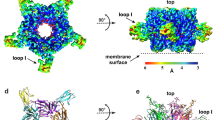
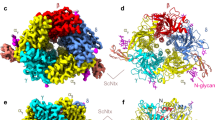
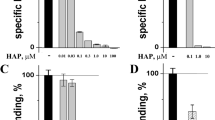
Abstract
SNAKE venom α-toxins1 in combination with reversible2,3 or alkylating4,5 cholinergic ligands give a selective labelling of the cholinergic (nicotinic) receptor protein (AChR)6–8. Since this protein is membrane-bound and therefore expected to possess hydrophobic properties, two different methods have been used for its dissolution and purification: (1) chloroform–methanol extraction9 and (2) non-denaturing detergent extraction in aqueous media2,3. The former solubilises the so-called “cholinergic proteolipid” which, still in organic media, binds charged cholinergic ligands9. The latter procedure has made possible the purification of the AChR by affinity chromatography and the study of the binding of the above-mentioned ligands in physiological media (for reviews see refs 6–8). Furthermore, the serum of rabbits immunised against the purified AChR10–12 blocks in vivo the physiological response to cholinergic agonists10,11, thereby confirming that the detergent-extracted AChR is indeed involved in the permeability change caused by acetylcholine. On the other hand, the physiological importance of the “cholinergic proteolipid” remains undetermined, though the challenge to the actual purification13 has recently been refuted14. It is therefore the aim of the present work to compare the “cholinergic proteolipid” and the detergent-extracted AChR from the same sources: the electric organs of Electrophorus electricus and Torpedo marmorata using the selective labels α-toxin15 and the covalent affinity reagent 4-(N-maleimido)-phenyltrimethylammonium iodide4 in combination with immunodiffusion tests11.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, C. Y., Clinical Toxicology, 3, 457–472 (1970).
Changeux, J. P., Kasai, M., and Lee, C. Y., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 67, 1241–1247 (1970).
Miledi, R., Molinoff, P., and Potter, L. T., Nature, 229, 554–557 (1971).
Karlin, A., and Winnik, M., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 60, 668–674 (1968).
Karlin, A., and Cowburn, D., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 70, 3636–3640 (1973).
Cohen, J. B., and Changeux, J. P., A. Rev. Pharmac., 15, 83–103 (1975).
Karlin, A., Life Sci., 14, 1385–1415 (1974).
Rang, H. P., Q. Rev. Biophys., 7, 283–399 (1975).
De Robertis, E., Science, 171, 963–971 (1971).
Patrick, J., and Lindstrom, J., Science, 180, 871–872 (1973).
Sugiyama, H., Benda, P., Meunier, J. C., and Changeux, J. P., FEBS Lett., 35, 124–128 (1973).
Heilbronn, E., and Mattson, C., J. Neurochem., 22, 315–317 (1974).
Levinson, S. R., and Keynes, R. D., Biochim. biophys. Acta, 288, 241–247 (1972).
Donellan, J. F., and Cattell, K. J., Biochem. Soc. Trans., 3, 106–109 (1975).
Menez, A., Morgat, J. L., Fromageot, P., Ronseray, A. M., Boquet, P., and Changeux, J. P., FEBS Lett., 17, 333–335 (1971).
La Torre, J. L., Lunt, G. S., and de Robertis, E., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 65, 716–720 (1970).
Izumi, F., and Freed, S., FEBS Lett., 41, 151–155 (1974).
Meunier, J. C., Sealock, R., Olsen, R., and Changeux, J. P., Eur. J. Biochem., 45, 371–394 (1974).
Cohen, J. B., Weber, M., Huchet, M., and Changeux, J. P., FEBS Lett., 26, 43–47 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BARRANTES, F., CHANGEUX, J., LUNT, G. et al. Differences between detergent-extracted acetylcholine receptor and “cholinergic proteolipid”. Nature 256, 325–327 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/256325a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/256325a0
This article is cited by
-
Eduardo de Robertis
Molecular Neurobiology (1992)
-
Similarities between “cholinergic proteolipid” and detergent-extracted cholinergic proteins
Nature (1976)
-
Similarities between “cholinergic proteolipid” and detergent-extracted cholinergic proteins (reply)
Nature (1976)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.