Abstract
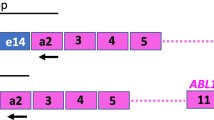
Individualized PCR strategies hamper comparability of molecular results between different laboratories in several fields of medicine. To harmonize BCR-ABL mRNA quantification an international multicenter trial involving 37 laboratories in 14 countries was initiated using 10 samples, each containing various dilutions (10, 2, 1 and 0.1%) of b3a2 or b2a2 BCR-ABL positive in normal leukocytes and negative controls. A novel control plasmid (pME-2) was designed for external calibration containing BCR-ABL and glucuronidase-β (GUS) sequences. Median BCR-ABL/ABL ratios were 9.1, 1.8, 0.85 and 0.11% in b3a2 samples and 9.5, 1.6, 0.84 and 0.11% in b2a2 samples. Median BCR-ABL/GUS ratios were 3.4, 0.77, 0.37 and 0.042% in b3a2 samples and 2.8, 0.48, 0.29 and 0.031% in b2a2 samples. The coefficients of variation were 0.62 for ratios BCR-ABL/ABL and 1.03 for ratios BCR-ABL/GUS. Five of 37 evaluable participating laboratories (13%) detected low BCR-ABL copy numbers in negative control samples; one laboratory failed to detect BCR-ABL in a low-level sample. We conclude that the use of a common control plasmid does indeed improve comparability of BCR-ABL mRNA quantification results. However, further standardizing efforts like introducing a calibrator and regular control rounds are needed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cross NC, Feng L, Chase A, Bungey J, Hughes TP, Goldman JM . Competitive polymerase chain reaction to estimate the number of BCR-ABL transcripts in chronic myeloid leukemia patients after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1993; 82: 1929–1936.
Hochhaus A, Reiter A, Saussele S, Reichert A, Emig M, Kaeda J et al. Molecular heterogeneity in complete cytogenetic responders after interferon-alpha therapy for chronic myelogenous leukemia: low levels of minimal residual disease are associated with continuing remission. German CML Study Group and the UK MRC CML Study Group. Blood 2000; 95: 62–66.
Hughes TP, Kaeda J, Branford S, Rudzki Z, Hochhaus A, Hensley ML et al. Frequency of major molecular responses to imatinib or interferon alfa plus cytarabine in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 1423–1432.
Müller MC, Gattermann N, Lahaye T, Deininger MW, Berndt A, Fruehauf S et al. Dynamics of BCR-ABL mRNA expression in first-line therapy of chronic myelogenous leukemia patients with imatinib or interferon alpha/ara-C. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2392–2400.
Baccarani M, Saglio G, Goldman J, Hochhaus A, Simonsson B, Appelbaum F et al. Evolving concepts in the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2006; 108: 1809–1820.
Hughes T, Deininger M, Hochhaus A, Branford S, Radich J, Kaeda J et al. Monitoring CML patients responding to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: review and recommendations for harmonizing current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts and kinase domain mutations and for expressing results. Blood 2006; 108: 28–37.
Burmeister T, Maurer J, Aivado M, Elmaagacli AH, Grunebach F, Held KR et al. Quality assurance in RT-PCR-based BCR/ABL diagnostics—results of an interlaboratory test and a standardization approach. Leukemia 2000; 14: 1850–1856.
Müller MC, Hördt T, Paschka P, Merx K, La Rosee P, Hehlmann R et al. Standardization of preanalytical factors for minimal residual disease analysis in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Acta Haematol 2004; 112: 30–33.
Weisser A, La Rosee P, Burmeister T, Raff T, Kneba M, Hehlmann R et al. Sensitivity, quality and comparability of BCR-ABL quantification by RT-PCR: results of an interlaboratory analysis. [Abstract]. Blood 2001; 98 (Suppl 1): 320a.
Müller MC, Saglio G, Lin F, Pfeifer H, Press RD, Tubbs RR et al. An international study to standardize the detection and quantitation of BCR-ABL transcripts from stabilized peripheral blood preparations by quantitative RT-PCR. Haematologica 2007; 92: 970–973.
Müller MC, Merx K, Weisser A, Kreil S, Lahaye T, Hehlmann R et al. Improvement of molecular monitoring of residual disease in leukemias by bedside RNA stabilization. Leukemia 2002; 16: 2395–2399.
Gabert J, Beillard E, van der Velden V, Bi W, Grimwade D, Pallisgaard N et al. Standardization and quality control studies of ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of fusion gene transcripts for residual disease detection in leukaemia—a Europe Against Cancer program. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2318–2357.
Emig M, Saussele S, Wittor H, Weisser A, Reiter A, Willer A et al. Accurate and rapid analysis of residual disease in patients with CML using specific fluorescent hybridization probes for real time quantitative RT-PCR. Leukemia 1999; 13: 1825–1832.
Beillard E, Pallisgaard N, van der Velden V, Bi W, Dee R, van der SE et al. Evaluation of candidate control genes for diagnosis and residual disease detection in leukemic patients using ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR)—a Europe Against Cancer program. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2474–2486.
Branford S, Cross NC, Hochhaus A, Radich J, Saglio G, Kaeda J et al. Rationale for the recommendations for harmonizing current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1925–1930.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the Competence Network ‘Acute and chronic leukemias,’ sponsored by the German Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Projektträger Gesundheitsforschung; DLR e.V.- 01 GI9980/6), the European LeukemiaNet (WP 4+12) within the 6th European Framework Programme for Research and Technological Development, the German José Carreras-Foundation, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany, and Novartis Pharma, Nürnberg, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Participating laboratories
Division of Hematology and Internal Medicine, Department of Clinical and Biological Sciences, University of Turin, Turin, Italy (Giuseppe Saglio, Enrico Gottardi); Klinisches Institut für Medizinische und Chemische Labordiagnostik, Ehemalige I. Medizinische Universitätsklinik, Vienna, Austria (Harald Esterbauer); Molecular Biology, Children's Cancer Research Institute, Vienna, Austria (Thomas Lion); Department of Molecular Genetics, Institute of Hematology and Blood Transfusion, Prague, Czech Republic (Jana Rulcova, Cedric Haskovec); Department of Hematology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark (Charlotte Guldborg Nyvold); Department of Pathology, Odense University Hospital, Odense, Denmark (Niels Pallisgaard); Laboratoire Central d'Hématologie, Hôpital Saint-Louis, Paris, France (Jean-Michel Cayuela); Luminy Biotech Entreprises, Marseille, France (Fabienne Hermitte); INSERM U 817, Institut de Recherche contre le Cancer, Lille, France (Claude Preudhomme); INSERM E 217, Université Victor Segalen, Bordeaux, France (Francois-Xavier Mahon); Laboratoire de cytogénétique et biologie moléculaire, Centre hospitalier Lyon sud, Pierre Bénite, France (Sandrine Hayette); Klinik für Hämatologie, Onkologie und klinische Immunologie, Universität Düsseldorf, Düsseldorf, Germany (Ralf Kronenwett); Zell- und Molekularpathologie, Medizinische Hochschule, Hannover, Germany (Nils von Neuhoff); MLL-Munich Leukemia Lab, München, Germany (Susanne Schnittger); II. Medizinische Klinik, Universität Leipzig, Leipzig, Germany (Thoralf Lange); III. Medizinische Klinik, Universität Ulm, Ulm, Germany (Konstanze Döhner); Medizinische Klinik und Poliklinik I, Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany (Christian Thiede); III. Medizinische Klinik, Universität Mainz, Mainz, Germany (Georg Heß); Klinik für Innere Medizin C, Universtität Greifswald, Greifswald, Germany (Frank Schüler); Institute of Hematology and Medical Oncology, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy (Angela Poerio, Giovanni Martinelli); Department of Hematology, University of Naples, Naples, Italy (Fabrizio Pane); Department of Hematology, Jagiellonian University, Cracow, Poland (Tomasz Sacha); Department of Hematology at Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau, Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain (Josep Nomdedeu); Department of Hematopathology, University of Barcelona, Hospital Clinic, Barcelona, Spain (Dolors Colomer); Hematology Department, Hospital Universitario de Salamanca, Salamanca, Spain (Marcos Gonzalez Diaz); Laboratorio de Biologia Molecular, Hospital Universitario La Fe, Valencia, Spain (Pascual Bolufer); Molecular Medicine and Surgery, Karolinska Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden (Gisela Barbany); Molekulare Diagnostik, Inselspital, Bern, Switzerland (Elisabeth Oppliger-Leibundgut); Department of Hematology, VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands (Quinten Waisfisz); Department of Genetics, Istanbul University , Istanbul, Turkey (Ugur Ozbek); Department of Clinical Haematology, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Manchester, United Kingdom (Abida Awan); Molecular Haematology, Glasgow Royal Infirmary, Glasgow, United Kingdom (Fiona Reid, Jan Baird); Department of Haematology, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, United Kingdom (Richard E Clark); II. Medizinische Klinik, Universität Frankfurt, Germany (Heike Pfeifer); Department of Pathology, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland OR, USA (Richard D Press); Department of Clinical Pathology, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, Cleveland, OH, USA (Raymond R Tubbs).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, M., Erben, P., Saglio, G. et al. Harmonization of BCR-ABL mRNA quantification using a uniform multifunctional control plasmid in 37 international laboratories. Leukemia 22, 96–102 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404983
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404983
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ASXL1 mutations predict inferior molecular response to nilotinib treatment in chronic myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2022)
-
Standardization of molecular monitoring of CML: results and recommendations from the European treatment and outcome study
Leukemia (2022)
-
Assessment of individual molecular response in chronic myeloid leukemia patients with atypical BCR-ABL1 fusion transcripts: recommendations by the EUTOS cooperative network
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2021)
-
Nilotinib first-line therapy in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-negative/BCR-ABL-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: ENEST1st sub-analysis
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2017)
-
Development and evaluation of a secondary reference panel for BCR-ABL1 quantification on the International Scale
Leukemia (2016)