Abstract
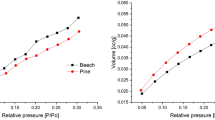
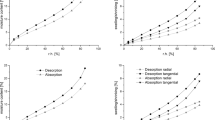
IT is important in the field of forest products science to know the sorption mechanism of water in wood. Adsorption of water onto hygroscopic natural polymers, such as wood and cellulose, is thought to depend entirely on the hydroxyl groups on the surface1. The mechanism of water adsorption in wood can therefore be studied by evaluating the quantity and the state of the adsorption sites, hydroxyl groups. Until now, in order to measure the number of adsorption sites of water in wood, it has been usual to draw a sorption isotherm from which the adsorbed area can be calculated assuming monomolecular layer adsorption according to the BET theory2. Little is known of the sorption mechanism on the molecular level, however. We report here the use of a hydrogen–deuterium exchange method to determine the adsorption sites of water in wood. Hydrogen–deuterium exchange is a well established method which has been widely used to determine hydroxyl group accessibility3,8,9.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Venkateswaran, A. Chem. Rev. 70, 619 (1970).
Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H. & Teller, E. J. Am. chem. Soc. 60, 309 (1938).
Browning, B. L. in Method of Wood Chemistry 2, 504–508 (Wiley, New York, 1967).
Taniguchi, T., Harada, H. & Nakato, K. J. Japan Wood Res. Soc. 12, 215 (1966).
Ramsden, D. K. & Moore, J. C. Polymer 18, 185 (1977).
Pimentel, G. C. & McClellan, A. L. The Hydrogen Bond 210 (Freeman, London, 1960).
McClellan, A. L. & Harnsberger, H. F. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 23, 577 (1967).
Mann, J. in High Polymer V, Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives 4 (eds Bikales, N. M. & Segal, L.) 89–116 (Wiley, New York, 1971).
Liang, C. Y. in Instrumental Analysis of Cotton Cellulose and Modified Cotton Cellulose (ed. O'Connor, R. T.) 79–82 (Decker, New York, 1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
TANIGUCHI, T., HARADA, H. & NAKATO, K. Determination of water adsorption sites in wood by a hydrogen–deuterium exchange. Nature 272, 230–231 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/272230a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/272230a0
This article is cited by
-
A chemo-mechanical model for describing sorption hysteresis in a glassy polyurethane
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Water sorption in wood cell walls–data exploration of the influential physicochemical characteristics
Cellulose (2023)
-
Mechanism of moisture adsorption in plant fibers surface-modified with glycerol evaluated by LF-NMR relaxation technique
Cellulose (2022)
-
Effect of drying on the hydroxyl accessibility and sorption properties of pressurized hot water extracted wood
Wood Science and Technology (2021)
-
Humidity-dependence of the hydroxyl accessibility in Norway spruce wood
Cellulose (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.