Abstract
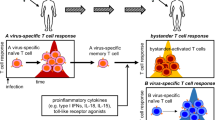
PRODUCTS of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) are important as target structures in T lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis. In mice, virus (or hapten)-sensitised T cells are cytotoxic for specific virus-infected (or hapten-modified) target cells exclusively when syngeneic or at least identical for either the K or D region of the MHC1–5. These findings led to the ‘altered-self’ hypothesis6 which assumed that cytotoxic T cells do not recognise specific viral antigens, but rather a modification of histocompatibility antigens induced by the viral infection. One prediction of this theory was that murine cells expressing viral antigens but lacking H–2 determinants would be resistant to T cell-mediated lysis. Indeed, this fact was established recently by Zinkernagel and Oldstone using murine F 9 teratoma cells7. There is still no evidence for the involvement of HLA antigens in the process of immune killing of virus-infected target cells by human T lymphocytes. But, Svedmyr and Jondal have shown that peripheral T cells from patients with infectious mononucleosis (IM)—and not from normal donors—killed specifically Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) genome-carrying B lymphoblastoid cell lines8 and Burkitt's lymphoma cells9. By contrast, these T cells were devoid of any cytotoxic activity against EBV negative cell lines. Similar data were obtained by other workers10,11. Thus, peripheral T cells from patients with infectious mononucleosis seemed to be sensitised to viral coded determinants, and could presumably be used in a model to study T-lymphocyte killing of virus-infected cells in human. If, in man as well as mouse, the MHC is directly involved in the target structure recognised by virus-sensitised cytolytic T lymphocytes, HLA-lacking target cells should be resistant to immune T-ceil killing. We report here that Daudi cells, originating from a human Burkitt's lymphoma line and lacking HLA products12–14, are resistant to lysis by EBV-sensitised peripheral T lymphocytes from patients with infectious mononucleosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zinkernagel, R. M. & Doherty, P. C. Nature 248, 701–702 (1973).
Koszinowski, U. & Ertl, H. Nature 255, 522–524 (1975).
Shearer, G. M. Eur. J. Immun. 4, 527–533 (1974).
Schrader, J. W. & Edelman, G. M. J. exp. Med. 143, 601–614 (1976).
Burakoff, S. J., Germain, R. N., Dorf, M. E. & Benacerraf, B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 13, 625–629 (1976).
Doherty, P. C., Blanden, R. V. & Zinkernagel, R. M. Transplant. Rev. 29, 89–124 (1976).
Zinkernagel, R. M. & Oldstone, M. B. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 3666–3670 (1976).
Svedmyr, E. & Jondal, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72, 1622–1626 (1975).
Jondal, M., Svedmyr, E., Klein, E. & Singh, S. Nature 255, 405–407 (1975).
Hutt, L. M., Huang, Y., Dascomb, H. E. & Pagano, J. S. J. Immun. 115, 243–248 (1975).
Royston, I., Sullivan, J. L., Periman, P. O. & Perlin, E. New Engl. J. Med. 293, 1159–1163 (1975).
Fellous, M., Mortchelewicz, F., Kamoun, M. & Dausset, J. in Histocompatibility Testings (ed. Kissmeyer-Nielson) 708–711 (Munksgaard Copenhagen, 1975).
Jones, E. A., Goodfellow, P. N., Bodmer, J. G. & Bodmer, W. F. Nature 256, 650–653 (1975).
Reisfeld, R. A., Sevies, E. D., Pellegrino, M. A., Ferrone, S. & Poulik, M. D. Immunogenetics 2, 184–197 (1975).
Cerrotini, J. C. & Brunner, K. T. in In Vitro Methods in Cell Mediated Immunity (eds Bloom, B. R. & Glade, P. R.) 369 (Academic, New York and London, 1971).
Orkin, S. H., Buchanen, P. D., Ryount, W. G., Reisner, H. & Littlefields, G. W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70, 2401–2405 (1973).
Pious, D., Bodmer, G. J. & Bodmer, W. F. Tissue Antigens 4, 247–256 (1974).
Steinitz, M. & Klein, G. Virology 70, 570–573 (1976).
Tursz, T., Preudhomme, J. L., Labaume, S., Matuchansky, C. & Seligmann, M. J. clin. Invest. 60, 405–410 (1977).
Klein, G., Wiener, F., Zech, L., Zur Hausen, H., & Reedman, B. Int. J. Cancer 14, 54–64 (1974).
Jondal, M. Clin. exp. Immun. 15, 1–5 (1976).
Dick, H. M., Bodmer, J. G., Steel, C. M., Crichton, W. B. & Evans, J. in Histo-compatibility Testings (ed. Kissmeyer-Nielsen) 671–676 (Munksgaard, Copenhagen, 1975).
Garrido, F., Schirrmacher, V., Festenstein, H. Nature 259, 228–229 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
TURSZ, T., FRIDMAN, W., SENIK, A. et al. Human virus-infected target cells lacking HLA antigens resist specific T-lymphocyte cytolysis. Nature 269, 806–808 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/269806a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/269806a0
This article is cited by
-
The role of the human major histocompatibility complex in cytotoxic T-cell responses to virus-infected cells
Journal of Clinical Immunology (1982)
-
HLA-restricted T-cell recognition of Epstein–Barr virus-infected B cells
Nature (1980)
-
HLA restriction of human cytotoxic T cells
Springer Seminars in Immunopathology (1980)
-
Virus-induced cell surface antigens and cell-mediated immune responses
Springer Seminars in Immunopathology (1979)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.