Abstract
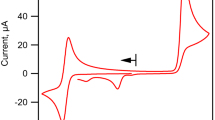
Redox proteins catalyse1 the reactions of a wide variety of otherwise intractable substrates, such as dinitrogen, alkalies, arenes, terpenes and steroids. Two major factors impede the utilization of these enzymes—the inefficient electron transfer between the enzyme and electrode, and the properties often, but not inevitably, associated with enzymes, such as instability, complexity, and expense. We have now shown that the former can be overcome and that proteins can be coupled, via electrodes, to a number of energy sources; the latter is2 the subject of much effort elsewhere. We demonstrated previously3–6 that certain redox proteins can be reduced very efficiently electrochemically (Fig. 1a). Light and hydrogen are the two other convenient energy sources that could be used for such reductions, and we now report the reduction of cytochrome c by these means.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyer, P. D. (ed.) The Enzymes Vols XII, XIII (Academic, New York, 1975, 1976).
Chibate, I. Immobilized Enzymes; Recent Developments (Wiley, New York, 1978).
Eddowes, M. J. & Hill, H. A. O. Chem. Commun. 771–772 (1977).
Eddowes, M. J. & Hill, H. A. O. J. Am. chem. Soc. 101, 4461–4464 (1979).
Eddowes, M. J., Hill, H. A. O. & Uosaki, K. J. Am. chem. Soc. 101, 7113 (1979).
Eddowes, M. J., Hill, H. A. O. & Uosaki, K. Bioelectrochem. Bioenergetics (in the press).
Vorkink, W. P. & Cusanovich, M. A. Photochem. Photobiol. 19, 205–215 (1974).
Honda, K. & Fujishima, J. Nature 238, 37–38 (1972).
Higgins, I. J. & Hill, H. A. O. U.K. Patent application 33388178.
Higgins, I. J. et al. in Hydrocarbons in Biotechnology (Harrison, D. E. F., Higgins, I. J. & Watkinson, R. J.) (Institute of Petroleum, London, in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cass, A., Eddowes, M., Hill, H. et al. Electrochemical, photoelectrochemical, electrocatalytic and catalytic reduction of redox proteins. Nature 285, 673–674 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/285673a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/285673a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.