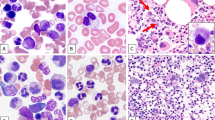
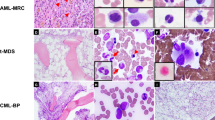
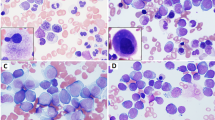
Abstract
The unbalanced translocation, der(1;7)(q10;p10), is one of the characteristic cytogenetic abnormalities found in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and other myeloid neoplasms. Although described frequently with very poor clinical outcome and possible relationship with monosomy 7 or 7q- (−7/7q-), this recurrent cytogenetic abnormality has not been explored fully. Here we analyzed retrospectively 77 cases with der(1;7)(q10;p10) in terms of their clinical and cytogenetic features, comparing with other 46 adult −7/7q- cases without der(1;7)(q10;p10). In contrast with other −7/7q- cases, where the abnormality tends to be found in one or more partial karyotypes, der(1;7)(q10;p10) represents the abnormality common to all the abnormal clones and usually appears as a sole chromosomal abnormality during the entire clinical courses, or if not, is accompanied only by a limited number and variety of additional abnormalities, mostly trisomy 8 and/or loss of 20q. der(1;7)(q10;p10)-positive MDS cases showed lower blast counts (P<0.0001) and higher hemoglobin concentrations (P<0.0075) at diagnosis and slower progression to acute myeloid leukemia (P=0.0043) than other −7/7q- cases. der(1;7)(q10;p10) cases showed significantly better clinical outcome than other −7/7q cases (P<0.0001). In conclusion, der(1;7)(q10;p10) defines a discrete entity among myeloid neoplasms, showing unique clinical and cytogenetic characteristics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Willem P, Pinto M, Bernstein R . Translocation t(1;7) revisited. Report of three further cases and review. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1988; 36: 45–54.
Shaffer L, Tommerup NE . An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2005). Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2005.
Horiike S, Taniwaki M, Misawa S, Nishigaki H, Okuda T, Yokota S et al. The unbalanced 1;7 translocation in de novo myelodysplastic syndrome and its clinical implication. Cancer 1990; 65: 1350–1354.
Mauritzson N, Albin M, Rylander L, Billstrom R, Ahlgren T, Mikoczy Z et al. Pooled analysis of clinical and cytogenetic features in treatment-related and de novo adult acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes based on a consecutive series of 761 patients analyzed 1976–1993 and on 5098 unselected cases reported in the literature 1974–2001. Leukemia 2002; 16: 2366–2378.
Sandberg AA, Morgan R, Hecht BK, Hecht F . Translocation (1;7)(p11;p11): a new myeloproliferative hematologic entity. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1985; 18: 199–206.
Lee DS, Kim SH, Seo EJ, Park CJ, Chi HS, Ko EK et al. Predominance of trisomy 1q in myelodysplastic syndromes in Korea: is there an ethnic difference? A 3-year multi-center study. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2002; 132: 97–101.
Toyama K, Ohyashiki K, Yoshida Y, Abe T, Asano S, Hirai H et al. Clinical implications of chromosomal abnormalities in 401 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: a multicentric study in Japan. Leukemia 1993; 7: 499–508.
Mertens F, Johansson B, Heim S, Kristoffersson U, Mitelman F . Karyotypic patterns in chronic myeloproliferative disorders: report on 74 cases and review of the literature. Leukemia 1991; 5: 214–220.
Reilly JT, Snowden JA, Spearing RL, Fitzgerald PM, Jones N, Watmore A et al. Cytogenetic abnormalities and their prognostic significance in idiopathic myelofibrosis: a study of 106 cases. Br J Haematol 1997; 98: 96–102.
Wang L, Ogawa S, Hangaishi A, Qiao Y, Hosoya N, Nanya Y et al. Molecular characterization of the recurrent unbalanced translocation der(1;7)(q10;p10). Blood 2003; 102: 2597–2604.
Scheres JM, Hustinx TW, Geraedts JP, Leeksma CH, Meltzer PS . Translocation 1;7 in hematologic disorders: a brief review of 22 cases. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1985; 18: 207–213.
Morrison-DeLap SJ, Kuffel DG, Dewald GW, Letendre L . Unbalanced 1;7 translocation and therapy-induced hematologic disorders: a possible relationship. Am J Hematol 1986; 21: 39–47.
Imai Y, Yasuhara S, Hanafusa N, Ohsaka A, Enokihara H, Tomizuka H et al. Clonal involvement of eosinophils in therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome with eosinophilia, translocation t(1;7) and lung cancer. Br J Haematol 1996; 95: 710–714.
Pedersen B . Survival of patients with t(1;7)(p11;p11). Report of two cases and review of the literature. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1992; 60: 53–59.
Pedersen B, Norgaard JM, Pedersen BB, Clausen N, Rasmussen IH, Thorling K . Many unbalanced translocations show duplication of a translocation participant. Clinical and cytogenetic implications in myeloid hematologic malignancies. Am J Hematol 2000; 64: 161–169.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Sole F, Luno E, Sanzo C, Espinet B, Sanz GF, Cervera J et al. Identification of novel cytogenetic markers with prognostic significance in a series of 968 patients with primary myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 2005; 90: 1168–1178.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 1982; 51: 189–199.
Christiansen DH, Andersen MK, Pedersen-Bjergaard J . Mutations of AML1 are common in therapy-related myelodysplasia following therapy with alkylating agents and are significantly associated with deletion or loss of chromosome arm 7q and with subsequent leukemic transformation. Blood 2004; 104: 1474–1481.
Plata E, Viniou N, Abazis D, Konstantopoulos K, Troungos C, Vaiopoulos G et al. Cytogenetic analysis and RAS mutations in primary myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1999; 111: 124–129.
Mitelman F, Johansson B, Martens FE . Mitelman database of chromosome aberrations in cancer. In: http://cgap.nci.nih.gov/Chromosomes/Mitelman.
Hsiao HH, Ito Y, Sashida G, Ohyashiki JH, Ohyashiki K . De novo appearance of der(1;7)(q10;p10) is associated with leukemic transformation and unfavorable prognosis in essential thrombocythemia. Leuk Res 2005; 29: 1247–1252.
Hsiao HH, Sashida G, Ito Y, Kodama A, Fukutake K, Ohyashiki JH et al. Additional cytogenetic changes and previous genotoxic exposure predict unfavorable prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia with der(1;7)(q10;p10). Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2006; 165: 161–166.
Forrest DL, Horsman DE, Jensen CL, Berry BR, Dalal BI, Barnett MJ et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome with hypereosinophilia and a nonrandom chromosomal abnormality dic(1;7): confirmation of eosinophil clonal involvement by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1998; 107: 65–68.
Kim SH, Suh C, Choi SJ, Kim JG, Lee JH, Kim SB et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome that progressed to acute myelomonocytic leukemia with eosinophilia showing peculiar chromosomal abnormality: a case report. J Korean Med Sci 1999; 14: 448–450.
Niimi H, Harada H, Harada Y, Ding Y, Imagawa J, Inaba T et al. Hyperactivation of the RAS signaling pathway in myelodysplastic syndrome with AML1/RUNX1 point mutations. Leukemia 2006; 20: 635–644.
Pedersen-Bjergaard J, Christiansen DH, Desta F, Andersen MK . Alternative genetic pathways and cooperating genetic abnormalities in the pathogenesis of therapy-related myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1943–1949.
Padua RA, West RR . Oncogene mutation and prognosis in the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 2000; 111: 873–874.
Christiansen DH, Andersen MK, Desta F, Pedersen-Bjergaard J . Mutations of genes in the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)/RAS-BRAF signal transduction pathway in therapy-related myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2005; 19: 2232–2240.
Smith SM, Le Beau MM, Huo D, Karrison T, Sobecks RM, Anastasi J et al. Clinical-cytogenetic associations in 306 patients with therapy-related myelodysplasia and myeloid leukemia: the University of Chicago series. Blood 2003; 102: 43–52.
Sole F, Espinet B, Sanz GF, Cervera J, Calasanz MJ, Luno E et al. Incidence, characterization and prognostic significance of chromosomal abnormalities in 640 patients with primary myelodysplastic syndromes. Grupo Cooperativo Espanol de Citogenetica Hematologica. Br J Haematol 2000; 108: 346–356.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the late Professor Hisamaru Hirai, who initially promoted and encouraged this work. We also thank Dr Masaaki Takatoku of Jichi Medical School and Dr Hiroshi Harada of Showa University Fujigaoka Hospital, Dr Yukihiro Arai of Dokkyo University, Dr Akira Matsuda and Dr Motohiro Misumi of Saitama Medical School, Dr Yuta Koyama of Honma Hospital, Dr Ikuo Miura of Akita University, Dr Hideaki Mizoguchi of Tokyo Women's Medical University and Dr Takuhei Murase of Nishio Municipal Hospital for providing case reports. This work was supported by Research on Measures for Intractable Diseases, Health and Labor Sciences Research Grants, Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare and by Research on Health Sciences focusing on Drug Innovation, The Japan Health Sciences Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanada, M., Uike, N., Ohyashiki, K. et al. Unbalanced translocation der(1;7)(q10;p10) defines a unique clinicopathological subgroup of myeloid neoplasms. Leukemia 21, 992–997 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404619
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404619