Abstract
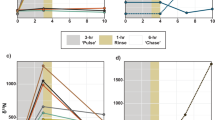
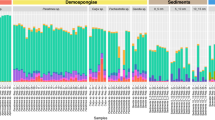
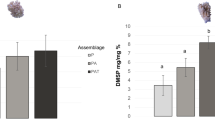
NITROGEN FIXATION by endosymbiotic cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) results in an important input of nitrogen into terrestrial ecosystems1; however, there is as yet little information on its significance in the marine environment2,3. Symbiosis of cyanobacteria with marine animals, although rare, is known to occur in an echiuroid worm4 and in sponges from coral reefs5 and the Mediterranean6. In the present study of sponge–cyanobacterial symbioses, several sponges from a coral reef in the Red Sea were tested, using the acetylene reduction technique7, immediately after their collection on reef-based platforms for their ability to fix nitrogen. Nitrogenase activity was detected in two sponges with cyanobacteria but not in a third with no cyanobacteria. This is the first demonstration of nitrogenase activity in an animal with symbiotic cyanobacteria. In two previous reports of nitrogen fixation in marine animals, the activity was attributed to bacteria in the gut8,9. Although these preliminary experiments are not sufficient to assess the significance of cyanobacterial nitrogenase activity in sponges, it is possible that any additional fixed nitrogen would be beneficial to sponges in tropical waters which are low in available nitrogen10 and in particulate nutrients11,12.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Millbank, J. W. in The Biology of Nitrogen Fixation (ed. Quispel, A.) 238–264 (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1974).
Fogg, G. E. in Ecol. Bull. (Stockholm) 26, 11–19 (1978).
Stewart, W. D. P. in Proc. 9th European Marine Biology Symp. (ed. Barnes, H.) 637–660 (University Press, Aberdeen, 1975).
Kawaguti, S. in Aspects of the Biology of Symbiosis (ed. Cheng, T. C.) 265–273 (University Park, Baltimore, 1971).
Wilkinson, C. R. Mar. Biol. 49, 177–185 (1978).
Vacelet, J. J. Microsc. 12, 363–380 (1971).
Stewart, W. D. P., Fitzgerald, G. P. & Burris, R. H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 58, 2071–2078 (1967).
Carpenter, E. J. & Culliney, J. L. Science 187, 551–552 (1975).
Guerinot, M. L., Fong, W. & Patriquin, D. G. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 34, 416–420 (1977).
Thomas, W. H. & Owen, R. W. Fish. Bull. Calif. 69, 87–92 (1971).
Johannes, R. E., Coles, S. L. & Kuenzel, N. T. Limnol. Oceanogr. 15, 579–586 (1970).
Reiswig, H. M. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 141, 568–591 (1971).
Vacelet, J. & Donadey, C. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 30, 301–314 (1977).
Flett, R. J., Hamilton, R. D. & Campbell, N. E. R. Can. J. Microbiol. 22, 43–51 (1976).
Cox, R. M. & Fay, P. Proc. R. Soc. B172, 357–366 (1969).
Hardy, R. W. F., Burns, R. C. & Holsten, R. D. Soil Biol. Biochem. 5, 47–81 (1973).
Imhoff, J. F. & Trüper, H. G. Microb. Ecol. 3, 1–9 (1976).
Lange, W. Can. J. Microbiol. 17, 303–314 (1971).
Paerl, H. W. Microb. Ecol. 4, 215–231 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WILKINSON, C., FAY, P. Nitrogen fixation in coral reef sponges with symbiotic cyanobacteria. Nature 279, 527–529 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/279527a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/279527a0
This article is cited by
-
Taurine as a key intermediate for host-symbiont interaction in the tropical sponge Ianthella basta
The ISME Journal (2023)
-
Coral reef ecological pump for gathering and retaining nutrients and exporting carbon: a review and perspectives
Acta Oceanologica Sinica (2023)
-
Examining the giant barrel sponge species complex: molecular and microbial differentiation of Xestospongia testudinaria in Singapore
Marine Biology (2023)
-
Harnessing solar power: photoautotrophy supplements the diet of a low-light dwelling sponge
The ISME Journal (2022)
-
The Nitrogen-Cycling Network of Bacterial Symbionts in the Sponge Spheciospongia vesparium
Journal of Ocean University of China (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.