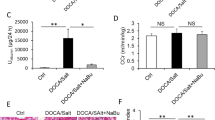
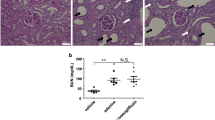
Abstract
PREVIOUS studies have revealed a close relationship between the prostaglandin (PG) and the renin–angiotensin systems in the kidney1–4 and we assume that both systems are intimately involved in the regulation of salt and volume homeostasis and of blood pressure. Changes in NaCl and water balance were found to be important determinants of the activity and function of the renin–angiotensin system5 and it has been suggested that PG synthesis is also modified by these variables2,6,7. One factor influencing the pathway and, thus, the consequences of altered PG formation is the enzyme PGE2-9-ketoreductase, which catalyses the interconversion of the antagonistically acting PGE2 and PGF2α (ref. 8). First direct evidence is presented here that PGE2-9-ketoreductase activity is under the control of NaCl ingestion. We suggest that this enzyme is an important mediator of salt intake-related prostaglandin–renin interaction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larsson, C., Weber, P. & Änggård, E. Eur. J. Pharmac. 28, 391–394 (1974).
Weber, P. C., Holzgreve, H., Stephan, R. & Herbst, R. Eur. J. Pharmac. 34, 299–304 (1975).
Änggård, E., Larsson, C. & Weber, P. C. in Advances in Proslaglandin and Thromboxane Research 2 (eds. Samuelsson, B. & Paoletti, R.) 587–594 (Raven, New York, 1976).
Bolger, P. M., Eisner, G. M., Ramwell, P. W. & Slotkoff, L. M. Nature 259, 244–245 (1976).
Gross, F. in Kidney Hormones (ed. Fischer, J. W.) 102–116 (Academic, New York, 1971).
McGiff, J. C., Itskovitz, H. D., Terragno, A. & Wong, P. Y.-K. Fedn Proc. 35, 175–180 (1976).
Tobian, L., O'Donnell, M. & Smith, D. Circulat. Res. 35, suppl. I, 83–86 (1974).
Leslie, C. A. & Levine, L. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 52, 717–724 (1973).
Stone, K. J. & Hart, M. Prostaglandins 10, 273–288 (1975).
Katzen, D. R., Pong, S.-S. & Levine, L. Res. Com. Chem. Path. Pharmac. 12, 781–787 (1975).
Frölich, J. C. et al. J. clin. Invest. 55, 763–770 (1975).
Gill, J. R. et al. Am. J. Med. 61, 43–51 (1976).
Weber, P. C. et al. Circulat. Res. 39, 868–874 (1976).
Dew, M. E. & Michelakis, A. M. Pharmacologist 16, 198A (1974).
Weber, P. C., Scherer, B. & Larsson, C. Eur. J. Pharmac. (in press).
Stitzer, S. O. & Martinez-Maldonado, M. Am. J. Physiol. 230, 1550–1554 (1976).
Orloff, J., Handler, J. S. & Bergström, S. Nature 205, 397–398 (1965).
Lipson, L. C. & Sharp, G. W. G. Am. J. Physiol. 220, 1046–1052 (1971).
Gimbrone, M. A., Jr, & Alexander, R. W. Science 189, 219–220 (1975).
Wong, P. Y.-K., Terragno, A. N., Terragno, A. & McGiff, J. C. Physiologist 18, 455A (1975).
Swales, J. D., Tange, J. D. & Thurston, H. Circulat. Res. 37, 96–100 (1975).
Guyton, A. C., Coleman, T. G. & Granger, H. J. in A. Rev. Physiol. 34, 13–46 (1972).
Weber, P. C., Held, E., Uhlich, E. & Eigler, J. O. C., Kidney Int. 7, 331–341 (1975).
Weeks, J. R., Schulz, J. R. & Brown, W. E. J. appl. Physiol. 25, 783–785 (1968).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. & Randall, R. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WEBER, P., LARSSON, C. & SCHERER, B. Prostaglandin E2-9-ketoreductase as a mediator of salt intake-related prostaglandin-renin interaction. Nature 266, 65–66 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/266065a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/266065a0
This article is cited by
-
Novel actions of angiotensin II via its renal type-2 (AT2) receptor
Current Hypertension Reports (1999)
-
Effects of obstruction on renal functions
Pediatric Nephrology (1988)
-
Sickle cell nephropathy: New insights into its pathophysiology
Kidney International (1985)
-
Prostaglandin excretion after furosemide in normal and low-renin essential hypertension
Klinische Wochenschrift (1984)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.