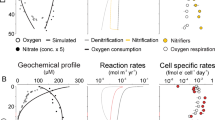
Previous estimates of the global organic carbon (Corg) budget have generally considered the anaerobic consumption of Corg to be of minor importance. Data for the rates of bacterial sulphate reduction in various morphological zones of the oceans indicate, however, that approximately 14% of the total Corg reaching the sediment–water interface is consumed by anaerobic processes. Of this, some 70% is taken up in sediments on the continental shelves and slopes in water depths of less than 1,000 m. Although this represents only a small fraction of the global primary carbon productivity, it may have important consequences for models of the carbon and sulphur cycles.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Romankevich, E. A. Geochemistry of Organic Matter in Ocean (Nauka, Moscow, 1977).
Ryther, J. H. Science 166, 72–76 (1969).
Riley, G. A. J. mar. Res. 6, 54–73 (1946).
Steemann-Nielsen, E. J. Cons. Perm. Int. Explor. Mer. 19, 309–328 (1953).
Schuelenberger, E. & Reid, J. L. Deep-Sea Res. 28A, 901–919 (1981).
Li, W. K. W. et al. Science 219, 292–295 (1983).
Jannasch, H. W. & Wirsen, C. O. Bioscience 29, 592–598 (1979).
Karl, D. M. & Knauer, G. A. Deep-Sea Res. 31, 221–243 (1984).
Honjo, S., Manganini, S & Cole, J. Deep-Sea Res. 29, 609–625 (1982).
Jorgensen, B. B. in The Major Biogeochemical Cycles and Their Interactions (eds Bolin, B. & Cook, R. B.) 477–509 (Wiley, Chichester, 1983).
Emery, K. O. & Rittenberg, S. C. Bull. Am. Ass. Petrol. Geol. 36, 735–806 (1952).
Bordovsky, O. K. Accumulation and Transformation of Organic Matter in Sea Sediments (Nedra, Moscow, 1964).
Rozanov, A. G., Volkov, I. I. & Sokolov, V. S. in Geochemistry and Diagenesis of the Pacific Ocean Sediments, 22–46 (Nauka, Moscow, 1980).
Strakhov, N. M. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Geol. 1, 34–51 (1955).
Strakhov, N. M. Problems of the Geochemistry of the Recent Oceanic Lithogensis (Nauka, Moscow, 1976).
Ivanov, M. V., Lein, A. Y. & Kashparova, E. A. in Biogeochemistry of the Diagenesis of Ocean Sediments, 171–179 (1976).
Ivanov, M. V. & Lein, A. Y. in Geochemistry of Diagenesis of the Pacific Ocean Sediments, 117–134 (Nauka, Moscow, 1980).
Entsh, Ch. S. in Oceanographic Encylopedia 362–364 (Gidrometeoizdat, Lengingrad, 1974).
Belyayev, S. S., Lein, A. Y. & Ivanov, M. V. Geochimia 3, 437–445 (1981).
Lein, A. Y. & Ivanov, M. V. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR, 252, 217–219 (1980).
Lein, A. Y., Grinenko, V. A., Matrosov, A. G. & Tokarev, V. E. in Geochemical Activity of Microrganisms in the Pacific Ocean Sediments, 134–167 (Pushino, 1981).
Berner, R. A. in Changing Chemistry of the Oceans (eds Dyrssen, D. & Jagner, D.) 347–361 (Stockholm, 1972).
Goldhaber, M. B. & Kaplan, I. R. Soil Sci. 119, 42–55 (1975).
van Andel, T. H. in Marine Geology of the Gulf of California (eds van Andel, T. H. & Shor, G. G.) 216–310 (American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Tulsa, 1964).
Lisitzin, A. N. Sedimentation in Oceans (Nauka, Moscow, 1974).
Mopper, K. & Degens, E. T. in The Global Carbon Cycle (eds Bolin, B., Degens, E. T., Kempe, S. & Keiner, P.) 293–316 (Wiley, Chichester, 1979).
Volkov, I. I., Rozanov, A. G. & Zhabina, N. N. in Geochemistry of Diagenesis of the Pacific Ocean Sediments 61–64 (Nauka, Moscow, 1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lein, A. Anaerobic consumption of organic matter in modern marine sediments. Nature 312, 148–150 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/312148a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/312148a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.